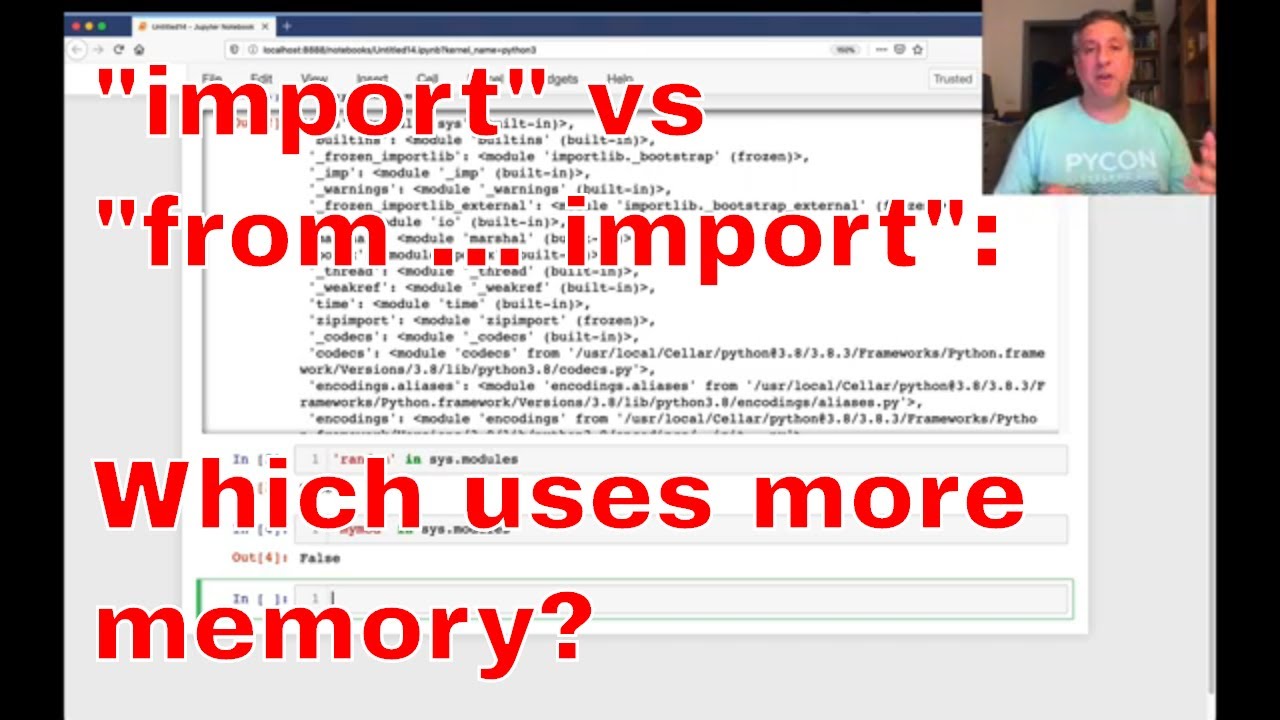
How do I import a package into Python?
How do I import a package into Python?
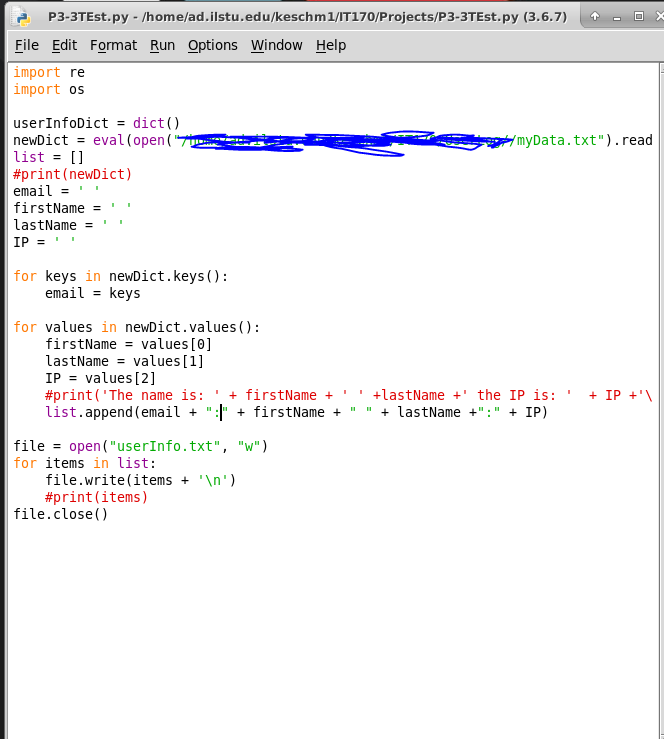
To import a package (or module) into Python, you can use the import statement followed by the name of the package or module you want to access.
