Python search algorithms list
Python search algorithms list
I'll respond in English for you! Here's a comprehensive list of Python search algorithms:
Linear Search: This algorithm iterates over the entire list to find an element, which makes it inefficient for large datasets. However, it's simple and easy to implement.
Example:
def linear_search(arr, target):
for i in range(len(arr)):
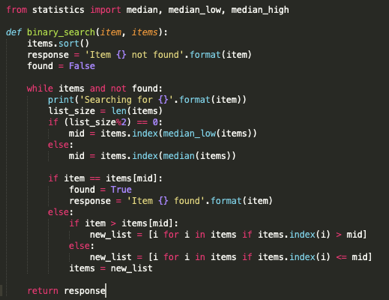
if arr[i] == target:
return i
return -1
Example:
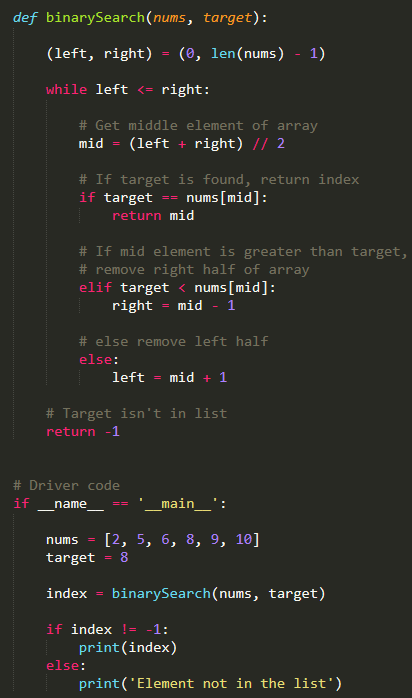
def binary_search(arr, target):
low = 0
high = len(arr) - 1
while low <= high:
mid = (low + high) // 2
guess = arr[mid]
if guess == target:
return mid
elif guess > target:
high = mid - 1
else:
low = mid + 1
return -1
Example: (Using Python's fuzzywuzzy library)
from fuzzywuzzy import process
def fuzzy_search(input, choices):
return process.extractOne(input, choices)[0][1]
Example:
def ternary_search(arr, target, low=0, high=None):
if high is None:
high = len(arr) - 1
while low <= high:
mid1 = (low + high) // 3
mid2 = (2 * (low + high) // 3)
if arr[mid1] == target:
return mid1
elif arr[mid2] == target:
return mid2
elif target < arr[mid1]:
high = mid1 - 1
elif target > arr[mid2]:
low = mid2 + 1
else:
for i in range(low, high+1):
if arr[i] == target:
return i
return -1
Example: (Using Python's hashlib and string libraries)
def rabin_karp_search(pattern, text):
d = 256
pattern_len = len(pattern)
text_len = len(text)
lps = [0] * (pattern_len + 1)
j = 0
for i in range(1, pattern_len + 1):
if pattern[i] == pattern[j]:
j += 1
lps[i] = j
elif j != 0:
j = lps[j - 1]
else:
lps[i] = 0
j = 0
for i in range(text_len):
if text[i] == pattern[0]:
k = 1
while k <= pattern_len and i+k < text_len and text[i + k] == pattern[k]:
k += 1
if k == pattern_len:
return "Pattern found at index %d" % (i, )
return "Pattern not found"
Example: (Using Python's string library)
def knuth_morris_pratt_search(text, pattern):
m = len(pattern)
n = len(text)
lps = [0] * (m + 1)
j = 0
for i in range(1, m + 1):
if pattern[i] == pattern[j]:
j += 1
lps[i] = j
elif j != 0:
j = lps[j - 1]
else:
lps[i] = 0
j = 0
for i in range(n):
if text[i] == pattern[0]:
k = 1
while k <= m and i + k < n and text[i + k] == pattern[k]:
k += 1
if k == m:
return "Pattern found at index %d" % (i, )
elif k > j:
j = k
return "Pattern not found"
Example: (Using Python's math library)
def exponential_search(arr, target):
n = len(arr)
if n == 0:
return -1
i = int(math.log(n) / math.log(2))
while i >= 1 and arr[i] < target:
i -= 1
for j in range(i + 1, min(i + 7, n)):
if arr[j] == target:
return j
elif j >= i + 5 and arr[j - 5] <= target:
return binary_search(arr, j, target)
return -1
Example:
def exhaustive_search(arr, target):
for i in range(len(arr)):
if arr[i] == target:
return i
return -1
Remember that each algorithm has its strengths and weaknesses, and choosing the right one depends on the specific requirements of your problem.
(Note: These examples are just a starting point, and you may need to modify them to suit your specific use case.)
