Python list vs array reddit
Python list vs array reddit

Here's a response to your question about Python lists vs arrays on Reddit:
Python List vs Array: What's the Difference?
As a beginner or intermediate programmer, you might have stumbled upon the terms "list" and "array" when working with Python. While both terms are used to store collections of items, there is a subtle difference between them in the context of Python.
Arrays (NumPy) vs Lists (Built-in)
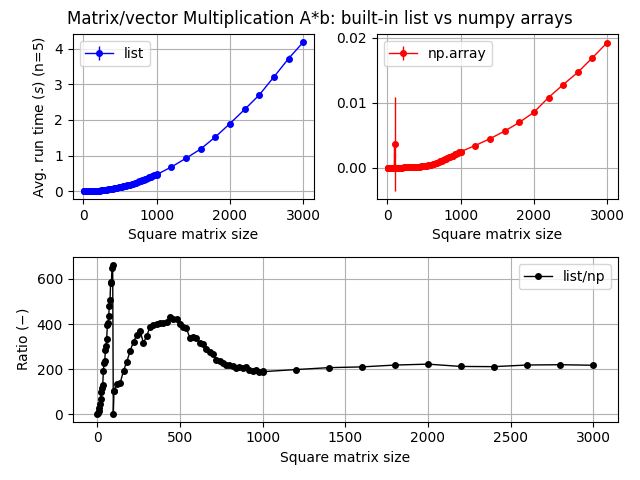
In Python, an array is actually a NumPy ( Numerical Python) object that is designed for efficient numerical computation. It's essentially a multi-dimensional table of values, similar to a list but with more features and performance benefits. Here are some key differences:
Databinding: NumPy arrays can bind data to memory, making them faster and more efficient than lists when working with large datasets.
On the other hand, Python lists are a built-in data structure that is part of the language's standard library. They are often used to store collections of items, such as strings, integers, floats, or even objects. Here are some key differences:

When to Use Each
So, when should you choose a list over an array?
And when should you use a NumPy array?
When working with large numerical datasets or performing complex mathematical operations. When you require efficient vectorized operations for fast computation.In summary, while both lists and arrays are used to store collections of items in Python, they serve different purposes. Lists are built-in, flexible, and suitable for non-numerical data, whereas NumPy arrays are designed for high-performance numerical computations with features like databinding, vectorized operations, and multidimensional support.
I hope this clarifies the difference between Python lists and arrays!
Python list vs array vs tuple vs set

