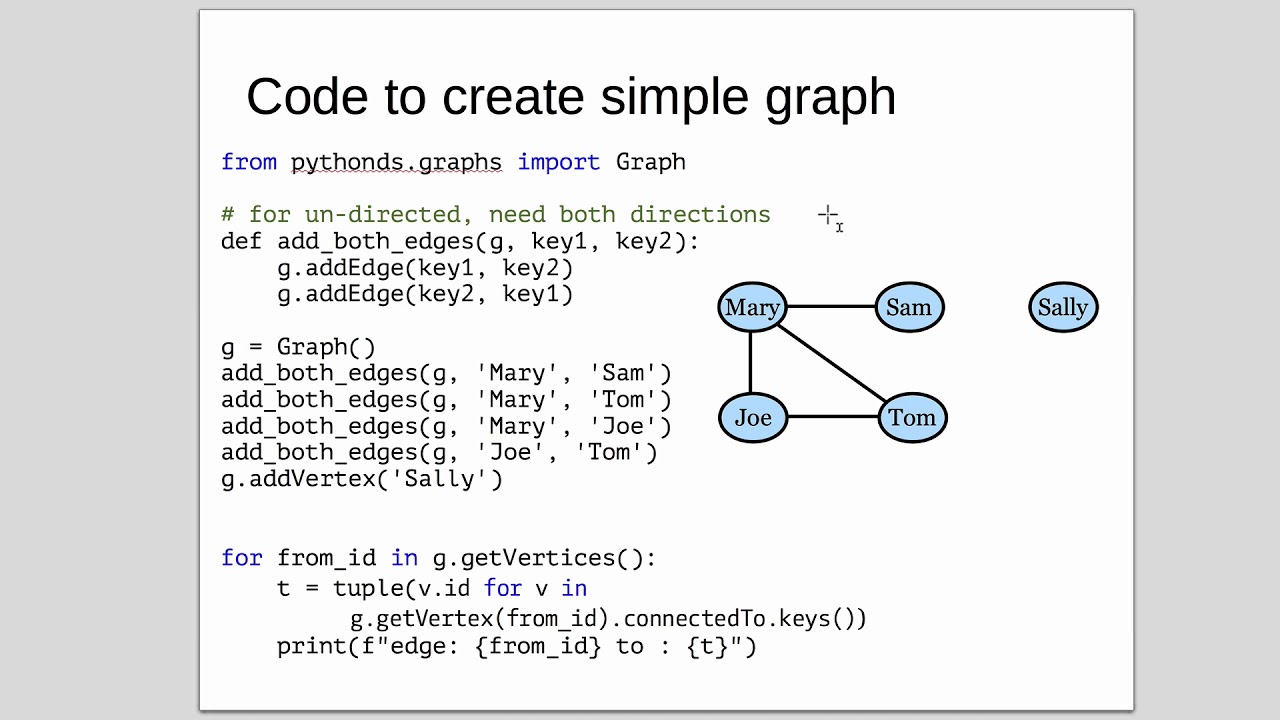
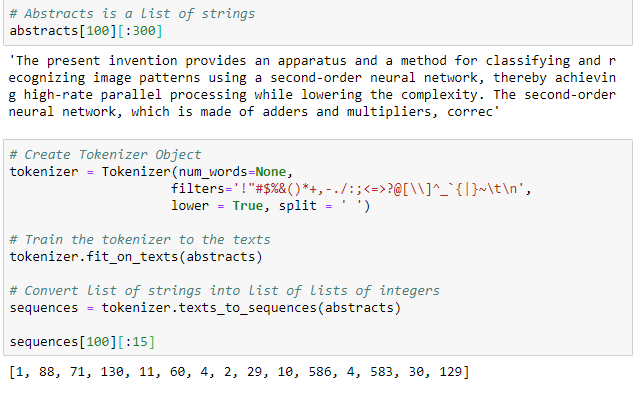
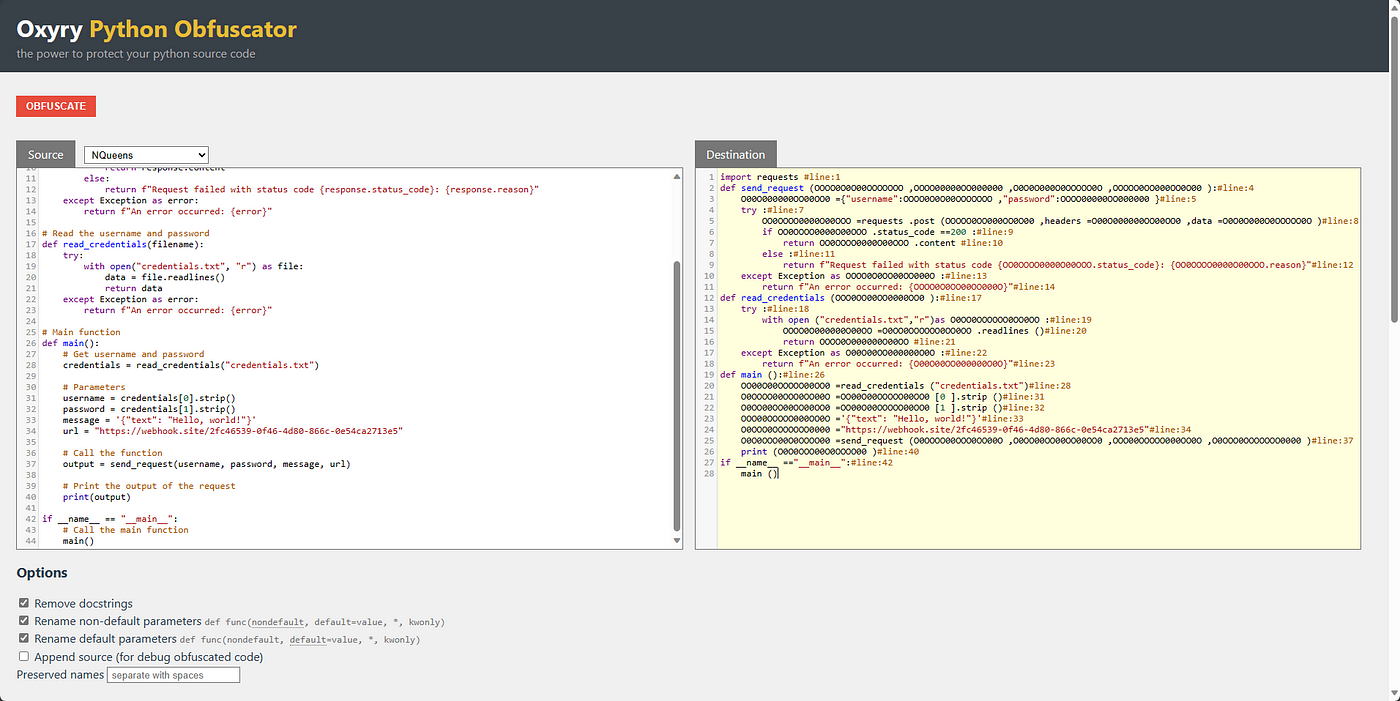
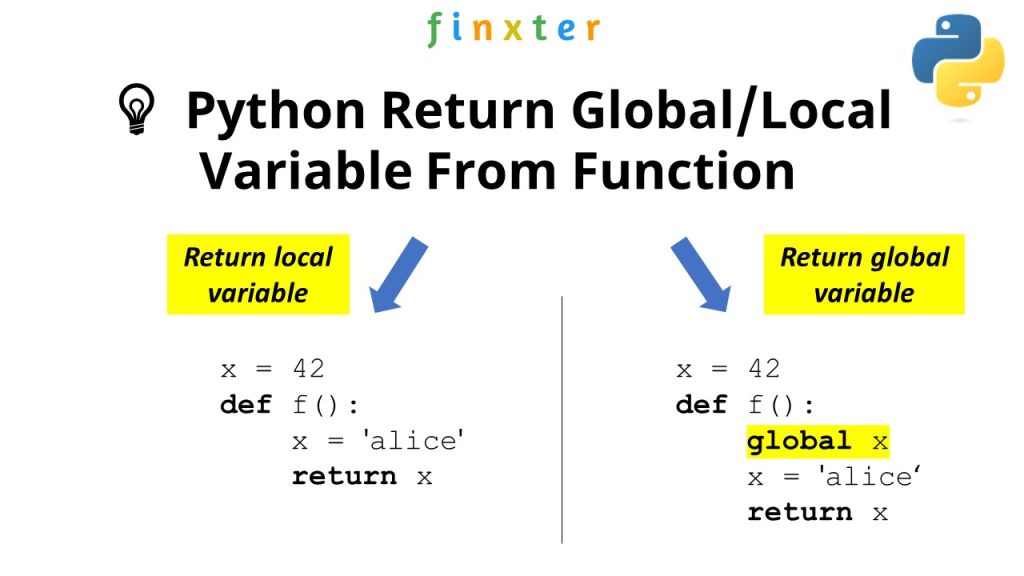
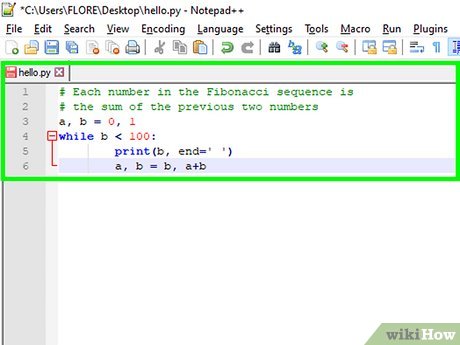
What is the difference between elif and if in Python
What is the difference between elif and if in Python
I'm happy to respond in English for you this time!
In Python, both if and elif (short for "else if") are used to implement conditional logic in your code. However, there is a key difference between the two:
If Statement
An if statement is used to check a condition and execute a block of code only if that condition is true. If the condition is false, the code inside the if block will not be executed.
For example:
x = 5
if x > 10:
print("x is greater than 10")
In this example, since x is less than 10, the code inside the if block will not be executed, and no output will be printed.
Elif Statement
An elif statement is used to check another condition if the previous if or elif condition was false. It's essentially a "else if" clause that allows you to chain multiple conditions together.
For example:
x = 5if x > 10:
print("x is greater than 10")
elif x == 5:
print("x is equal to 5")
In this example, since x is not greater than 10 (the first condition), the code inside the first if block will not be executed. Then, since x is indeed equal to 5 (the second condition), the code inside the elif block will be executed and print "x is equal to 5".
