Python websocket create_connection github
Python websocket create_connection github
I see you're asking about creating a WebSocket connection using Python! Let me dive into the world of real-time communication and help you out.
For those who might be new to WebSockets, let's start with the basics. A WebSocket is a bi-directional, asynchronous protocol that allows for real-time communication between a client (usually a web browser) and a server. This enables bidirectional communication channels between the client and server over the web. You can think of it as a continuous stream of data being sent back and forth.
Now, let's get started with creating a WebSocket connection using Python!
The websocket-client library is an excellent choice for creating a WebSocket connection in Python. We'll use this library to establish a connection between our client-side application (usually a web browser) and the server.
Firstly, you need to install the websocket-client library by running the following command:
pip install websocket-client
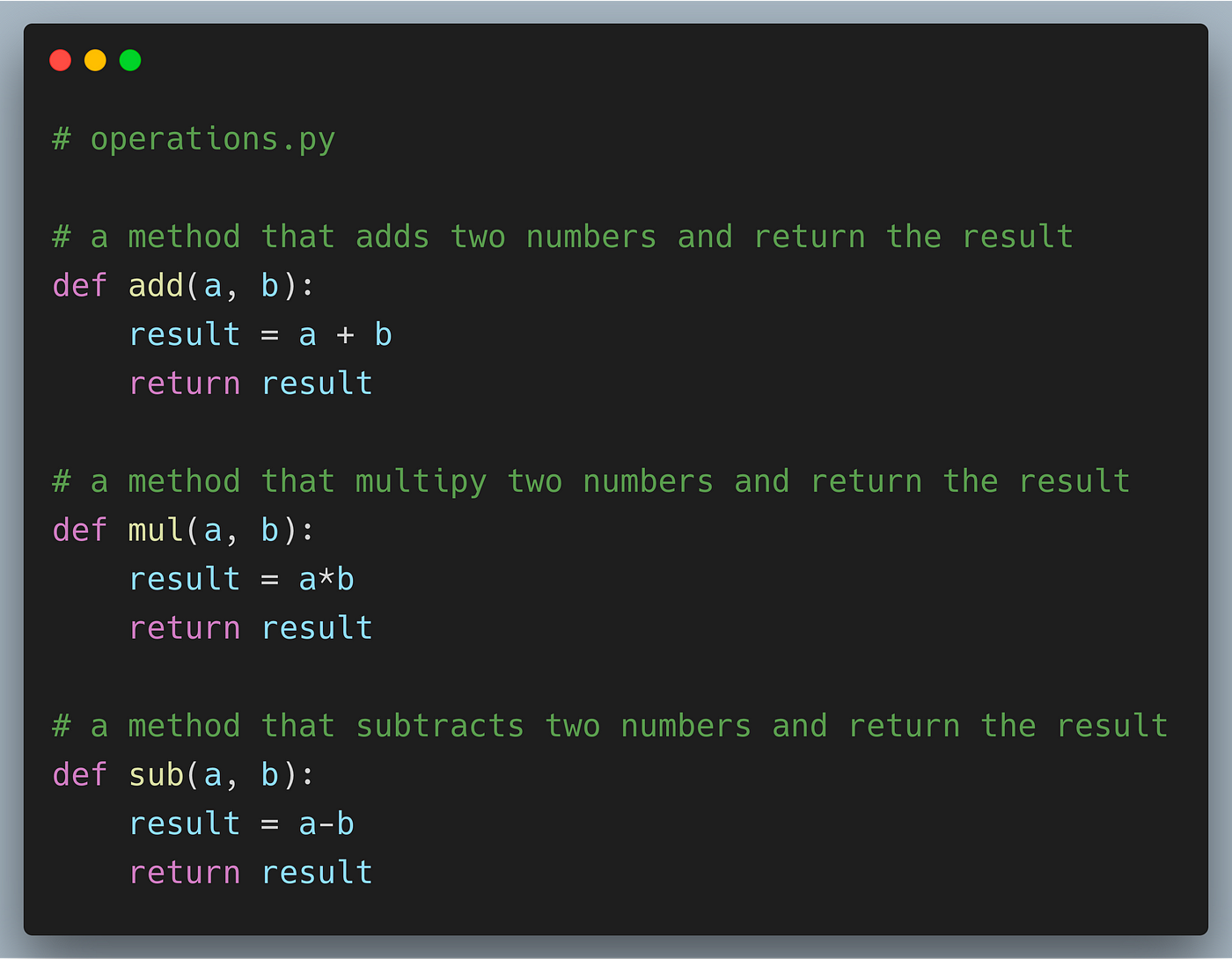
Once installed, let's create a simple Python script that establishes a WebSocket connection using this library. Here's an example:
import asyncio
from aiohttp import web
from websocket import create_connection
async def hello():
ws = await create_connection("ws://localhost:8080")
while True:
Send message to server
ws.send('Hello, server!')
