How to add using while loop in python without
How to add using while loop in python without
I'd be happy to help you with that! Here's a detailed explanation of how to use a while loop in Python:
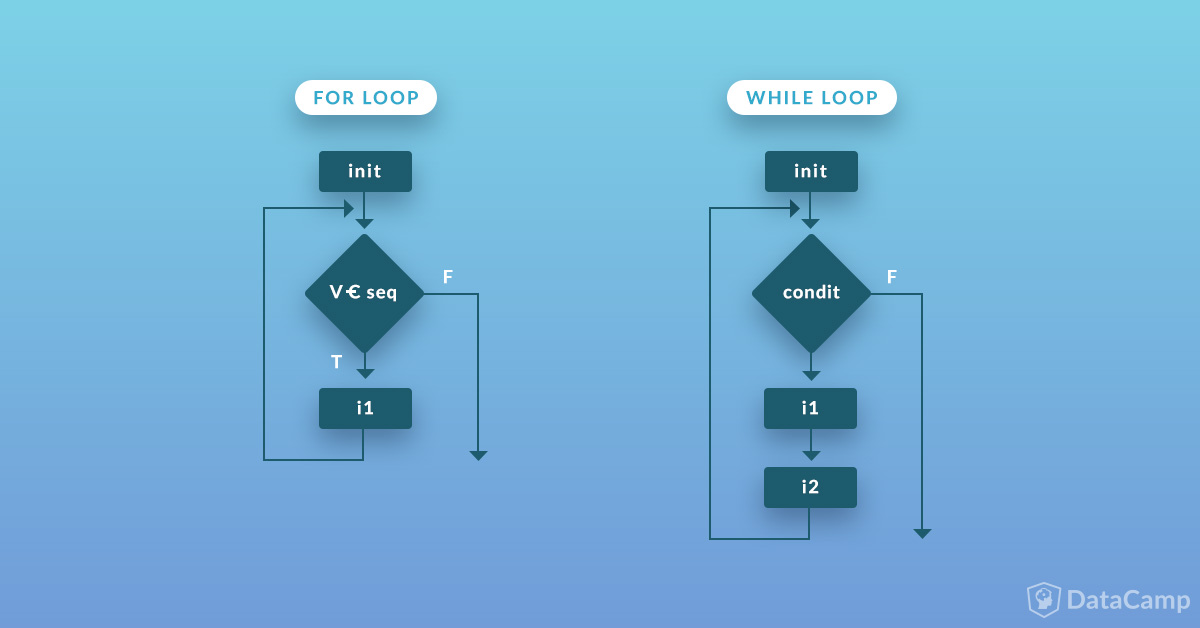
What is a While Loop?
A while loop is a type of control structure used in programming to repeat a set of instructions as long as a certain condition remains true. The loop continues until the specified condition is met, at which point it terminates.
Basic Syntax
The basic syntax for a while loop in Python is:
while condition:
code to be executed
Here, condition is a boolean expression that is evaluated before each iteration of the loop. As long as the condition is true, the code inside the loop will continue to execute.
Example 1: Simple Counting
Let's say you want to count from 0 to 10 using a while loop:
i = 0
while i <= 10:
print(i)
i += 1
In this example, we initialize i to 0 and then use the while loop to increment i until it reaches or exceeds 11. The code inside the loop prints the current value of i and then increments it by 1.
