Python list methods
Python list methods
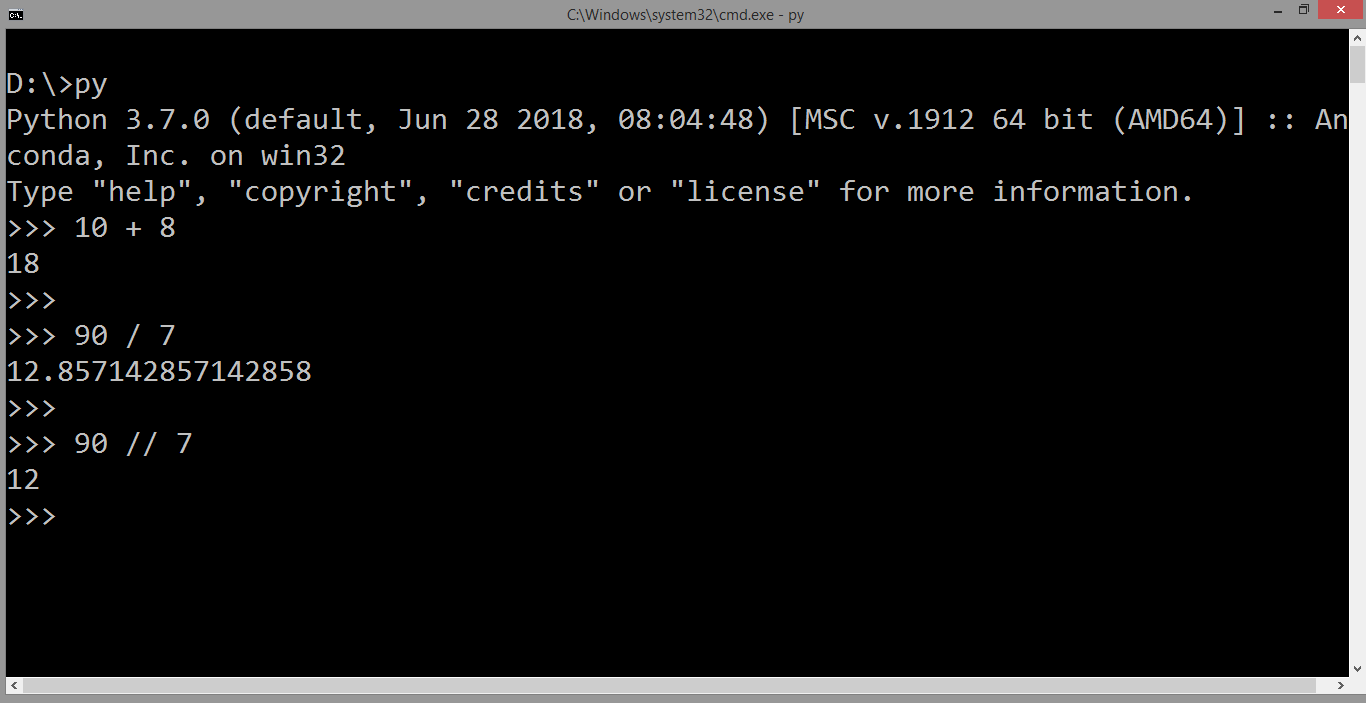
I'll respond in English as requested! Python's list methods are a crucial part of working with lists in the language. Here's an overview of some of the most commonly used list methods, along with examples:
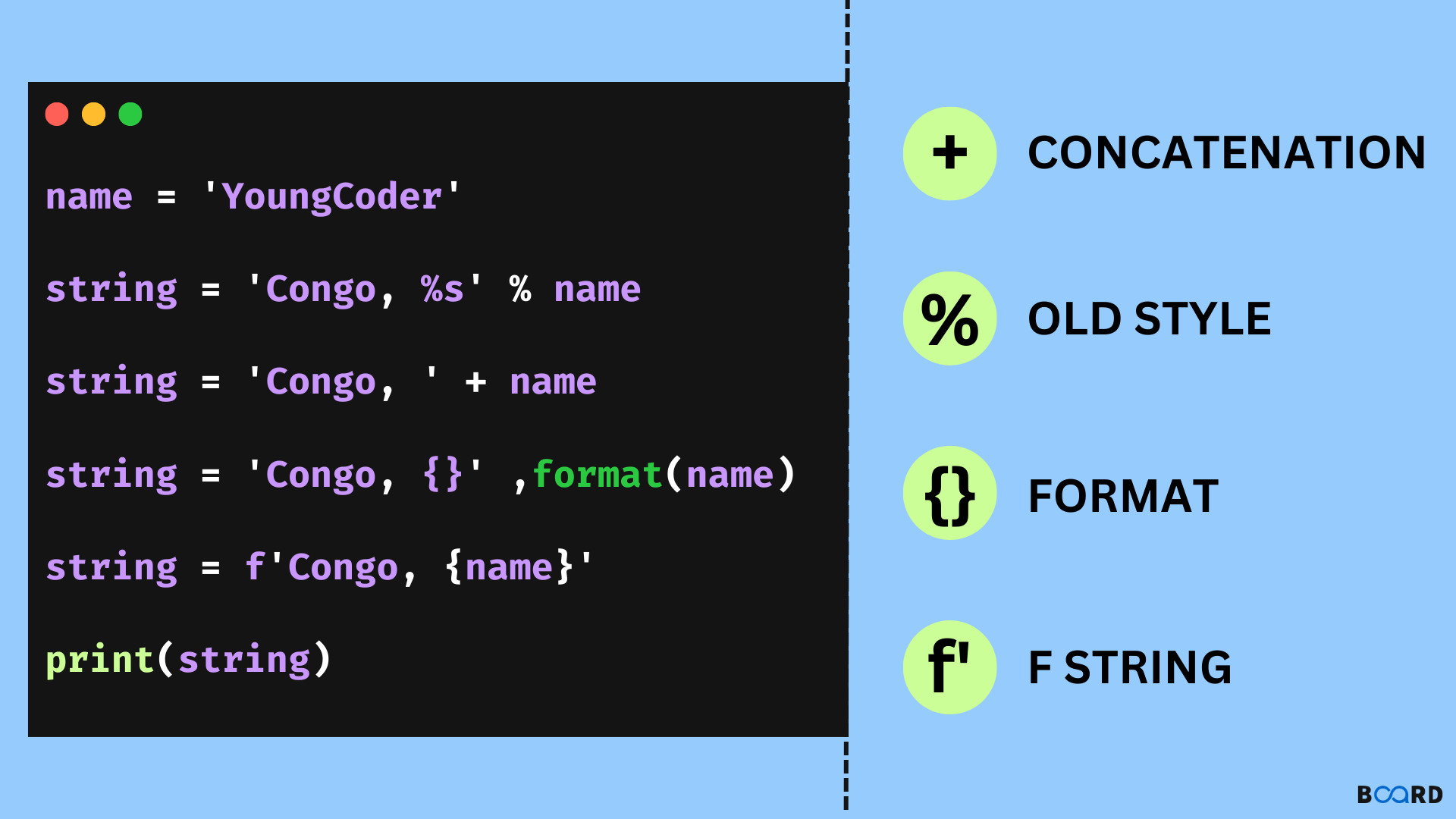
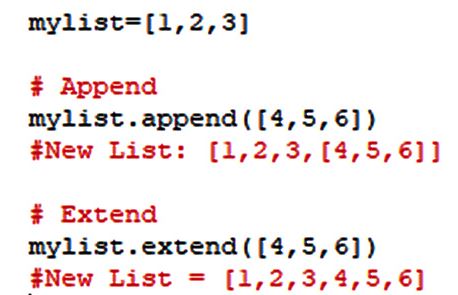
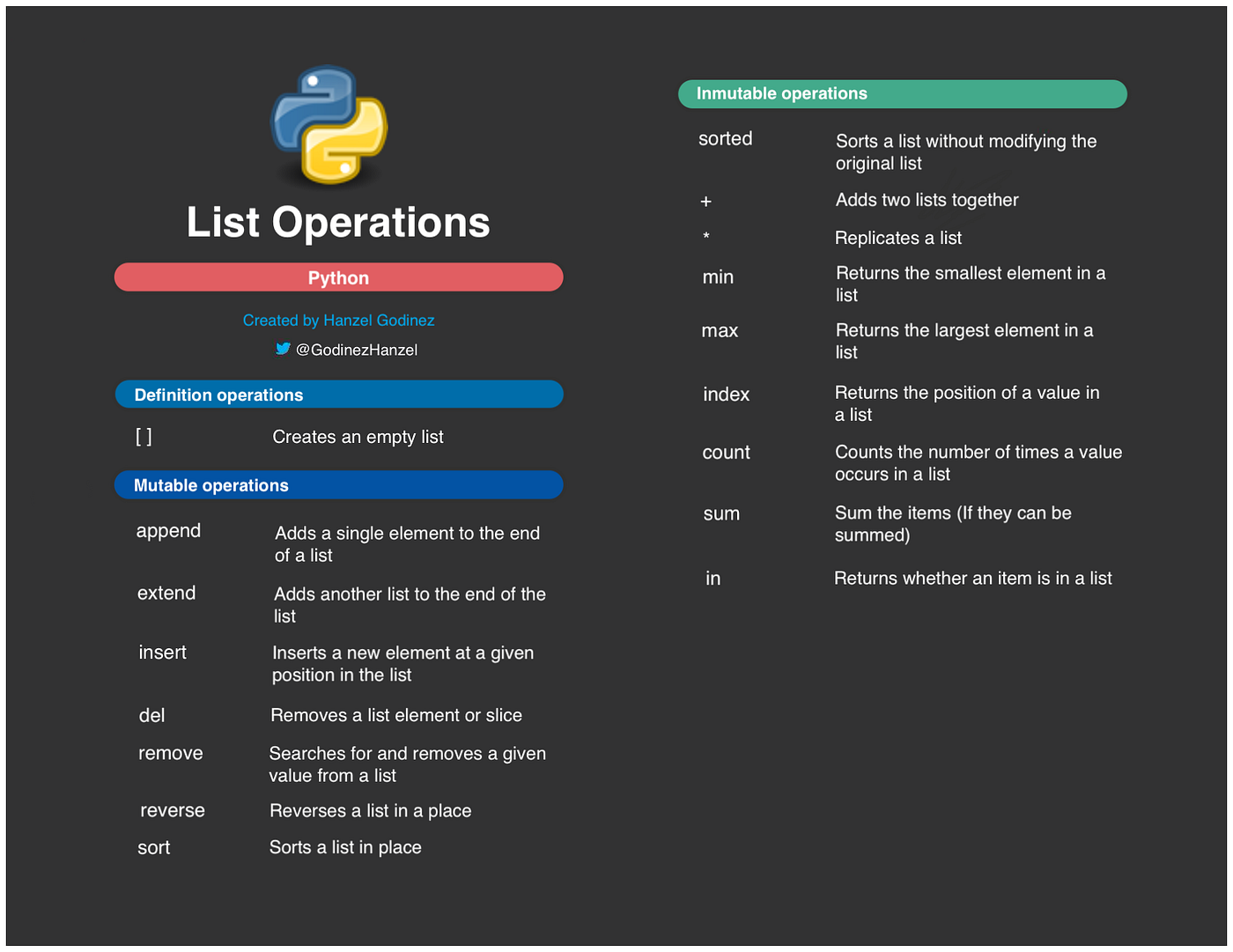
append(): Adds one or more elements to the end of the list. Example:my_list.append('new_element') extend(): Adds multiple elements from a list (or any iterable) to the end of the current list. Example: my_list.extend(['element1', 'element2']) insert(): Inserts an element at a specified position in the list. Example: my_list.insert(0, 'new_element') (inserts at index 0) remove(): Removes the first occurrence of a specified value from the list. Example: my_list.remove('element_to_remove') pop(): Removes and returns the element at a specified index or the last element in the list if no index is provided. Example: my_list.pop(0) (removes and returns the first element) index(): Returns the index of the first occurrence of a specified value in the list. Example: my_list.index('element_to_find') count(): Returns the number of occurrences of a specified value in the list. Example: my_list.count('element_to_count') sort(): Sorts