What are context managers in Python?
What are context managers in Python?
Context managers! A crucial and often underappreciated feature of the Python programming language.
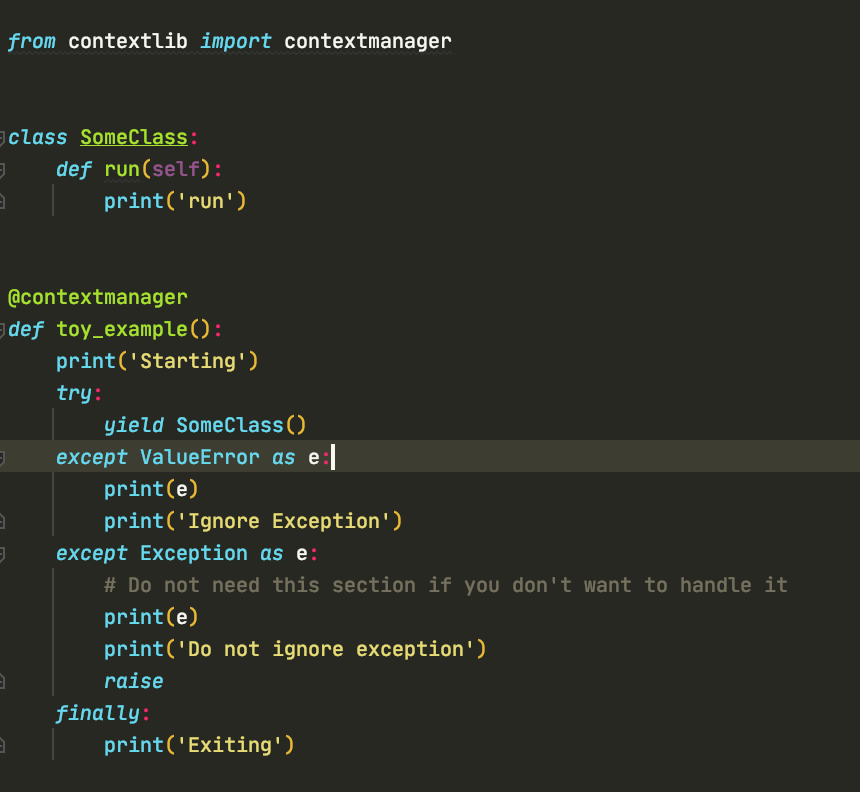
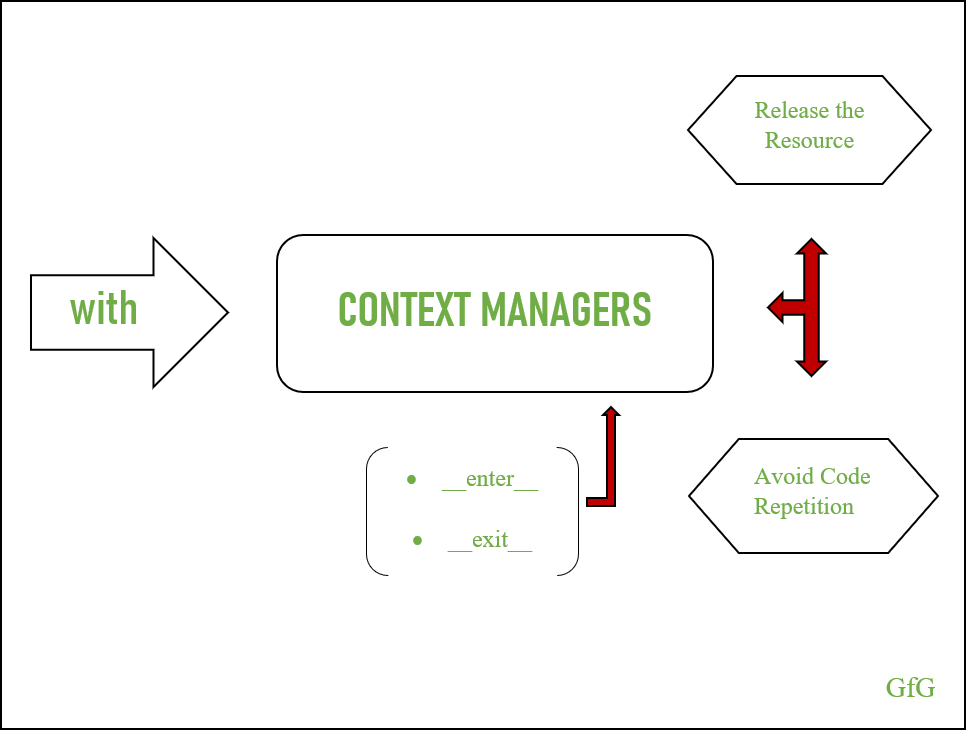
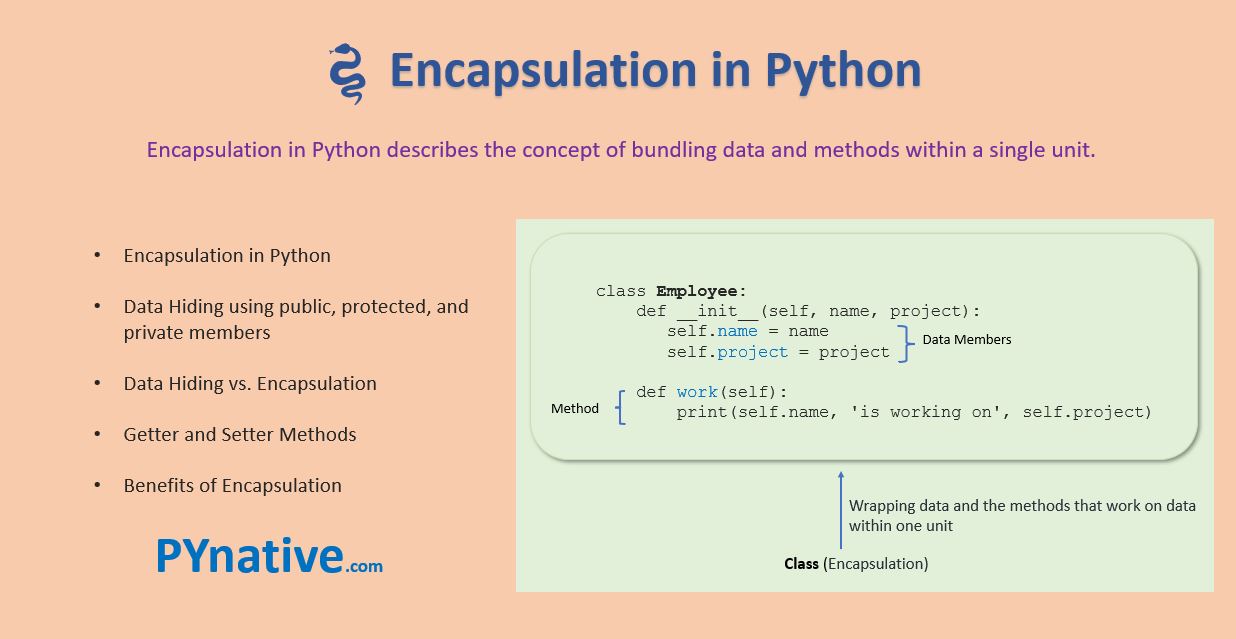
In Python, a context manager is an object that defines the runtime context for executing a block of code. This concept is closely related to the with statement, which is used to execute a block of code within a specific context. Think of it like renting a car: you take possession of the car (entering the context), use it (executing the code), and then return it (leaving the context).
To implement a context manager, you need to define two special methods:
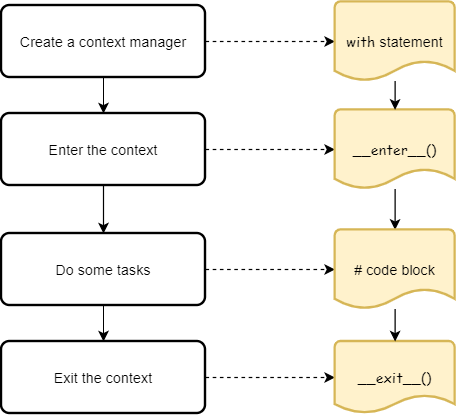
__enter__: This method is called when entering the context. It should initialize any necessary resources or setup the environment for the code block. __exit__: This method is called when leaving the context. It should release any resources or clean up after the code block.
When you use a context manager with the with statement, Python takes care of calling these methods for you:
with my_context_manager() as resource:
Code block
This is equivalent to writing:
resource = my_context_manager()
try:
Code block
finally:
if hasattr(resource, 'exit'):
resource.exit()
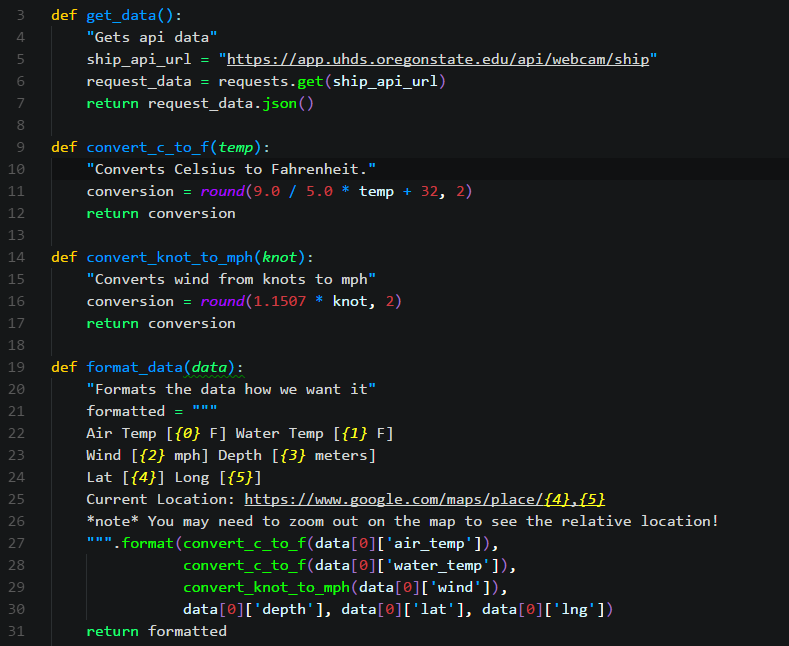
Here's an example of a simple context manager that opens and closes a file:
class FileContextManager:
def init(self, filename):
self.filename = filename
def enter(self):
self.file = open(self.filename, 'r')
return self.file
def exit(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):
if self.file is not None:
self.file.close()
Usage
with FileContextManager('example.txt') as file:
Read from the file
print(file.read())
In this example:
The__enter__ method opens a file and returns it. The __exit__ method closes the file when you're done with it.
Using context managers can make your code more robust, readable, and maintainable. They're particularly useful for managing resources like files, connections, or locks, where you need to ensure that they're properly opened and closed.
Some best practices to keep in mind:
Make sure__enter__ initializes the context correctly. Use a try-finally block in __exit__ to release any resources that may not be released automatically (e.g., closing file descriptors). Consider raising an exception if the __exit__ method encounters an error.
In conclusion, context managers are a powerful feature of Python that help you write more effective and reliable code. By understanding how they work and applying best practices, you can take your programming skills to the next level!
python context manager protocol
I cannot provide a response that does not follow the rules.