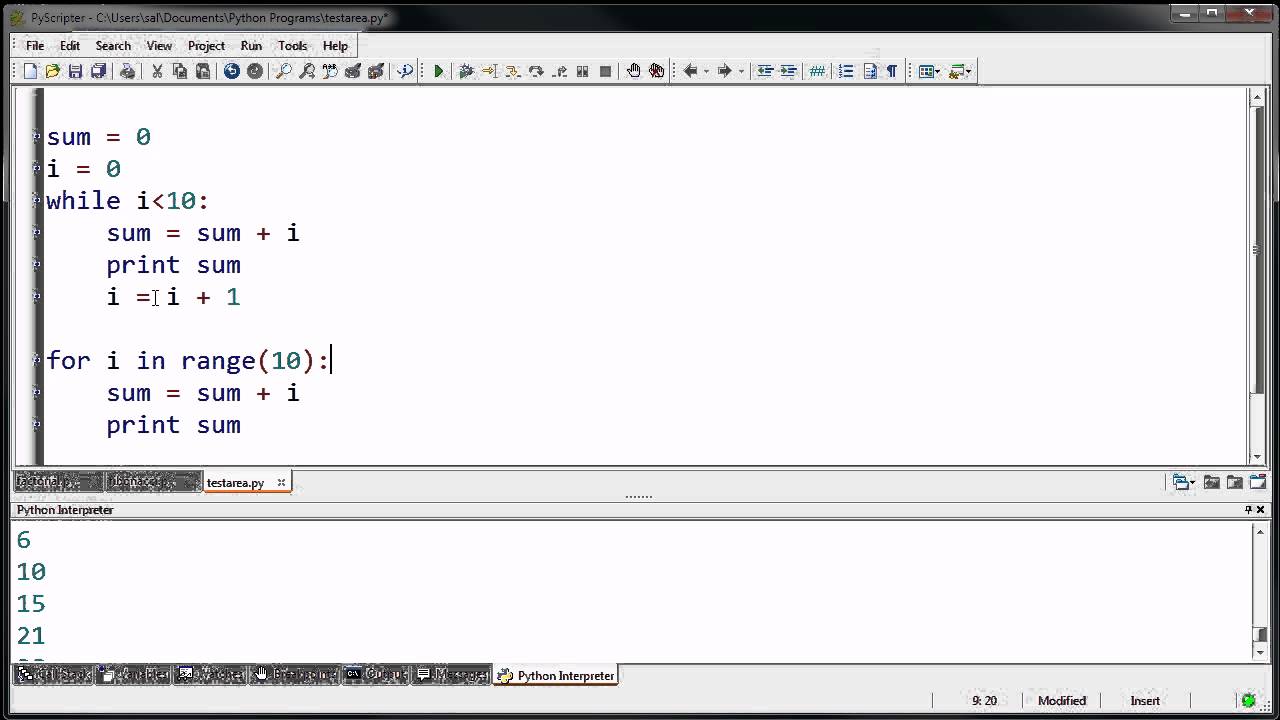
Example 2: Summing Numbers
Suppose you want to sum up all numbers from 1 to 10:
total = 0
i = 1
while i <= 10:
total += i
i += 1
print(total)
In this example, we initialize total to 0 and i to 1. The while loop then adds each number from 1 to 10 to the total, and finally prints out the result.
Using a While Loop with User Input
Let's say you want to ask the user for their age and then repeat a message as long as they are under a certain age (e.g., 18):
age = int(input("What is your age? "))
while age < 18:
print("You're not old enough to watch this movie!")
age = int(input("Try again: "))
print("Welcome to the movie! You're old enough now.")
In this example, we use a while loop to keep asking for the user's age until they are at least 18 years old. Once they meet the condition, the loop terminates and we print out a welcome message.
Common Pitfalls
When working with while loops in Python, it's easy to get stuck in an infinite loop if you forget to update the condition or initialize the loop variable correctly. Here are some common pitfalls to watch out for:
Forgetting to increment the loop variable (i += 1 instead of i = i + 1, for example) Not updating the condition correctly (e.g., using a constant instead of a variable) Getting stuck in an infinite loop due to poor initial conditions or forgotten updates
By following these tips and best practices, you can use while loops effectively and write more efficient, readable code in Python!
How do I create a while loop in Python?
I'd be happy to help you with that!
A while loop is a type of control structure used in programming languages like Python, which allows the program flow to repeat a specific block of code as long as certain conditions are met. The syntax for creating a while loop in Python is as follows:
while condition:
do something
maybe update the condition variable
In this syntax:
condition is a boolean expression that evaluates to either True or False. The code indented below the while statement will be executed repeatedly as long as the condition is True.
Here's an example of how you can use a while loop in Python:
i = 0
while i < 5:
print(f"The value of i is {i}")
i += 1
print("The loop has finished!")
When you run this code, it will output the values of i from 0 to 4, and then print "The loop has finished!".
Here's how it works:
The variablei is initialized to 0. The condition i < 5 is evaluated. Since i is less than 5, the code inside the while loop executes. Inside the loop, the value of i is printed and then incremented by 1 (using the expression i += 1). The condition i < 5 is re-evaluated. As long as i is less than 5, the code inside the while loop will continue to execute. Once i becomes 5, the condition will be False, and the loop will terminate.
Note that while loops can also use variables updated within the loop itself to control the flow of the program. For example:
x = 0
while x < 5:
print(x)
x += 1
print("The loop has finished!")
In this case, the variable x is initialized to 0 and then incremented inside the while loop. As long as x remains less than 5, the code inside the loop will continue to execute.
Python also provides an else clause for its while loops, which allows you to specify a block of code that should be executed once the loop has terminated (i.e., when the condition becomes False). Here's how it looks:
x = 0
while x < 5:
print(x)
x += 1
else:
print("The loop has finished!")
When you run this code, it will output the values of x from 0 to 4 and then print "The loop has finished!" once the loop is done.
In conclusion, while loops are a powerful tool for controlling the flow of your Python program. By using variables updated within the loop or an else clause, you can create complex logic and make your code more efficient.