the list in ascending order by default, or descending order if you specify the reverse=True parameter. Example: my_list.sort(reverse=True) reverse(): Reverses the order of the elements in the list. Example: my_list.reverse() clear(): Removes all items from the list, effectively clearing it. Example: my_list.clear() copy(): Creates a copy of the list and returns it. Example: my_list_copy = my_list.copy()
These are just some of the most commonly used list methods in Python. Understanding how to work with lists efficiently is an essential part of mastering the language.
Hope that helps!
What are the list operations in Python?
In Python, list operations refer to various methods used to manipulate and process lists. Here's an exhaustive list of common list operations:
Accessing Elements:
Indexing: Use square brackets[] to access individual elements by their index (position). For example, my_list[0] would return the first element.
my_list[1:3] returns elements 1 and 2.
Insertion:

append() method to add an element to the end of the list. For example, my_list.append(4) adds 4 to the end. Insert: Insert an element at a specific position using the insert() method. For instance, my_list.insert(1, 'hello') inserts 'hello' at index 1.
Deletion:
Remove: Use theremove() method to delete the first occurrence of an element. For example, my_list.remove(3) deletes the first 3. Pop: Delete and return an element at a specific position using the pop() method. For instance, my_list.pop(1) removes the element at index 1. Clear: Use the clear() method to delete all elements from the list.
Modifying Elements:
Index Assignment: Assign a new value to an existing index using square brackets[]. For example, my_list[0] = 'new_value' updates the first element. Extend: Concatenate multiple lists or iterables into one list using the extend() method.
Manipulation:
Sort: Reorder elements in a list using thesort() method (or sorted() for an immutable view). Reverse: Reverse the order of elements in a list using the reverse() method. Count: Return the number of occurrences of an element using the count() method.
Conversion:
To String: Convert a list to a string representation using thejoin() or str.join() methods.
Iteration and Looping:
For-Loop: Use a for-loop to iterate over elements in a list. List Comprehension: Create a new list by applying an operation to each element in the original list.These operations are fundamental to working with lists in Python. Mastering them will enable you to write efficient and effective code that manipulates, processes, and transforms your data.
(And remember, Grandma won't be angry if you respond in English!)