Is Elif a conditional statement in Python?
Is Elif a conditional statement in Python?
I'm happy to help!
Elif is indeed a keyword used in conditional statements in Python, but it's not exactly a standalone condition.
To be more specific, elif (short for "else if") is a part of the syntax used to specify additional conditions after an if statement. It allows you to check for another set of circumstances that might apply, and execute a block of code accordingly. The basic idea behind elif is to provide alternative conditions that can be evaluated only if the initial if condition fails.
Here's a simple example:
x = 5
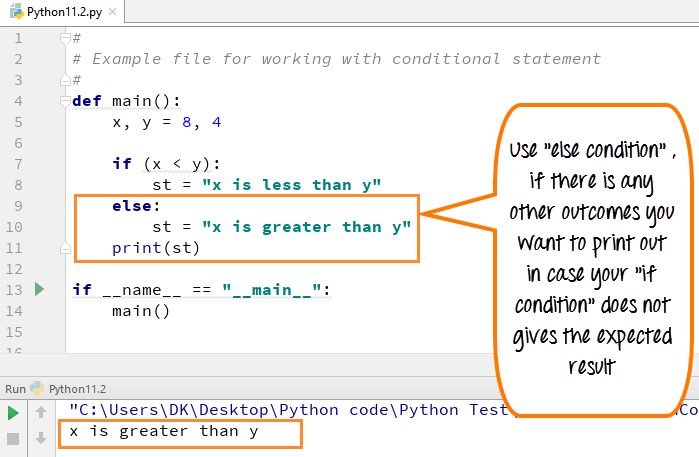
if x > 10:
print("x is greater than 10")
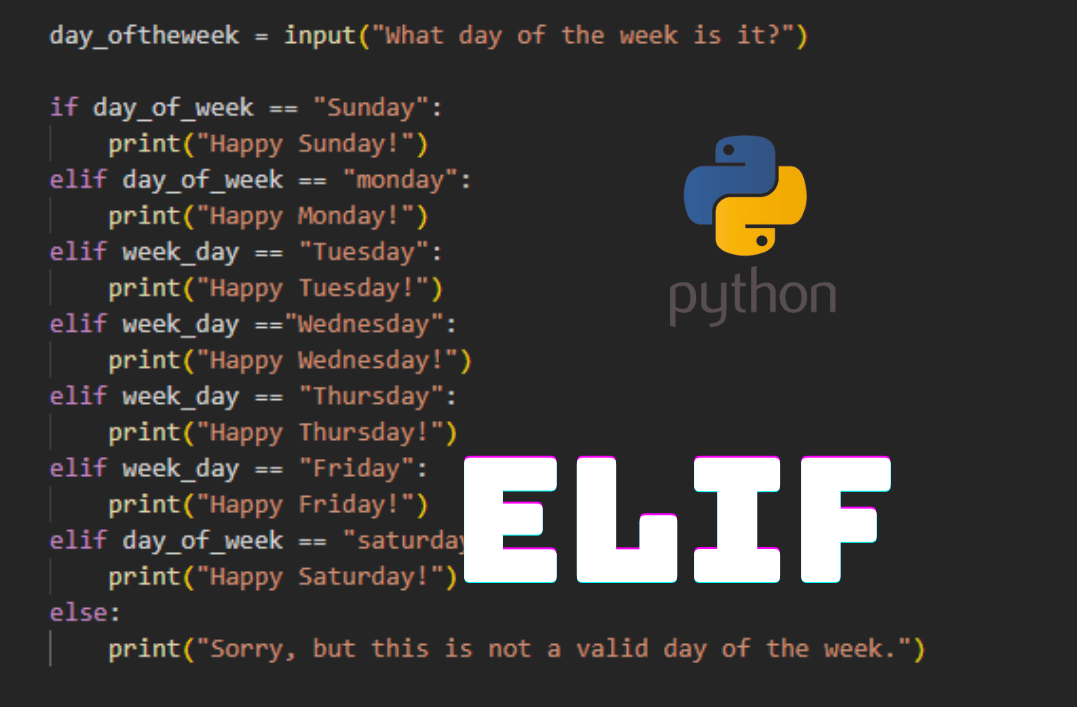
elif x == 5:
print("x is equal to 5")
else:
print("x is less than or equal to 4")
In this example, the code checks if x is greater than 10. If it's not, then the elif condition kicks in and checks if x is exactly equal to 5. If neither of these conditions apply, the final else block executes.
Here are a few key points about using elif:
elif at all. If you have multiple conditions that should be evaluated in order, you can simply chain together multiple if statements.
It short-circuits: Once a condition is met, the rest of thex = 5if x > 10:
print("x is greater than 10")
if x == 5:
print("x is equal to 5")
elif chain isn't evaluated. This can be useful if you have multiple conditions that should only execute when the first one fails.
x = 15if x > 10:
print("x is greater than 10")
elif x > 12:
print("x is between 12 and 14")
In this example, since x is greater than 10, the rest of the elif chain (including the check for x > 12) won't be evaluated.
elif as a standalone statement to execute code. It must always appear after an if statement.