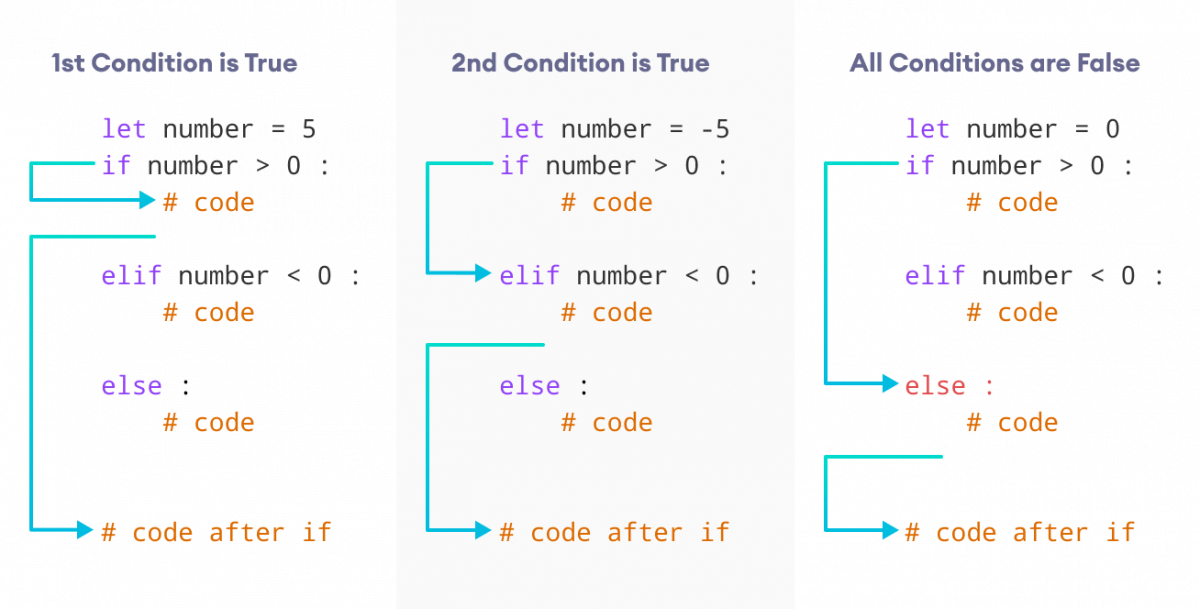
Notice that if you want to check multiple conditions and execute different blocks of code depending on which one is true, you would use an if statement followed by multiple elif statements. This is called a "chain of ifs" or "conditional chain".
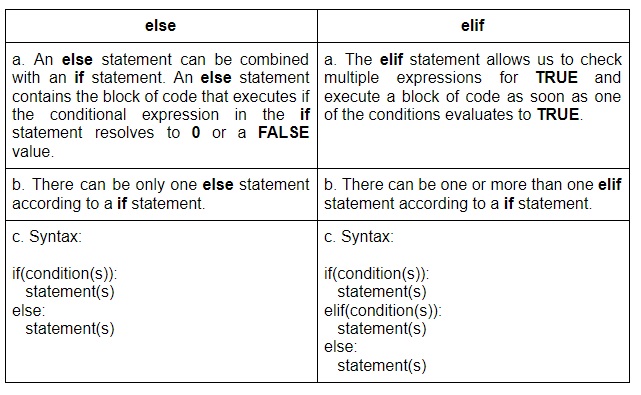
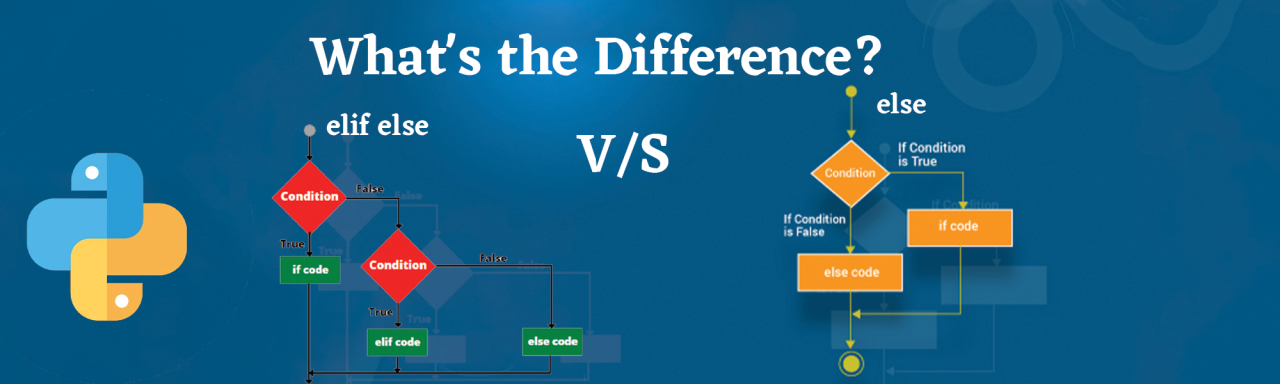
Key differences
Purpose: The primary purpose of anif statement is to check a condition and execute code only if that condition is true. An elif statement, on the other hand, is used to check another condition if the previous one was false. Order of execution: In Python, you can't mix and match if and elif statements randomly. The order of execution is as follows: if -> elif (if the if condition is false) -> else (if no other conditions are true). Code organization: Using elif statements allows you to group related conditions together, making your code more organized and easier to read.
