List comprehension python for loop example
List comprehension python for loop example
Here are some examples of using list comprehensions and for loops in Python:
List Comprehension
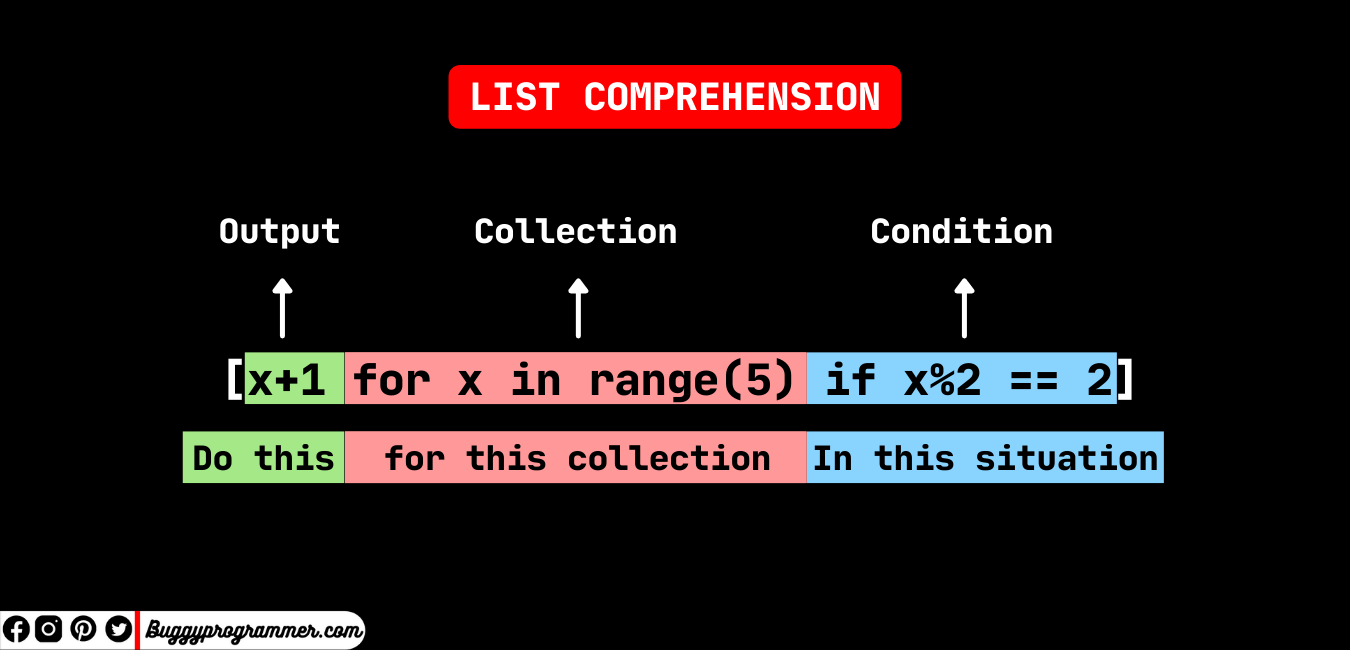
A list comprehension is a concise way to create a new list from an existing iterable by applying a transformation or filtering function. It's a single line of code that achieves the same result as multiple lines of code with a for loop.

Example:
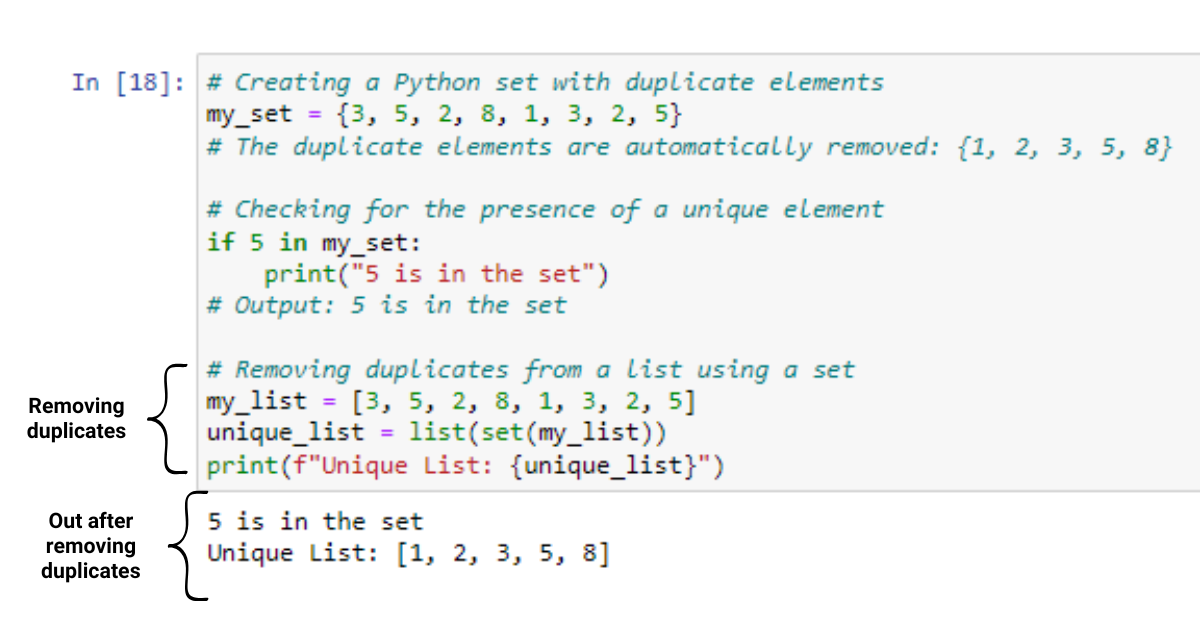
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
squared_numbers = [x**2 for x in numbers]
print(squared_numbers) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
In this example, the list comprehension creates a new list squared_numbers by squaring each number in the original list numbers. The resulting list contains the squares of the original numbers.