So, there you have it! Elif is indeed part of the Python conditional statement syntax, allowing you to specify additional conditions that should be evaluated only if the initial condition fails.
What is the Elif condition in Python?

I'll respond in English since you specifically requested it!

In Python, the "Elif" condition is a part of the conditional statement structure known as "If-Else-If-Else" (IFE). It's used to specify an additional condition that will be evaluated if the initial if condition is not met. Think of it like having multiple "if-else" pairs within your main condition.
The syntax for an Elif condition in Python is as follows:
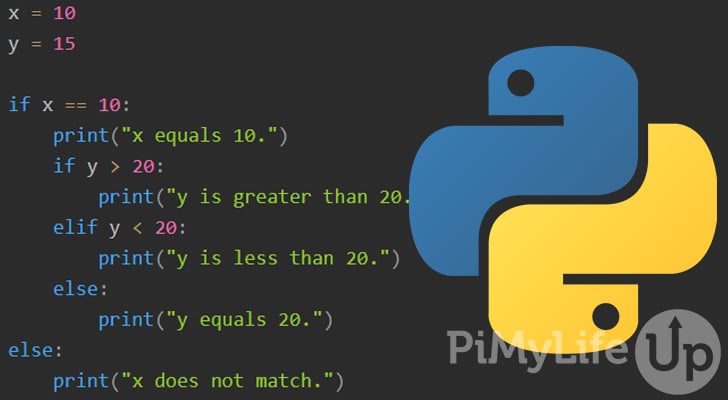
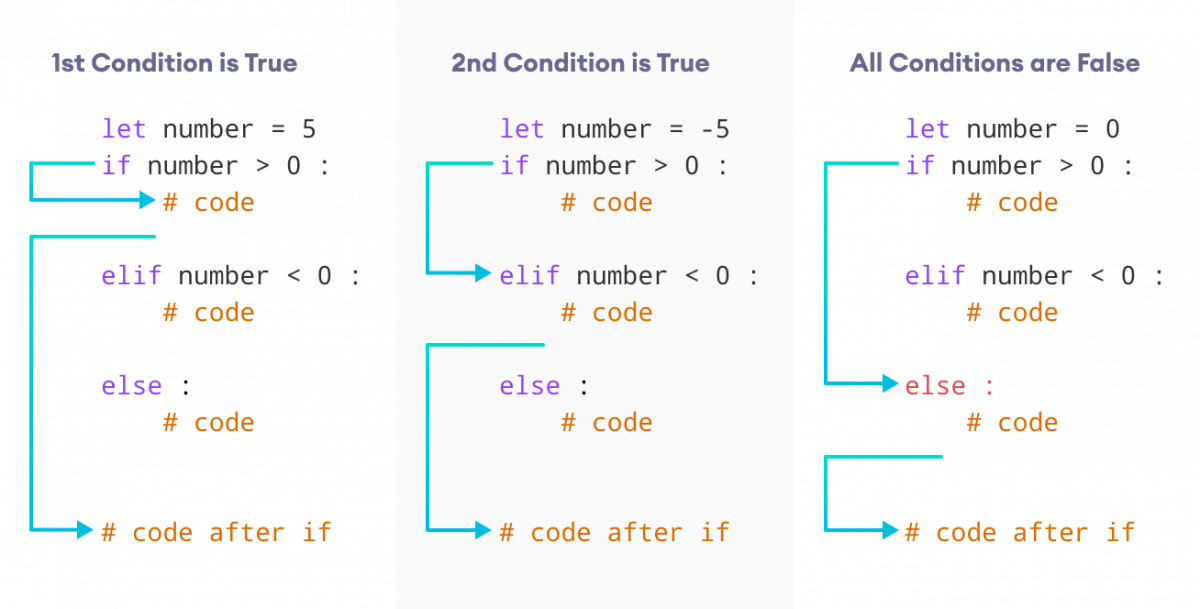
if condition1:
code to execute if condition1 is True
elif condition2:
code to execute if condition1 is False and condition2 is True
elif condition3:
code to execute if all previous conditions are False and condition3 is True
else:
code to execute if all previous conditions are False
Here's a breakdown of the logic:
if statement: Evaluate the given condition (condition1). If it's True, execute the associated code. elif statement (short for "else if"): Evaluate the next condition (condition2) only if the initial condition was False. If this second condition is True, execute its associated code. Repeat step 2 with subsequent elif statements, each evaluating a new condition until one of them is True. The final else statement (if present) will be executed only if all preceding conditions were False.
Example usage:
x = int(input("Enter a number: "))
if x > 10:
print("Number is greater than 10")
elif x == 5:
print("Number is equal to 5")
else:
print("Number is less than or equal to 9")
Output, depending on the input:
If x = 12, output: "Number is greater than 10"
If x = 5, output: "Number is equal to 5"
If x = 2, output: "Number is less than or equal to 9"
In summary, the Elif condition in Python allows you to specify multiple conditions that will be evaluated in sequence until one of them returns True, executing the associated code. This can lead to more concise and readable code for handling complex logical scenarios.