In summary, while both if and elif statements are used for conditional logic in Python, the key difference lies in their purpose, order of execution, and code organization. By understanding how to use these two statements effectively, you can write more efficient, readable, and maintainable code.
Can we use if and elif without else in Python?
The question of the day!
In Python, you can definitely use if statements with elif clauses without an else clause. In fact, it's a common and perfectly valid way to structure your conditional logic.
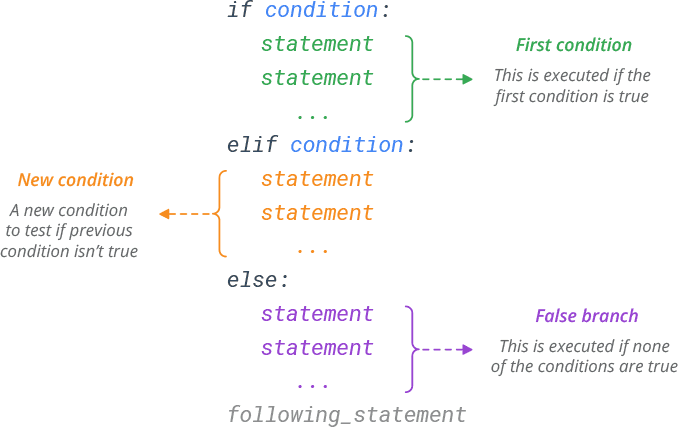
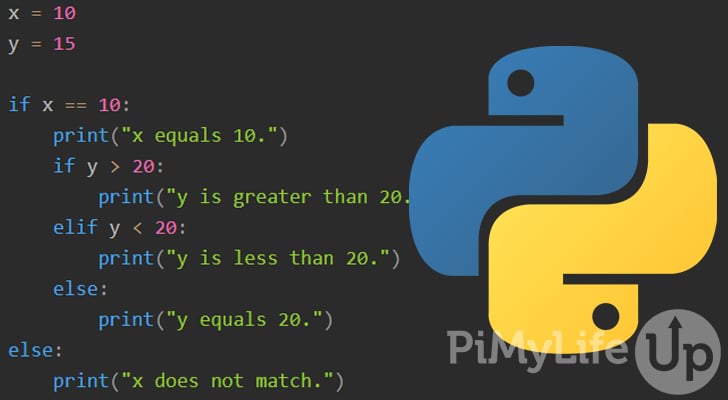
To understand why this is possible, let's take a step back and look at how if-elif-else statements work in Python:
if statement checks a condition and executes the code inside the block if the condition is True. If the condition is False, Python looks for an elif clause that matches the current situation. If no elif clause matches, Python skips to the next statement after the if-elif-else block.
Now, let's say you want to use if and elif without an else. You can do this by simply omitting the else clause:
def check_condition(x):
if x > 5:
print("x is greater than 5")
elif x == 5:
print("x is equal to 5")
No else clause here!
In this example, when you call check_condition(4), Python will execute the first two conditions (i.e., if and elif) but since neither matches (x is not greater than 5 nor equal to 5), it simply skips to the next statement after the function.
This might seem counterintuitive at first, but remember that else is optional in Python's if-elif-else statements. If you don't need an else clause, just omit it!
Some important notes:
if-elif without an else, be careful not to forget a crucial condition or accidentally skip over important logic. In some cases, using if-elif with an else can make your code more readable and easier to maintain.
In summary, yes, you can definitely use if statements with elif clauses without an else in Python. Just remember that if a condition doesn't match, Python will simply move on to the next statement, so be mindful of your logic flow!