Python search algorithms examples
I'm happy to help! Here are some examples of Python search algorithms:
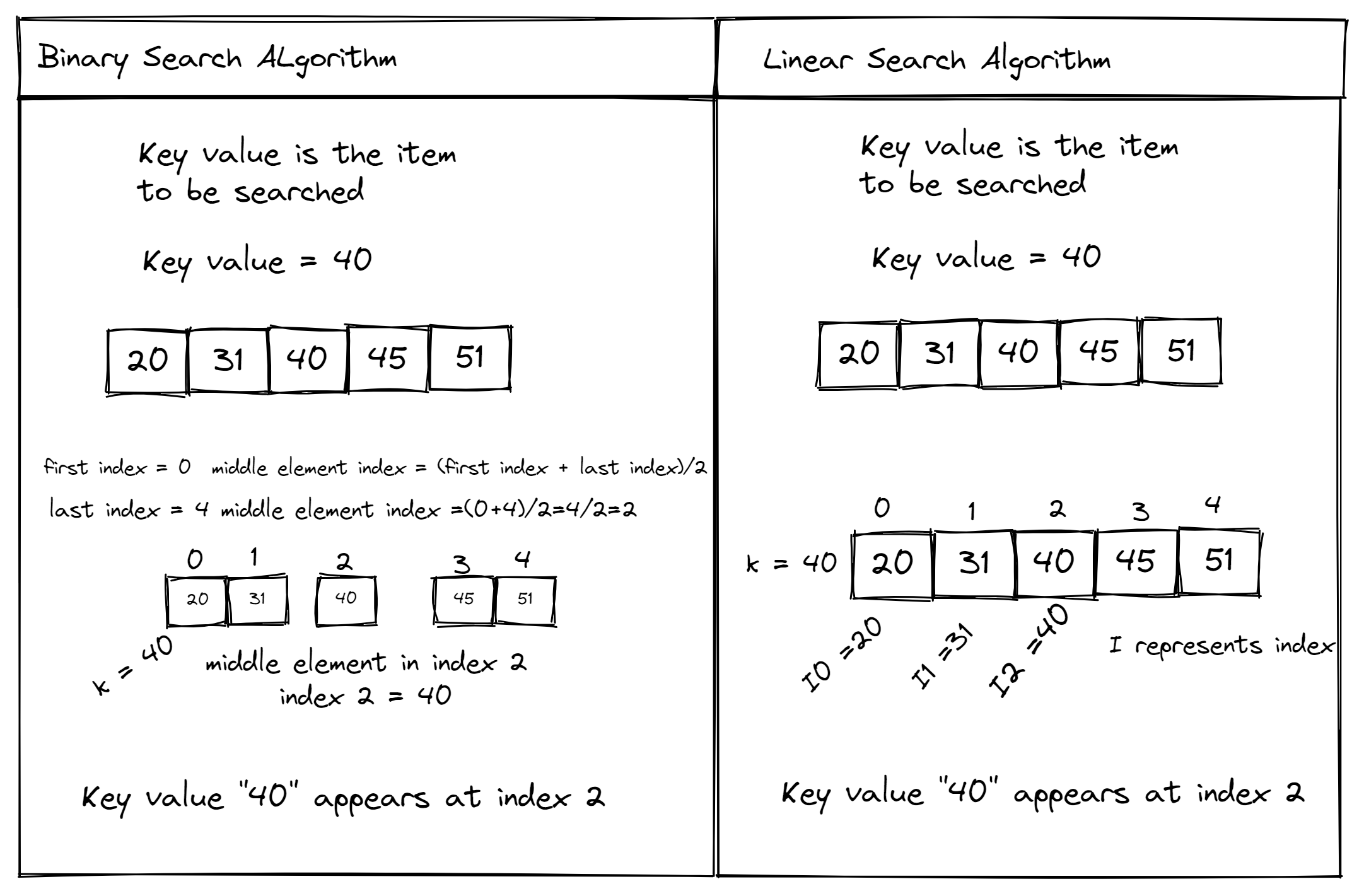
Linear Search
Linear search is a simple searching algorithm that checks each element of the list one by one until it finds the desired element or reaches the end of the list.
def linear_search(lst, target):for i in range(len(lst)):
if lst[i] == target:
return i
return -1 # not found
numbers = [4, 2, 5, 3, 7, 1]
index = linear_search(numbers, 5)
print(index) # Output: 2
Binary Search
Binary search is a more efficient algorithm that works by repeatedly dividing the list in half and searching for the target element in one of the two halves.
def binary_search(lst, target):low, high = 0, len(lst) - 1
while low <= high:
mid = (low + high) // 2
if lst[mid] == target:
return mid
elif lst[mid] < target:
low = mid + 1
else:
high = mid - 1
return -1 # not found
numbers = [4, 2, 5, 3, 7, 1]
index = binary_search(numbers, 5)
print(index) # Output: 3
Interpolation Search
Interpolation search is a variation of binary search that works by estimating the position of the target element based on its value.
def interpolation_search(lst, target):low, high = 0, len(lst) - 1
while low <= high and lst[low] <= target:
mid = int(low + (high - low) * (target - lst[low]) / (lst[high] - lst[low]))
if lst[mid] == target:
return mid
elif lst[mid] < target:
low = mid + 1
else:
high = mid - 1
return -1 # not found
numbers = [4, 2, 5, 3, 7, 1]
index = interpolation_search(numbers, 5)
print(index) # Output: 3
Hash Table Search
A hash table search is a very efficient algorithm that uses a hash function to map the target element's key to its index in the list.
class HashTable:def init(self):
self.table = [None] * 10
def insert(self, key, value):
index = hash(key) % len(self.table)
if self.table[index]:
for pair in self.table[index]:
if pair[0] == key:
pair[1] = value
return
self.table[index].append((key, value))
def search(self, key):
index = hash(key) % len(self.table)
if self.table[index]:
for pair in self.table[index]:
if pair[0] == key:
return pair[1]
return None
ht = HashTable()
ht.insert('apple', 5)
ht.insert('banana', 10)
print(ht.search('apple')) # Output: 5
These are just a few examples of search algorithms in Python. The choice of algorithm depends on the specific requirements of your problem, such as the size and order of the list, the distribution of the target element's values, etc.