What is scope of work in python geeksforgeeks
What is scope of work in python geeksforgeeks
I'd be happy to explain the concept of Scope of Work in Python to you!
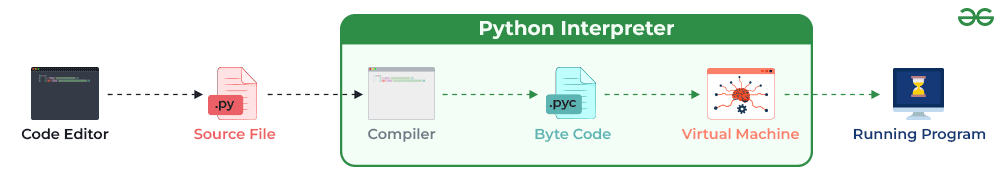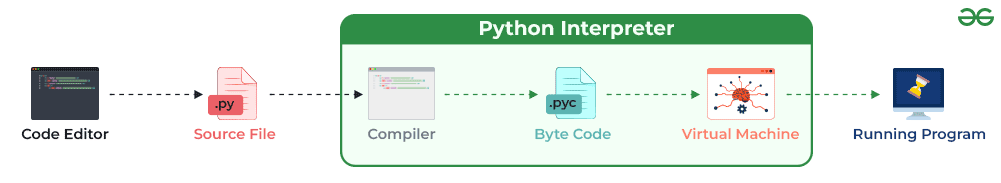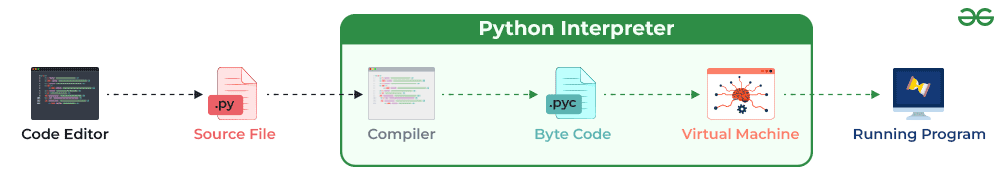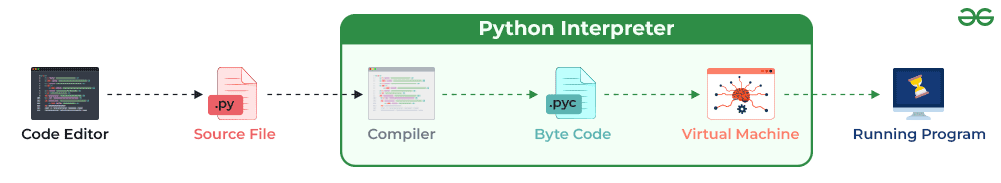
What is Scope of Work?
In programming, particularly in Python, the "Scope of Work" refers to the range or area within which a variable, function, or statement has an effect. In other words, it defines the boundaries beyond which a particular piece of code or data does not operate.
Think of scope as the territory where your code can access and manipulate variables, functions, or statements. It's like a map that shows you what areas are within reach or out of bounds for your programming endeavors!
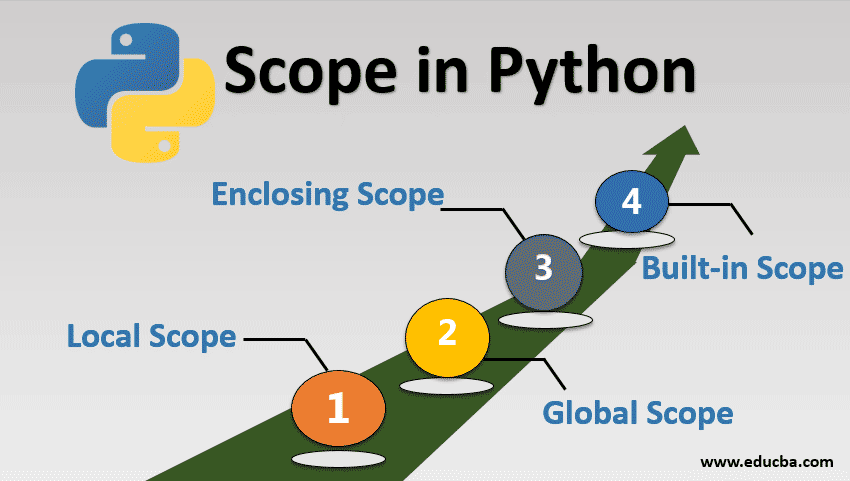
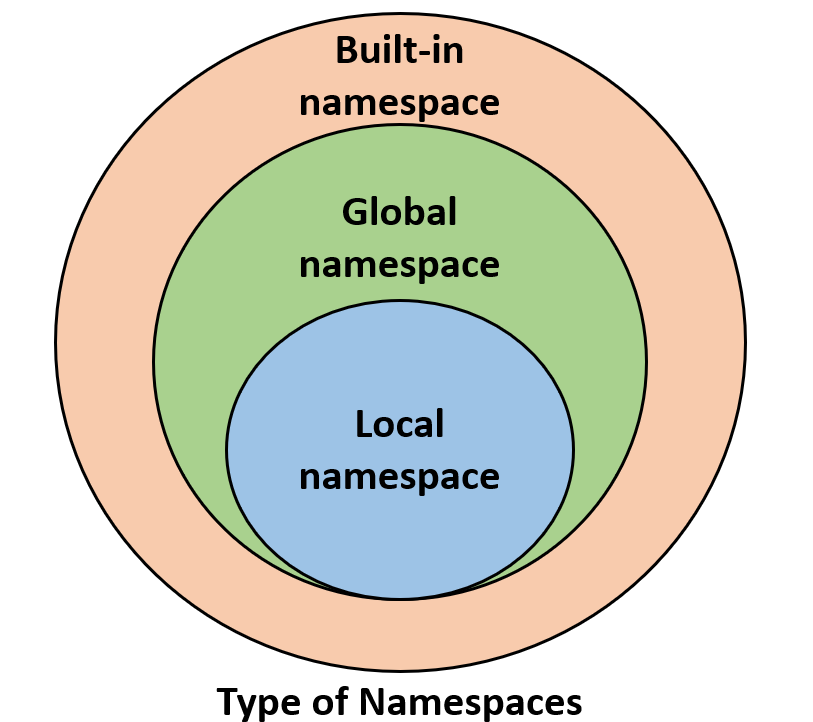
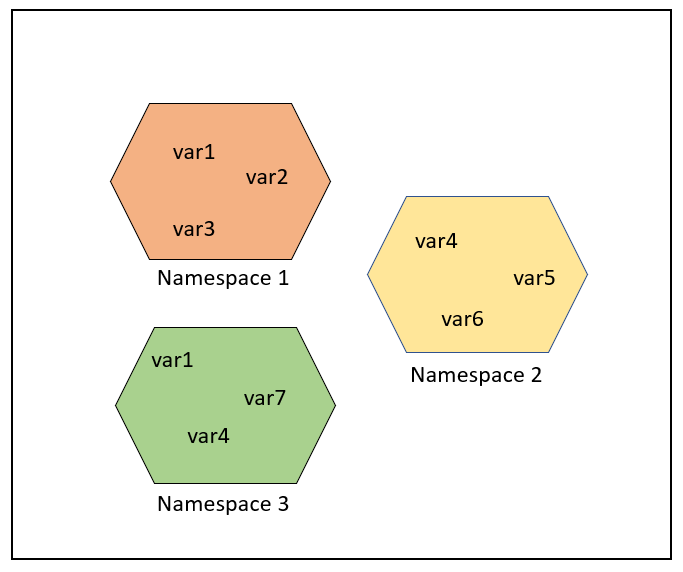
Types of Scope in Python
There are several types of scope in Python:
Why Understanding Scope is Important
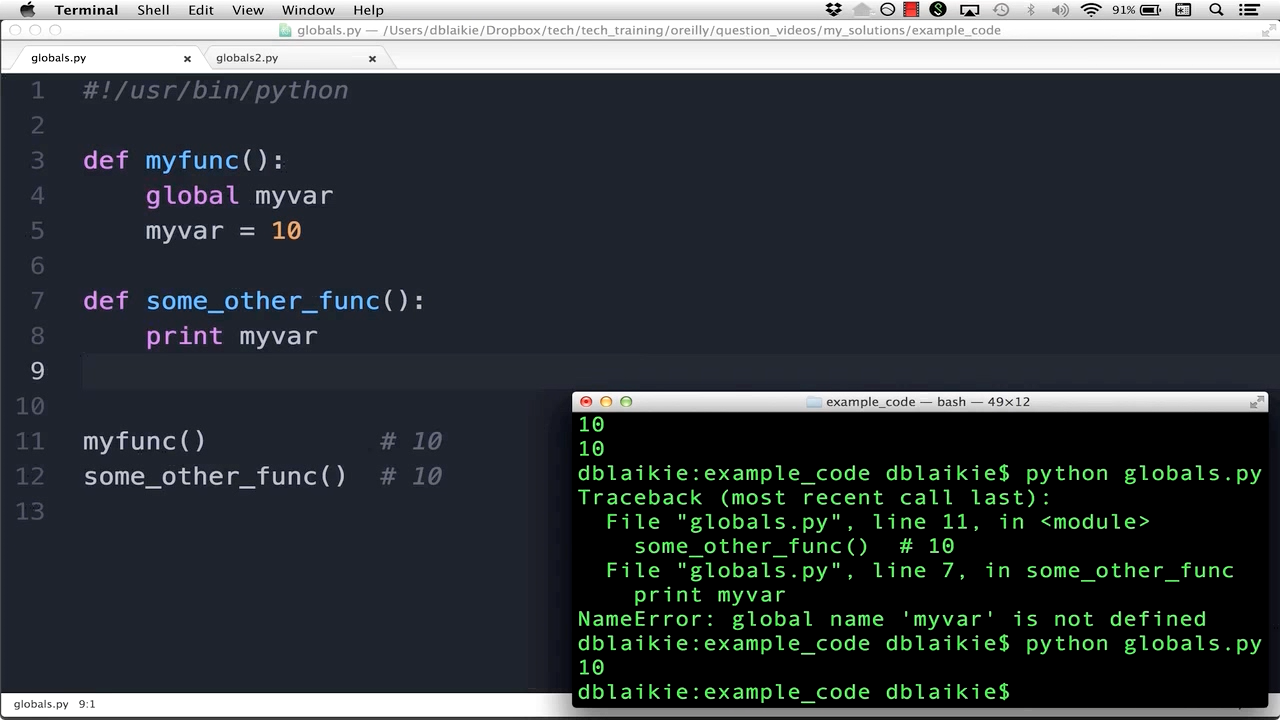
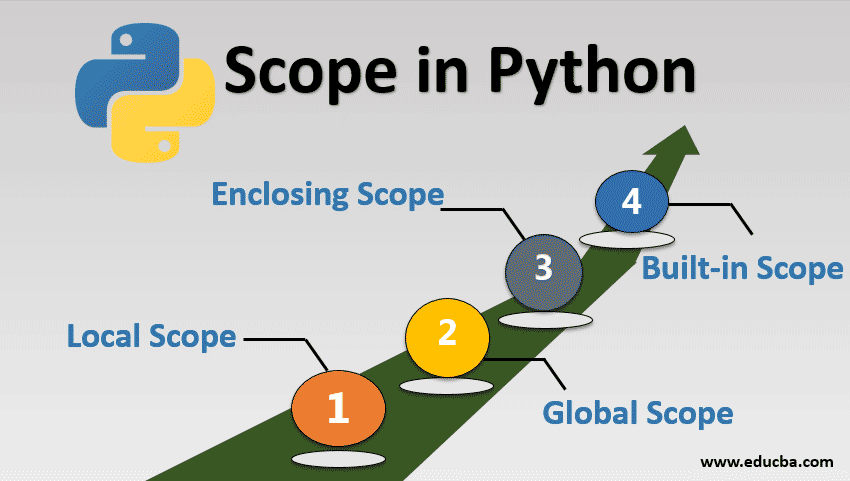
Variable Shadowing: When multiple variables have the same name but different scopes, Python will use the one that has the highest scope (e.g., global) to resolve the ambiguity. Namespace Pollution: Unintentionally polluting the namespace with variables or functions can cause confusion and errors when other parts of your code rely on those names having specific meanings.How Scope is Resolved