For Loop
A for loop is a more traditional way to iterate over an iterable and perform some action. It's useful when you need to perform multiple operations or access multiple values at once.
Example:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
result = []
for x in numbers:
result.append(x**2)
print(result) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
In this example, the for loop iterates over each number in the numbers list and appends its square to a new list result. The resulting list contains the squares of the original numbers.
Comparison
Here's a comparison of list comprehensions and for loops:
| | List Comprehension | For Loop |
| --- | --- | --- |
| Readability | Concise, easy to read | More verbose, harder to read |
| Performance | Fast, optimized by Python | Slower, not as optimized |
| Use cases | Simple transformations, filtering | Complex operations, multiple values |
When to use each
Use list comprehensions for: Simple transformations Filtering Creating a new list from an existing iterable Use for loops for: Complex operations Accessing multiple values at once Performing multiple actionsConclusion
In conclusion, both list comprehensions and for loops are useful tools in Python. List comprehensions are concise and optimized for simple transformations, while for loops are more flexible and suitable for complex operations. Choose the right tool for your specific problem to write clean, efficient, and readable code!
When to use list comprehension vs for loop in Python?
When it comes to iterating over a sequence (like a list) and creating new sequences (like lists, tuples, or strings), Python programmers often face the dilemma of choosing between using list comprehensions and for loops. Both methods have their own strengths and weaknesses, and in this response, we'll explore when to use each approach.
List Comprehensions:
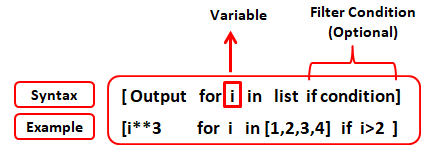
A list comprehension is a concise way to create a new list from an existing sequence or other iterable. It consists of brackets [] containing an expression followed by a for loop clause. The basic syntax is:
[expression for item in iterable]
Here are some characteristics that make list comprehensions shine:
Readability: List comprehensions are often more readable than equivalent for loops, especially when the iteration process is straightforward. Performance: In many cases, list comprehensions can be faster because they're implemented in CPython as a specialized function. Concise syntax: List comprehensions allow you to condense complex logic into a single line of code.When to use list comprehensions:
Simple transformations: When you need to create a new list by applying a simple transformation (e.g., squaring numbers) to each element in an existing iterable, a list comprehension is often the best choice. Filtering and mapping: List comprehensions are perfect for combining filtering and mapping operations on an iterable. Creating sequences with similar structure: If you need to create a sequence that has a similar structure (e.g., same length or type) as the original iterable, list comprehensions can be useful.For Loops:
A for loop is the most basic looping construct in Python. It's used when you need to iterate over a sequence and perform some operation on each item. The basic syntax is:
for variable in iterable: do something with variable
Here are some characteristics that make for loops valuable:
Flexibility: For loops give you more flexibility than list comprehensions, as you can add arbitrary code inside the loop. Complex logic: When your iteration process involves complex logic (e.g., nested loops or conditional statements), a for loop is usually more suitable. Debugging ease: With for loops, it's often easier to debug your code because you have more control over what happens within each iteration.When to use for loops:
Complex iterations: When the iteration process involves complex logic, multiple variables, or conditional statements, a for loop is usually the better choice. Mutable variables: For loops are essential when you need to modify the original iterable (e.g., append or remove elements) during the iteration. Side effects: If your iteration has side effects (e.g., printing something), a for loop is often more suitable because it allows you to explicitly handle these effects.In conclusion, list comprehensions are perfect for simple transformations, filtering, and mapping operations on iterables with similar structure. For loops are better suited for complex iterations, mutable variables, or code that requires side effects.
When the line blurs:
In some cases, both approaches might be applicable, and it's up to your personal preference or coding style to choose between them. A good rule of thumb is:
If you can express the logic in a concise way using list comprehensions, use them. If you need more control or complex logic within each iteration, opt for a for loop.Remember that mastering both techniques will make you a more versatile and effective Python programmer!