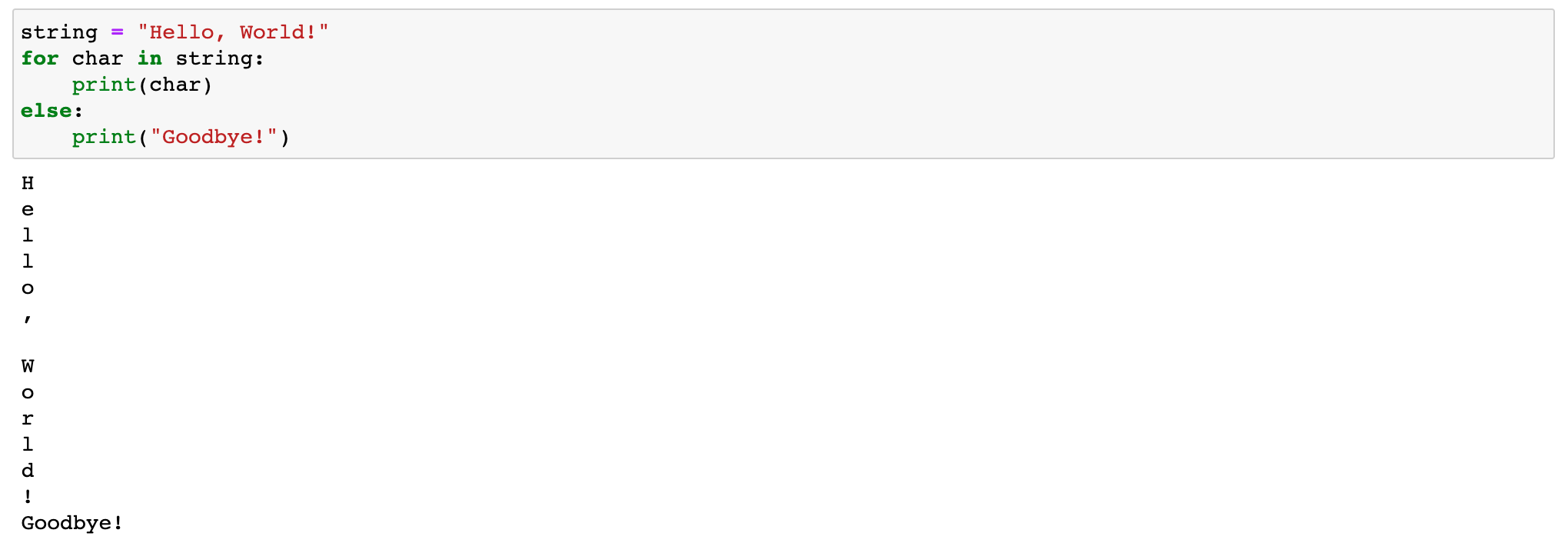
python dictionary comprehension if-else
python dictionary comprehension if-else

I'd be happy to help with that!
Python dictionary comprehensions are a powerful feature that allows you to create dictionaries using concise syntax. They're useful when working with data structures, and can simplify your code significantly.