Lexical Scoping: Python uses a concept called lexical scoping to resolve scope. This means that Python looks at the order in which you define variables, functions, and statements. Scope Resolution: When you access a variable or statement, Python first checks if it's within the local scope, then the enclosing scope, and finally the global scope.In conclusion, understanding Scope of Work is crucial for writing efficient, readable, and maintainable Python code! By grasping the concepts of local, global, and enclosing scopes, you'll avoid common pitfalls like variable shadowing and namespace pollution. Your coding adventures will be more enjoyable, and your peers will appreciate the clarity!
If you have any questions or need further clarification, feel free to ask!
What is scope of work in python with example
I'm happy to help!
In Python, the scope of work refers to the range of values within which a variable or expression is considered valid. In other words, it's the set of inputs for which an operation or function is defined and returns meaningful results.
Let's dive into some examples:
x assigned the value 5:
x = 5print(x) # Output: 5
In this case, the scope of work is the range of values that can be used to assign a new value to x. For example, if we try to assign x = "hello" or x = [1, 2, 3], Python will raise a TypeError because those are not numeric values.
if x > 5:print("x is greater than 5")
else:
print("x is less than or equal to 5")
print(x) # Output: 5 (since x is assigned the value 5)
Here, the scope of work for the conditional statement is the range of values that satisfy the condition x > 5. In this case, that would be any number greater than 5.
y and returns its square:
def square(y):return y ** 2
print(square(4)) # Output: 16
In this case, the scope of work for the square function is the range of values that can be used as input. For example, if we pass a string or a list as input (square("hello") or square([1, 2, 3])), Python will raise a TypeError. The function only makes sense when given a numeric value.
numbers = [x for x in range(10) if x % 2 == 0]print(numbers) # Output: [0, 2, 4, 6, 8]
Here, the scope of work is the range of values that can be used to generate the list comprehension. In this case, that would be the integers from 0 to 9.
In summary, the scope of work in Python refers to the set of inputs or conditions for which an operation or function is defined and returns meaningful results. It's essential to understand the scope of work when working with variables, conditional statements, functions, and data structures like lists.