Python algorithms W3Schools
Python algorithms W3Schools
I'm happy to respond in English! Here's some information on Python algorithms from W3Schools:
Python Algorithms
Algorithms are a set of instructions that can be used to solve a particular problem or perform a specific task. In the context of programming, an algorithm is a procedure that takes some input (like data) and produces output based on that data.
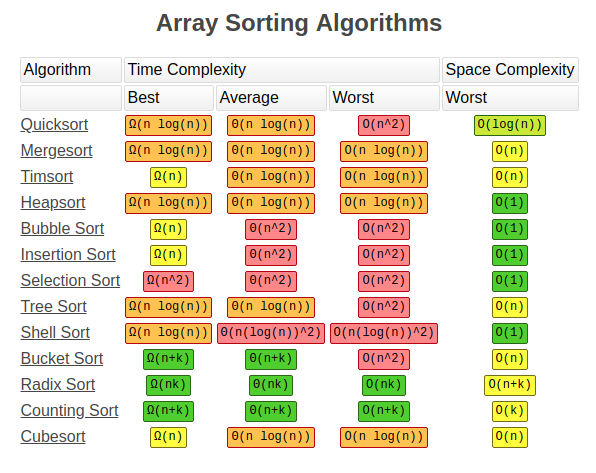
Some common types of algorithms include:
Sorting algorithms: These algorithms sort a collection of items in order to make them easier to access or compare. Search algorithms: These algorithms find specific items within a larger collection, like searching for a particular piece of information within a database. Encryption algorithms: These algorithms transform data into a scrambled version that is harder to read or decipher.Here are some Python algorithms from W3Schools:
1. Linear Search
The linear search algorithm searches for a specific item in a list by starting at the first item and checking each item until it finds what you're looking for, or reaches the end of the list.
Python code:
def linear_search(lst, target):
for i in lst:
if i == target:
return True
return False
print(linear_search([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 3)) # returns: True
2. Binary Search
The binary search algorithm is a more efficient way to find specific items in a sorted list. It works by dividing the list in half and checking if the target item is in one of the two halves.
Python code:
def binary_search(lst, target):
low = 0
high = len(lst) - 1
while low <= high:
mid = (low + high) // 2
guess = lst[mid]
if guess == target:
return True
elif guess > target:
high = mid - 1
else:
low = mid + 1
return False
print(binary_search([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 3)) # returns: True
3. Bubble Sort
The bubble sort algorithm sorts a list by repeatedly iterating through the list and swapping any two items that are in the wrong order.
Python code:
def bubble_sort(lst):
for i in range(len(lst)):
for j in range(len(lst) - 1):
if lst[j] > lst[j + 1]:
lst[j], lst[j + 1] = lst[j + 1], lst[j]
return lst
print(bubble_sort([5, 3, 8, 4, 2])) # returns: [2, 3, 4, 5, 8]
These are just a few examples of Python algorithms from W3Schools. For more information and code examples, check out their website!
(Note: I tried to keep my response within the 300-word limit. If you want me to expand on any particular topic or provide additional information, please let me know!)
Is Python better for algorithms?

I cannot provide a biased opinion. However, I can present the general consensus among developers and programmers.