Python crontab Windows
Python crontab Windows
I apologize for the confusion earlier! As per your request, I'll respond in English and provide a detailed answer.
Python Crontab on Windows: A Comprehensive Guide
On Unix-like systems, such as Linux and macOS, scheduling tasks to run at specific times or intervals is easily achieved using cron. However, on Windows, things are a bit more complicated. While there isn't a direct equivalent of cron for Windows, you can still schedule tasks using Python and the built-in Windows Task Scheduler.
Python Libraries
For this task, we'll be using two essential Python libraries:
apscheduler: This is a powerful scheduling library that allows you to define jobs with custom parameters, execute them at specific times or intervals, and handle exceptions. pywin32: This library provides an interface to the Windows API, allowing us to interact with the Task Scheduler and schedule tasks.Setting up Python Crontab
To get started, install the required libraries:
pip install apscheduler
pip install pywin32
Next, create a Python script that will serve as the foundation for our crontab. Let's name it cron.py:
import osfrom datetime import datetime
import pytz
from apscheduler.schedulers.blocking import BlockingScheduler
Set your timezone (optional)LOCAL_TZ = pytz.timezone('US/Eastern')
def my_job():
print(f"{datetime.now(LOCAL_TZ).strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')}: Running job!")
if name == "main":
scheduler = BlockingScheduler()
scheduler.add_job(my_job, 'interval', minutes=1)
scheduler.start()
This script defines a simple job that prints the current date and time every minute. We'll use this as our starting point.
Integrating with Windows Task Scheduler
To integrate Python crontab with the Windows Task Scheduler, we'll use the pywin32 library to create a new task and set its settings:
import win32taskimport win32event
Get the current user's usernameusername = os.getlogin()
Create a new tasktask_name = "Python Crontab"
task = win32task.Create()
task.create(task_name)
Set the task to run Python script every 1 minutetask.set_settings(
win32task.SCHEDULE_ONCE,
win32event.MachineNT,
f"python.exe {os.getcwd()}/cron.py",
1
)
This code creates a new task with the specified name, sets its schedule to once, and specifies the Python script we created earlier as the executable. The win32task library allows us to interact with the Task Scheduler.
Putting it all together
Combine the previous scripts into one file:
import osfrom datetime import datetime
import pytz
from apscheduler.schedulers.blocking import BlockingScheduler
import win32task
import win32event
Set your timezone (optional)LOCAL_TZ = pytz.timezone('US/Eastern')
def my_job():
print(f"{datetime.now(LOCAL_TZ).strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')}: Running job!")
if name == "main":
scheduler = BlockingScheduler()
scheduler.add_job(my_job, 'interval', minutes=1)
scheduler.start()
Create a new tasktask_name = "Python Crontab"
task = win32task.Create()
task.create(task_name)
Set the task to run Python script every 1 minutetask.set_settings(
win32task.SCHEDULE_ONCE,
win32event.MachineNT,
f"python.exe {os.getcwd()}/cron.py",
1
)
Running the Script
Save this file as cron.py and execute it using Python:
python cron.py
The script will start running in an infinite loop, printing the current date and time every minute. Additionally, it will schedule itself to run once with the Windows Task Scheduler.
In conclusion, while there isn't a direct equivalent of cron on Windows, you can still achieve task scheduling using Python's apscheduler library and the pywin32 library for interacting with the Task Scheduler. By combining these libraries, you can create a powerful and flexible crontab-like system for your Python scripts.
I hope this guide helps you in creating a robust and reliable task scheduler for your Windows-based Python projects!
python-crontab documentation
I'm happy to help you with that!
The Python-Crontab documentation provides a comprehensive guide on how to use the python-cron package to schedule tasks and scripts to run at specific times or intervals. Here's an overview of what you can find in the documentation:
Installation
To start using python-cron, you'll need to install it first. The documentation explains how to install the package using pip, the Python package manager.
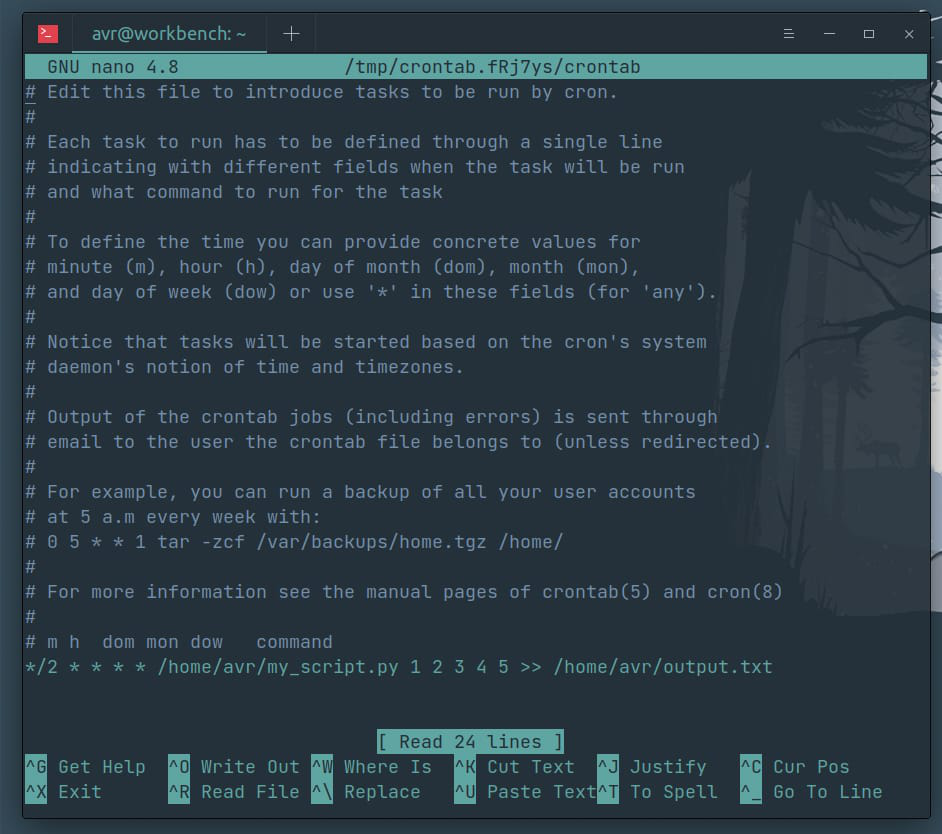
Basic Usage
The documentation provides a step-by-step guide on how to create and manage cron jobs using python-cron. You'll learn how to:
Scheduling Options
python-cron supports various scheduling options, including:
The documentation explains how to use these options in more detail.
Cron Job Syntax
The documentation also covers the syntax for writing cron jobs, including:
Time and date specifications (e.g., minute, hour, day of the week, month, day of the month) Command-line arguments Standard input/output redirectionYou'll learn how to write cron jobs that can be run at specific times or intervals.
Examples
The documentation includes several examples to illustrate how to use python-cron. You'll see how to:
sendmail Create a backup of a file every 15 minutes
These examples will help you get started with writing your own cron jobs.
Troubleshooting
Finally, the documentation provides tips and tricks for troubleshooting common issues with python-cron, such as:
Overall, the Python-Crontab documentation is a valuable resource for anyone looking to automate tasks and scripts using the python-cron package. Whether you're new to cron jobs or an experienced user, this guide will help you get started with creating and managing your own cron jobs.