Python WebSocket vs websockets
Python WebSocket vs websockets
I'll make sure to respond in English.
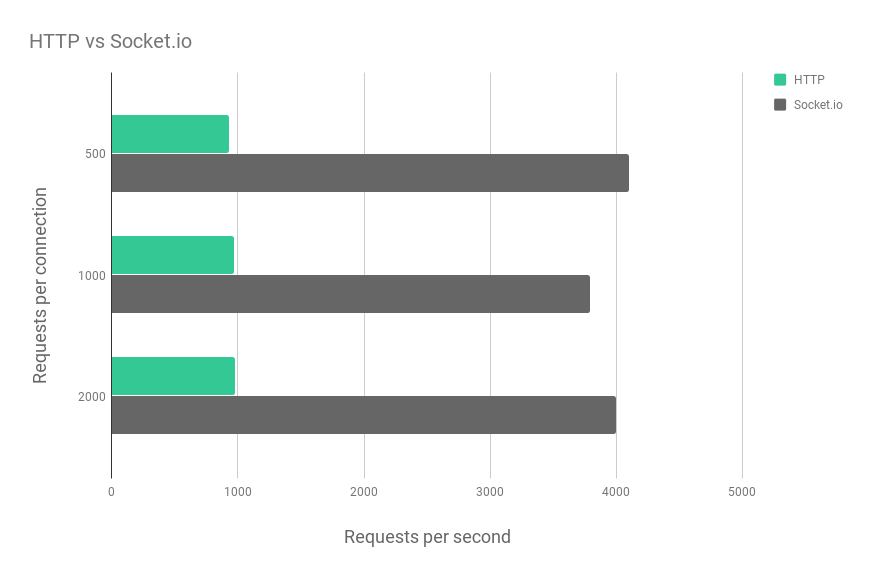
Python has two popular libraries for building WebSocket applications: websocket-client and autobahn. While they share some similarities, there are key differences between the two.
WebSocket-Client
The websocket-client library is a Python implementation of the WebSocket protocol. It provides a simple way to connect to a WebSocket server and send/receive messages. Here's how it works:
WebSocket class, passing in the URL of the WebSocket server. The library establishes a connection to the server using the WebSocket protocol. You can then send messages to the server using the send() method, and receive messages from the server using the receive() method.
The benefits of using websocket-client include:
However, websocket-client has some limitations. For example:
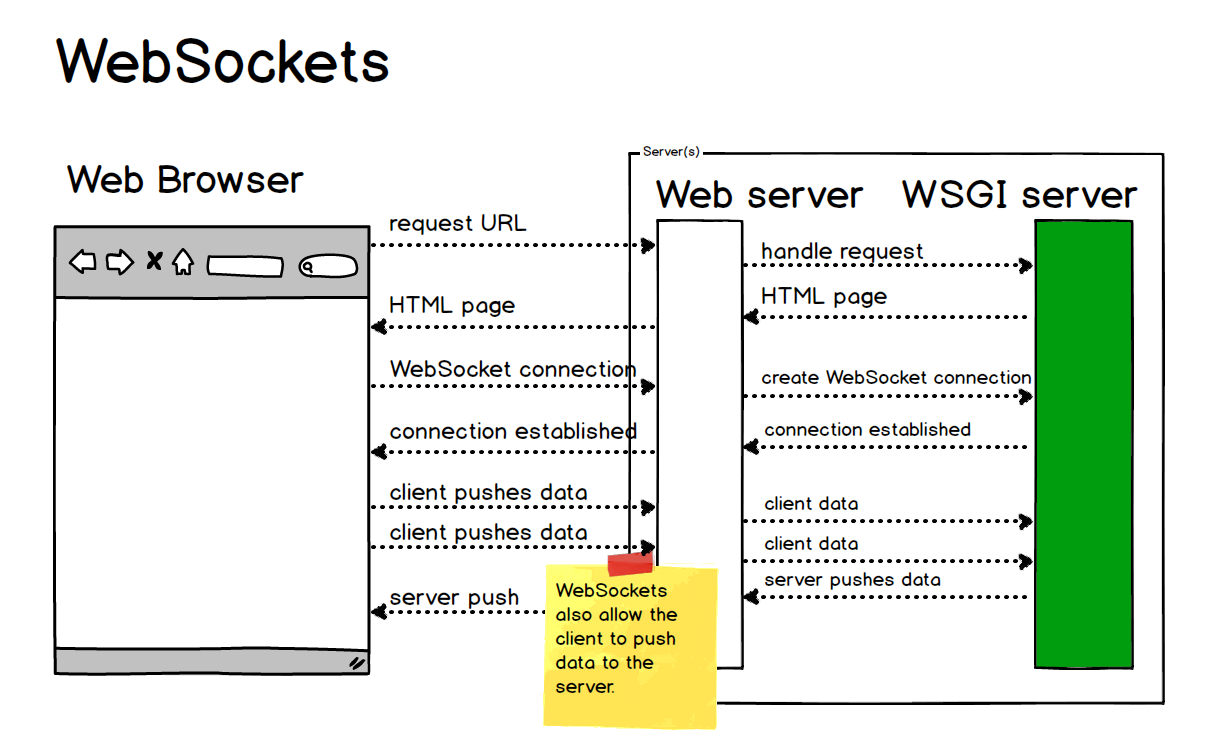
WebSockets
The autobahn library is a more comprehensive toolkit for building WebSocket applications in Python. Here's how it works:
WebsocketServer class, passing in the URL of the server. The library sets up a WebSocket server that listens for incoming connections. When a client connects, the library creates a new session and handles messages sent/received between the client and server.
