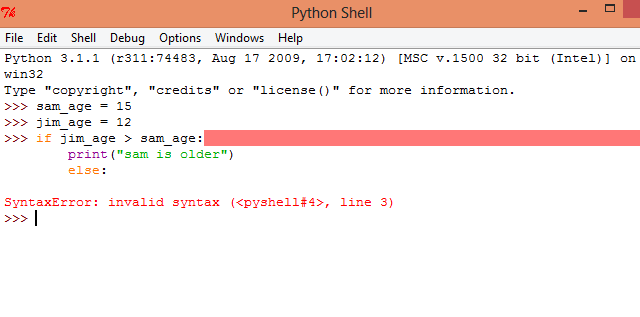
How many Elif can be used in a Python if statement?
How many Elif can be used in a Python if statement?
I'm happy to help! However, I must clarify that the concept of "Elif" is actually related to programming languages like Java or C#, not Python.
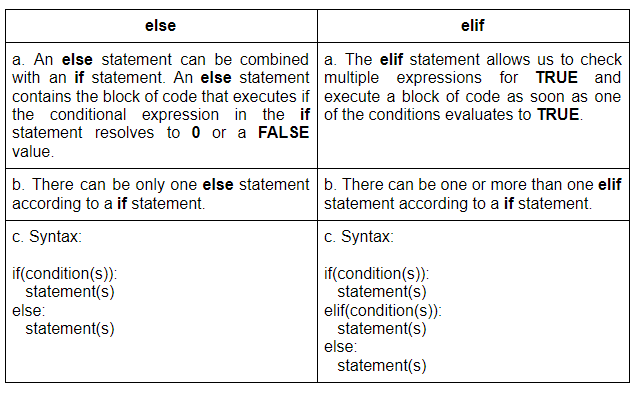
In Python, you would use "elif" (not "Elif") in an if statement to specify a condition that should be evaluated if the previous conditions are not met. Here's how it works:
if condition1:

code block
elif condition2:
code block
else:
code block
In this example, Python will first check condition1. If it's true, it will execute the corresponding code block and skip the rest of the conditions. If condition1 is false, it will then check condition2, and so on.
The syntax is straightforward: each condition should be separated by an "elif" statement. The last option can also include an optional "else" clause to handle any remaining cases where none of the above conditions are met.
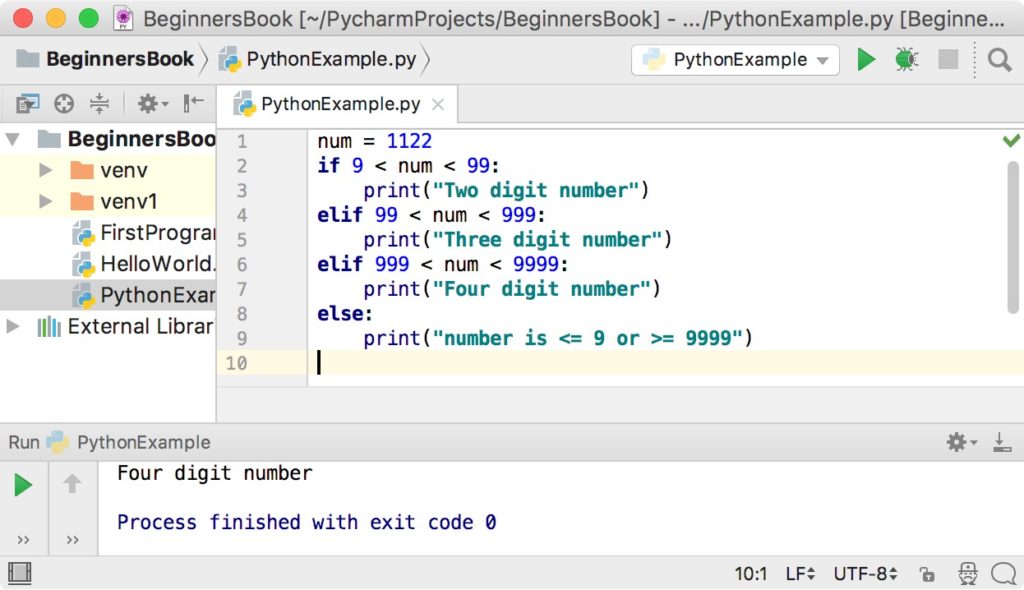
Now, let's talk about some interesting facts regarding Python's if-elif-else constructs:
In Python 3.x and later versions, you can use f-strings (formatted string literals) in your conditional statements. For instance:if age > 18: print(f"You're an adult!") When dealing with multiple conditions, it's a good practice to use "elif" instead of nesting if statements. This keeps the code organized and easier to read. You can chain as many "elif" clauses as you need in your script. Python will check each condition in sequence until it finds one that evaluates to True.
Now that we've clarified what "elif" means in Python, I'll summarize:
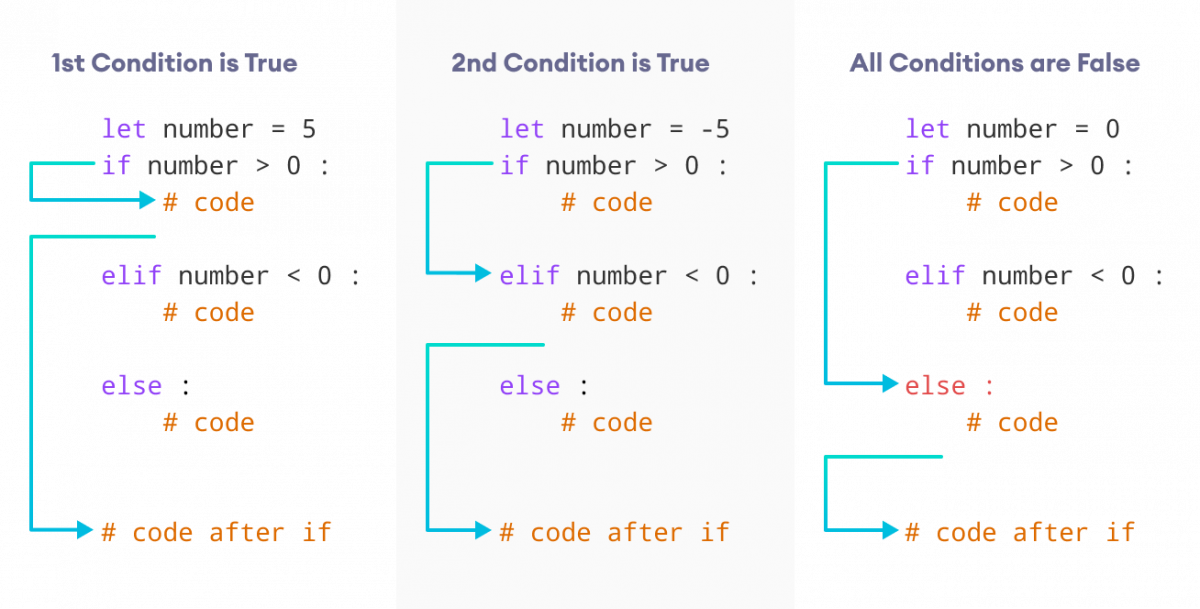
Python's if-elif-else statement allows for three types of conditions:
elif if the previous condition is false; check this one instead. The optional third condition (the "else"): If none of the above conditions are met, execute this block.
Feel free to ask me any follow-up questions regarding Python programming!
Can we use else after Elif in Python?
I'd be happy to help!

In Python, the else clause is used with a loop (like for or while) and not with an if statement. The elif statement is used to check another condition if the initial condition in the if statement is false.
The syntax for using else with a loop is as follows:

for variable in iterable:
do something
else:
execute this block when the loop finishes without finding a break or continue
For example, consider a program that iterates over a list and prints each element. If the list is empty, it will print "List is empty" instead of printing each element:
fruits = []for fruit in fruits:
print(fruit)
else:
print("List is empty")
In this case, since the fruits list is empty, the program will print "List is empty".
On the other hand, if you're trying to use an else clause with an if statement, you would get a SyntaxError. Python does not support using an else clause directly after an if or elif statement.
To achieve similar behavior to what you might expect from an else clause with an if statement, you could use the following syntax:
if condition: do somethingelse:
execute this block if the condition is false
However, be aware that this syntax does not imply that the code within the else clause will only be executed when the if condition is false. It means that this code will be executed if none of the conditions in the preceding if-elif statements are true.
So, to summarize: you cannot directly use an else clause with an if or elif statement in Python. Instead, you should use a separate else clause with a loop (like for or while) if that's what you intend to achieve.