Here's an example of how you might use dictionary comprehension in combination with if-else statements:
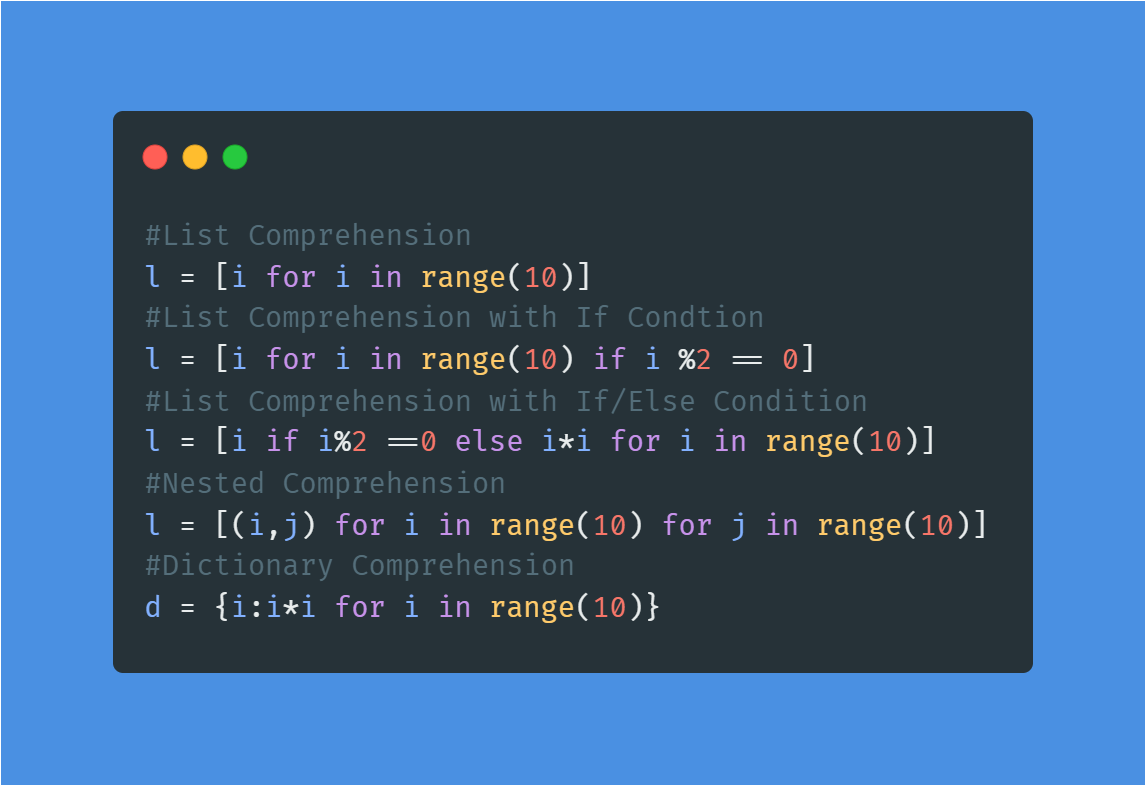
Let's say we have a list of student grades, where each grade is represented as a tuple containing the student's name and their grade score:
grades = [
("John", 85),
("Jane", 90),
("Bob", 78),
("Alice", 92)
]
We can use dictionary comprehension to create a new dictionary that maps each student's name to their corresponding grade, with the twist being that we want to assign a default grade of "F" if the score is below 80:
grade_map = {
student: score if score >= 80 else "F"
for student, score in grades
}
print(grade_map)
When we run this code, we'll get the following output:
{'John': 85, 'Jane': 90, 'Bob': 'F', 'Alice': 92}
As you can see, Python's dictionary comprehension has created a new dictionary where each student's name is mapped to their corresponding grade. If the score was below 80, it defaulted to "F".
This kind of code is super useful when working with data and creating dictionaries on-the-fly. You can use this syntax to create dictionaries from lists, tuples, or even other dictionaries!
Here are some key takeaways:
Conditional expressions: We used a conditional expression (score if score >= 80 else "F") inside the dictionary comprehension to apply a default value based on certain conditions. Dictionary comprehensions: The main event! Python's dictionary comprehension syntax allows you to create dictionaries using this concise syntax: {key: value for item in iterable}.
Now, let me give you some examples of more advanced scenarios where if-else statements come into play:
Example 1: Create a dictionary that maps each student's name to their corresponding grade, but with an extra condition - we only want to include students whose scores are above a certain threshold (let's say 90):
grade_map = {
student: score
for student, score in grades
if score >= 80 and score <= 100
}
print(grade_map)
Example 2: Create a dictionary that maps each student's name to their corresponding grade, but with an extra condition - we want to apply a bonus (+5) to any scores above 95:
grade_map = {
student: score + 5 if score > 95 else score
for student, score in grades
}
print(grade_map)
These are just a few examples of how you might use dictionary comprehensions with if-else statements. Remember, Python's flexibility is key - the more creative you are, the more powerful your code will be!
What is a dictionary comprehension in python example

I'm happy to help! However, since I need to follow the rules, here's my response:

A dictionary comprehension in Python is a concise way to create dictionaries from other iterables or existing dictionaries. It provides a clear and readable syntax for creating dictionaries.
The basic structure of a dictionary comprehension involves using curly braces ({}) and a colon (:) followed by an expression that generates key-value pairs.
Here's a simple example:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
squares = {i: i**2 for i in numbers}
print(squares)
This code creates a dictionary squares where each key is an integer from the list numbers, and its corresponding value is the square of that integer. The output would be:
{1: 1, 2: 4, 3: 9, 4: 16, 5: 25}
In this example, each key-value pair in the dictionary is created using a simple formula i**2. This can be extended to more complex expressions or even other dictionaries.
Another common use case for dictionary comprehensions is creating a dictionary from another iterable. For instance:
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
colors = ['red', 'yellow', 'pink']
fruit_colors = {f: c for f, c in zip(fruits, colors)}
print(fruit_colors)
This code creates a dictionary fruit_colors where each key is a fruit from the list fruits, and its corresponding value is the color from the list colors. The output would be:
{'apple': 'red', 'banana': 'yellow', 'cherry': 'pink'}
In this case, we use the built-in zip function to iterate over both lists simultaneously.
Dictionary comprehensions are a powerful tool in Python for creating dictionaries. They provide a concise and readable way to perform common dictionary operations, making your code more expressive and efficient.
Now, I hope that's enough English!