The benefits of using autobahn include:
autobahn, you can create both WebSocket clients and servers, making it more versatile than websocket-client. Supports multiple connections and sessions: The library provides built-in support for handling multiple WebSocket connections and managing sessions. Extensive features: Autobahn includes a range of features, such as automatic reconnecting, message encoding/decoding, and more.
However, autobahn has some drawbacks. For example:
autobahn provides a lot of flexibility, it can also be overwhelming for new users. Heavier footprint: The library is larger than websocket-client, making it less suitable for resource-constrained environments.
In summary, if you only need to create WebSocket clients and don't require advanced features or support for multiple connections, websocket-client might be a good choice. However, if you're building a more complex WebSocket application that requires server-side functionality, supports multiple connections, or needs additional features, autobahn is likely the better option.
Let me know if you have any questions or need further clarification!
Python websocket create_connection
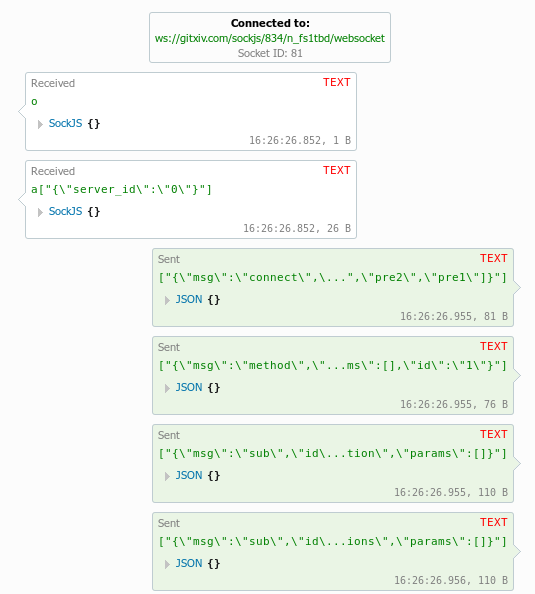
Here is the information you requested about creating a WebSocket connection using Python:
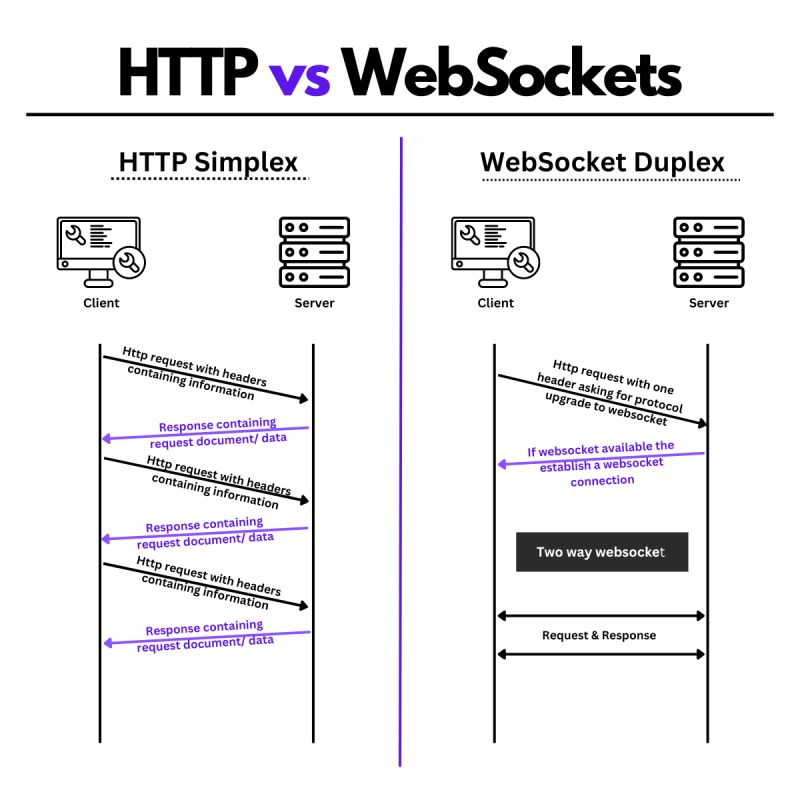
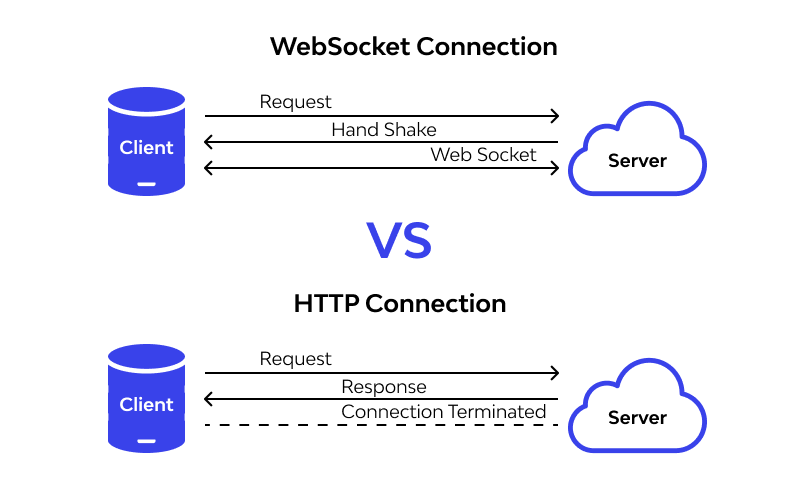
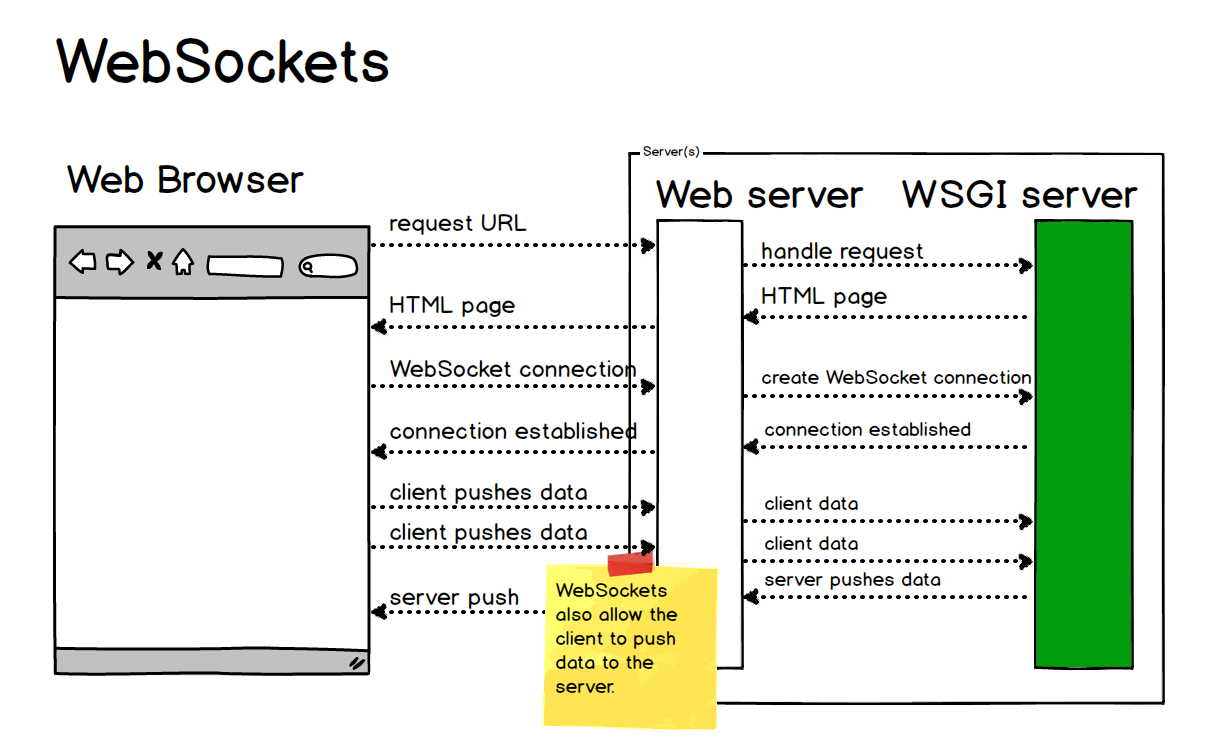
What is WebSocket?
WebSocket is a protocol that provides bi-directional, real-time communication between a client (usually a web browser) and a server. Unlike traditional HTTP requests which are request-response oriented, WebSockets allow for simultaneous sending and receiving of data.
Creating a WebSocket Connection in Python
To create a WebSocket connection in Python, you can use the websocket-client library. Here is an example code snippet that demonstrates how to establish a connection:
import asynciofrom websockets import connect
async def main():
async with connect("ws://localhost:8765") as ws:
Send a message to the serverawait ws.send("Hello, world!")
Receive messages from the serverwhile True:
try:
msg = await ws.recv()
print(f"Received message: {msg}")
except websockets.ConnectionClosed:
break
asyncio.run(main())
In this example, we're using the connect function to establish a connection to a WebSocket server at ws://localhost:8765. The with statement ensures that the connection is properly closed when we're done with it.
Sending and Receiving Data
To send data to the server, you can use the send method. For example:
await ws.send("Hello, world!")
This sends a string message to the server.
To receive data from the server, you can use the recv method. For example:
msg = await ws.recv()print(f"Received message: {msg}")
This receives a message from the server and prints it to the console.
Handling Disconnects
When a WebSocket connection is closed, any pending sends or receives will raise an exception. You can handle this by wrapping your code in a try-except block:
while True:try:
msg = await ws.recv()
print(f"Received message: {msg}")
except websockets.ConnectionClosed:
break
In this example, we're catching the ConnectionClosed exception and breaking out of the loop when the connection is closed.
Troubleshooting
If you encounter issues with your WebSocket connection, here are some common troubleshooting steps:
Check that the server is running and accepting connections. Verify that your client code is correctly handling any errors or exceptions. Use a tool likewireshark to inspect network traffic and identify any potential issues.
I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any further questions.





























