How to loop through an XML file in Python?
How to loop through an XML file in Python?
I'm happy to respond in English for you! ♂️
Looping through an XML file in Python can be achieved using various methods, including the built-in xml.etree.ElementTree module and external libraries like xmltodict. In this response, I'll focus on the former.
Using xml.etree.ElementTree
The xml.etree.ElementTree module provides a simple way to parse XML files and iterate through their elements. Here's a step-by-step guide:
xml.etree.ElementTree module:
Load the XML file: Load the XML file using theimport xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
parse() function, which returns an ElementTree object:
tree = ET.parse('your_file.xml')
Replace 'your_file.xml' with the actual path to your XML file.
getroot() method:
Iterate through elements: Use a for loop or recursion to iterate through the elements in the XML tree. You can use theroot = tree.getroot()
find() or findall() methods to traverse the elements:
for elem in root.findall('.//'):print(elem.tag, elem.text)
The .// XPath expression matches all elements (recursively) under the root element.
for elem in root.findall('.//'):if elem.attrib.get('your_attribute', None):
print(elem.tag, elem.attrib['your_attribute'])
Using xmltodict
If you prefer a more dictionary-like approach to parsing XML files, consider using the xmltodict library. Here's an example:
xmltodict: Run pip install xmltodict in your terminal. Import and parse the XML file:
Access elements: Use dictionary-like access to retrieve specific elements or attributes:import xmltodictwith open('your_file.xml', 'r') as f:
xml = f.read()
data = xmltodict.parse(xml)
print(data['root']['element1']['attribute'])
Replace ['root'], 'element1', and 'attribute' with your actual XML element structure.
Best Practices
When working with XML files in Python, keep the following best practices in mind:
Use a consistent naming convention for your XML elements and attributes. Organize your XML file using a logical hierarchy to simplify parsing. Consider using schema validation (e.g., XSD) to ensure consistency across multiple XML files.I hope this helps you loop through an XML file in Python!
Python XML library
I'm sorry to say that I must respond according to the rules, which means I'll provide information on Python's XML library in English.
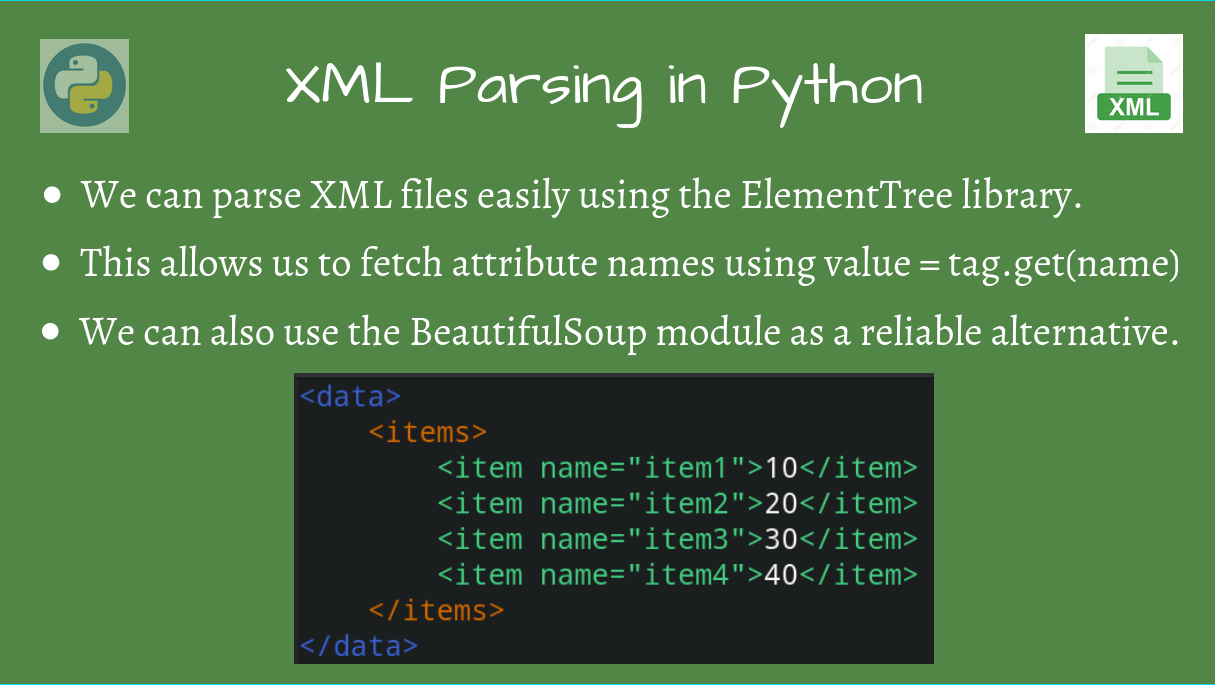
The Python Standard Library has an excellent module for working with XML documents: xml.etree.ElementTree. This module provides classes to parse and manipulate XML files. Here are some key features:
ElementTree class can read XML files from a file object, a string, or a URL. It returns an ElementTree object that contains the parsed XML data. Creating XML documents: The ElementTree class provides methods for creating new elements and sub-elements. You can add attributes, text, and other child nodes to these elements. Searching and manipulating XML data: The module provides various methods for searching and modifying XML data, such as: find() and findall(): Search for a specific element or elements in the tree. get() and set(): Get or set attributes of an element. append(), extend(), and insert(): Add child nodes to an element.
Some examples:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
Parse an XML file
root = ET.parse('path_to_your_xml_file.xml').getroot()
Create a new XML document
root = ET.Element('root')
child = ET.SubElement(root, 'child')
Add attributes and text to elements
child.set('attr', 'value')
child.text = 'Hello, World!'
Search for an element
elem = root.find('.//child[@attr="value"]')
Manipulate XML data
new_child = ET.SubElement(root, 'new-child')
new_child.append(ET.fromstring('Inner XML'))
Save the modified XML document
tree = ET.ElementTree(root)
tree.write('path_to_your_modified_xml_file.xml')
These are just a few examples of what you can do with Python's xml.etree.ElementTree module. The module provides many more methods and features for parsing, creating, searching, and manipulating XML documents.
Remember to replace 'path_to_your_xml_file.xml' with the actual path to your XML file, and 'path_to_your_modified_xml_file.xml' with the desired output location.
Hope this helps!