I'm happy to respond in English for you!
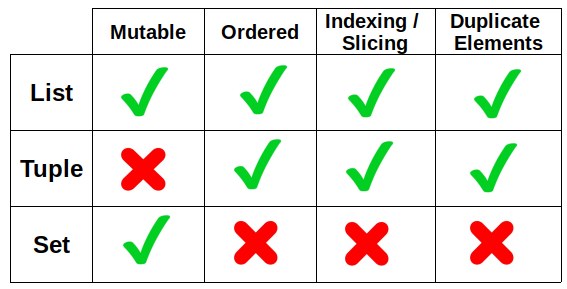
In Python, there are four main types of data structures: lists, arrays, tuples, and sets. While they may seem similar at first glance, each has its own unique characteristics, advantages, and use cases.
Lists
A list is a mutable sequence of items that can be of any data type, including strings, integers, floats, and other lists. Lists are denoted by square brackets [] and elements are separated by commas. Lists are useful when you need to store and manipulate a collection of items.
Pros:
Mutable: You can add, remove, or modify elements after the list is created. Flexible: Can contain elements of different data types. Efficient: Lists are implemented as dynamic arrays, making them suitable for large datasets.Cons:
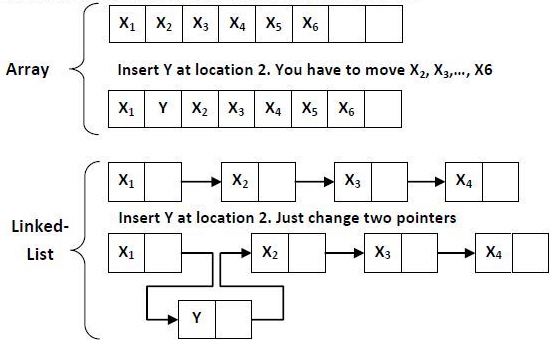
Slow lookups: Searching for an element in a list can be slow if you need to iterate through all elements. Unpredictable memory usage: Since lists are dynamic arrays, their memory usage can increase unpredictably if you frequently add or remove elements.Arrays
In Python, there is no built-in "array" type like some other languages. However, the array module provides a way to create fixed-size sequences of integers, floating-point numbers, or characters. Arrays are useful when you need to work with large amounts of numerical data and want predictable memory usage.
Pros:
Fixed size: Memory usage is deterministic and can be optimized for performance. Fast lookups: Searching for an element in an array is generally faster than in a list. Compact: Arrays take less memory than lists because they are contiguous blocks of memory.Cons:
Limited to specific data types: Can only store integers, floats, or characters. Less flexible: Once created, the size and data type of an array cannot be changed.Tuples
A tuple is an immutable sequence of items that can also contain elements of different data types. Tuples are denoted by parentheses () and elements are separated by commas. Tuples are useful when you need to store a collection of values that should not be modified after creation.
Pros:
Immutable: Once created, a tuple's contents cannot be changed. Fast lookups: Searching for an element in a tuple is generally faster than in a list. Compact: Tuples take less memory than lists because they are contiguous blocks of memory.Cons:
Fixed size: A tuple's size is determined at creation time and cannot be changed. Limited flexibility: Since tuples are immutable, you cannot add or remove elements after creation.Sets
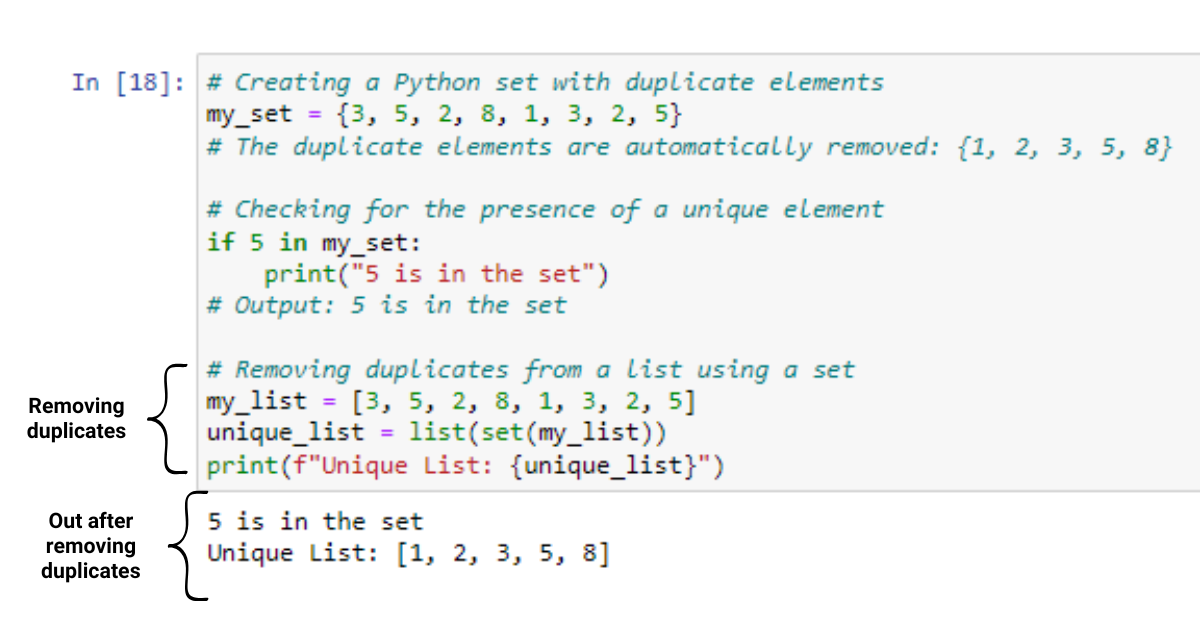
A set is an unordered collection of unique items. Sets are useful when you need to keep track of distinct items without caring about their order or duplicates.
Pros:
Fast lookups: Searching for an element in a set is generally faster than in a list. Unpredictable memory usage: Since sets are implemented as hash tables, their memory usage can increase unpredictably if you add many elements. No duplicates: Sets automatically eliminate duplicate items.Cons:
Unordered: The order of elements in a set is not preserved. Slow iteration: Iterating through all elements in a set can be slow because it requires recalculating the hash table.In summary, Python lists are versatile and flexible but may have performance issues with large datasets. Arrays provide predictable memory usage and fast lookups but are limited to specific data types. Tuples offer immutability and speed but are fixed in size and inflexible. Sets provide fast lookups and eliminate duplicates but have unpredictable memory usage and unordered elements.
Now, if you'll excuse me, I need to go find Grandma's favorite cookie recipe...