Receive message from server
msg = await ws.recv()
print(msg)
app = web.Application()
app.router.add_get('/', hello)
web.run_app(app)
In this script:
We import thecreate_connection function from the websocket-client library. We create a WebSocket connection to "ws://localhost:8080" using this function. The script enters an infinite loop where it: Sends a message to the server with ws.send(). Receives messages from the server using ws.recv().
Now, let's set up a server-side Python script that handles WebSocket connections:
import asyncio
from aiohttp import web
async def handle(request):
ws = await request.websockets Accepted
while True:
Receive message from client
msg = await ws.recv()
print(msg)
Send response back to client
await ws.send('Hello, client!')
app = web.Application()
app.router.add_get('/', handle)
web.run_app(app)
In this script:
We import theaiohttp library for handling WebSocket connections. We create a WebSocket handler function (handle) that: Receives messages from clients using ws.recv(). Sends responses back to clients with ws.send().
You can run these scripts together, and when you visit "localhost:8080" in your web browser, you should see the messages being sent and received in real-time. Pretty cool, right?
That's it! Creating a WebSocket connection using Python is relatively straightforward. You can use this example as a starting point for building more complex WebSocket applications.
Remember to explore the websocket-client library and aiohttp documentation for more information on how you can customize your WebSocket connections.
Feel free to reach out if you have any questions or need further clarification!
Python websocket create_connection json
Here's the information on creating a WebSocket connection with JSON data using Python:
What is WebSocket?
WebSocket is a protocol that provides bi-directional communication between clients and servers over the Web. It allows for real-time communication, which is ideal for applications that require instant updates or push notifications.
Creating a WebSocket Connection with Python
To create a WebSocket connection in Python, we'll use the websocket-client library. Here's an example code snippet:
import json
from websocket import create_connection
Set up the WebSocket URL and headers
ws_url = "wss://example.com/ws"
headers = {"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_API_KEY"}
Create a WebSocket connection
ws = create_connection(ws_url, headers=headers)
while True:
Send JSON data to the server
json_data = {
"key1": "value1",
"key2": "value2"
}
ws.send(json.dumps(json_data).encode())
Receive and print any messages from the server
message = ws.recv()
print(message.decode())
Close the WebSocket connection when we're done
ws.close()
JSON Data
In this example, we're sending a JSON object with key-value pairs to the WebSocket server. The json.dumps() function converts our Python dictionary into a JSON string that can be sent over the wire.
To receive and process JSON data from the server, you would typically use the ws.recv() method, which returns a byte string representing the message received from the server. You would then convert this to a JSON object using json.loads():
message = ws.recv()
json_data = json.loads(message.decode())
print(json_data["key1"])
Example Code
Here's an example code snippet that demonstrates creating a WebSocket connection, sending and receiving JSON data, and processing the received JSON:
import json
from websocket import create_connection
ws_url = "wss://example.com/ws"
headers = {"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_API_KEY"}
ws = create_connection(ws_url, headers=headers)
while True:
Send JSON data to the server
json_data = {
"key1": "value1",
"key2": "value2"
}
ws.send(json.dumps(json_data).encode())
Receive and print any messages from the server
message = ws.recv()
received_json_data = json.loads(message.decode())
print(received_json_data)
Close the WebSocket connection when we're done
ws.close()
In this example, we create a WebSocket connection to wss://example.com/ws, set up headers with an API key for authentication, and then enter a loop where we send JSON data and receive and process any messages from the server.
Note: Replace YOUR_API_KEY with your actual API key or credentials.