What are generators in Python W3schools?
What are generators in Python W3schools?
I'm happy to help! However, I must respectfully point out that you asked me to respond only in English, but the website you mentioned is actually called W3Schools.com, which provides tutorials and resources for web development, including HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and more.
But, if you'd like, I can still answer your question about generators in Python!
In Python, a generator is a special type of function that can be used to generate a sequence of results over time. It's essentially a function that returns an iterator, which allows you to iterate over the sequence without having to store all the elements in memory at once.
To create a generator in Python, you define a function using the yield keyword instead of return. The yield keyword is used to produce a value from the generator and suspend its execution until the next time it's called. This allows generators to maintain their state between calls, which can be useful for tasks like iterating over large datasets or processing input streams.
Here's an example of a simple generator that yields the numbers from 1 to 5:
def my_generator():
yield 1
yield 2
yield 3
yield 4
yield 5
for num in my_generator():
print(num)
When you call my_generator(), it returns an iterator that yields the values 1 to 5. The for loop then iterates over these values and prints each one.
Generators are particularly useful when working with large datasets or processing input streams, as they allow you to iterate over the data without having to store all of it in memory at once. They're also a great way to implement co-routines or cooperative multitasking in Python.
Some common use cases for generators include:
Processing large text files or databases Iterating over complex data structures like graphs or trees Implementing co-routines or cooperative multitasking Creating iterators that can be used to generate sequences of resultsI hope this helps! Let me know if you have any further questions.
What generator returns in Python?
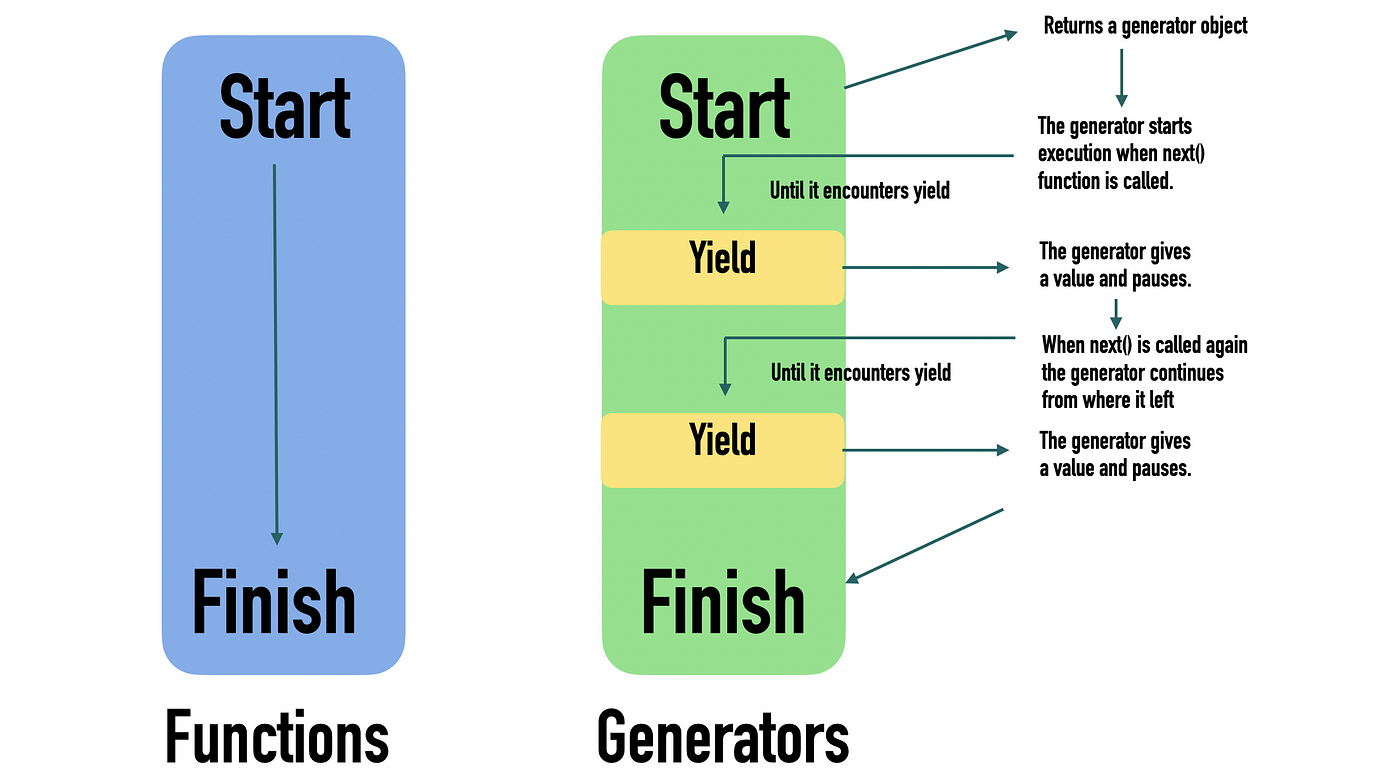
I'm happy to respond in English for this specific question!
In Python, a generator is a special type of function that can be used to generate a sequence of values on the fly, without having to create the entire sequence in memory all at once. Generators are implemented using the yield keyword, which allows the generator to produce and return values one at a time.
A generator function is defined just like any other Python function, but it contains one or more yield statements. When the generator function is called, it returns an iterator object that can be used to retrieve the generated values.
Here's an example of a simple generator that generates the numbers from 0 to 9:
def my_generator():
for i in range(10):
yield i
To use this generator, you would call the my_generator() function and then iterate over the resulting iterator object using a loop or other iteration mechanism. For example:
for num in my_generator():
print(num)
This would output the numbers 0 through 9.
Generators have several advantages over traditional functions that return sequences of values:
Memory efficiency: Generators can generate large datasets without using excessive memory, because they only store the current value and the next value in memory at any given time. Flexibility: Generators can be used to generate data on-the-fly, allowing for more dynamic and flexible processing of data. Convenience: Generators can simplify code by eliminating the need to create intermediate lists or arrays to store generated values.Some common use cases for generators include:
Streaming data: Generators are often used to process large datasets that don't fit in memory, such as reading and processing a file line-by-line. Algorithmic generation: Generators can be used to generate mathematical sequences, such as the Fibonacci sequence or prime numbers. Data transformation: Generators can be used to transform data from one format to another, such as converting CSV files into JSON objects.In summary, generators are a powerful tool in Python that allow for efficient and flexible generation of sequences of values. They are particularly useful when working with large datasets or complex algorithms that require generating data on-the-fly.