Here's an example of how you can do this:
import mypackage
Where mypackage is the name of the package or module you want to import. If the package has a specific function or class that you want to use, you can specify it like this:
from mypackage import MyClass
Or if the package has multiple functions or classes that you want to use, you can do something like this:
import mypackage as mp
Then access the module's contents using the alias
mp.MyClass()
mp.myfunction()
When importing a package, Python looks for it in the following places:
The current directory (i.e., the directory where your Python script is located). ThePYTHONPATH environment variable. The default path (i.e., the location where the Python interpreter installed its packages).
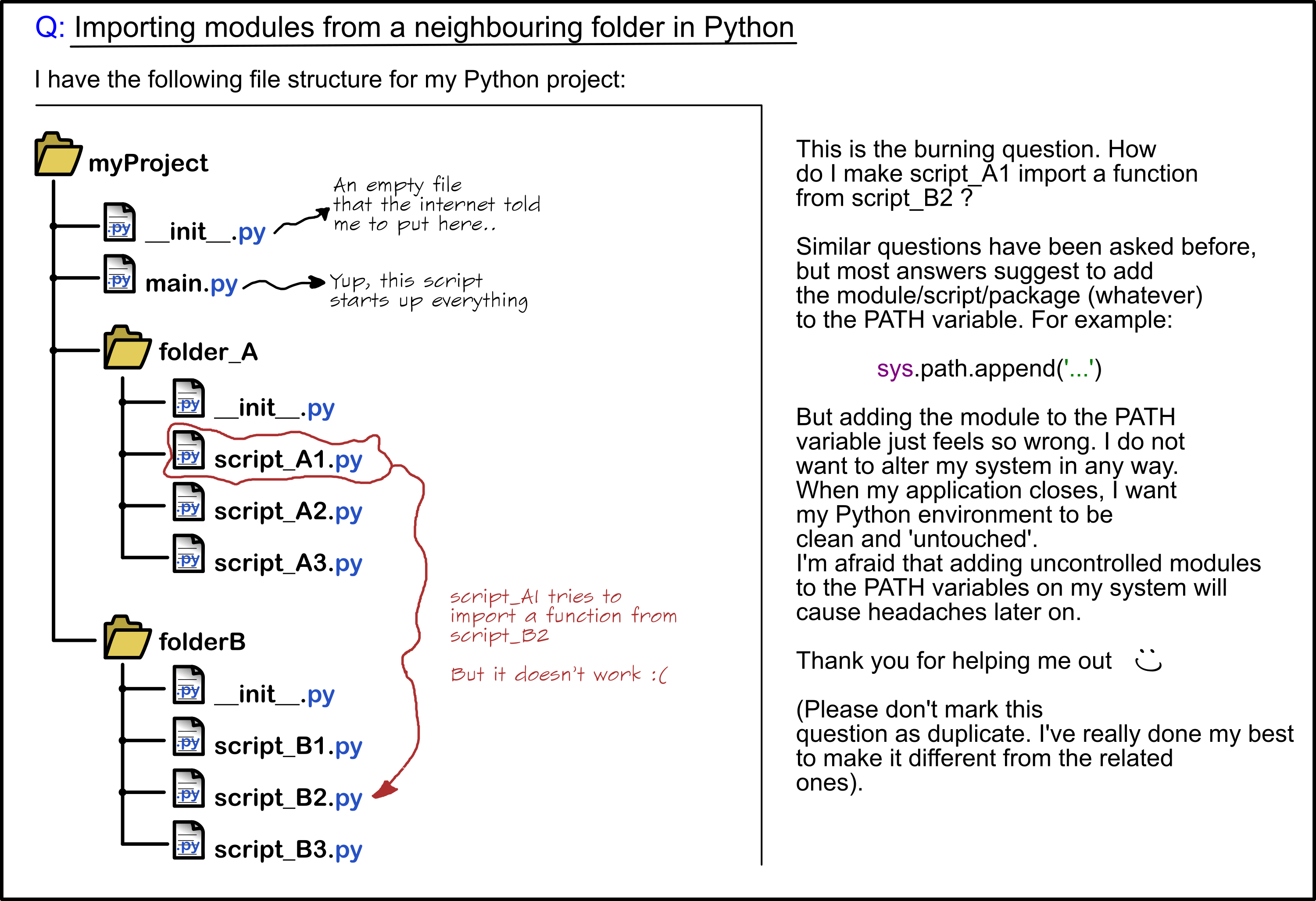
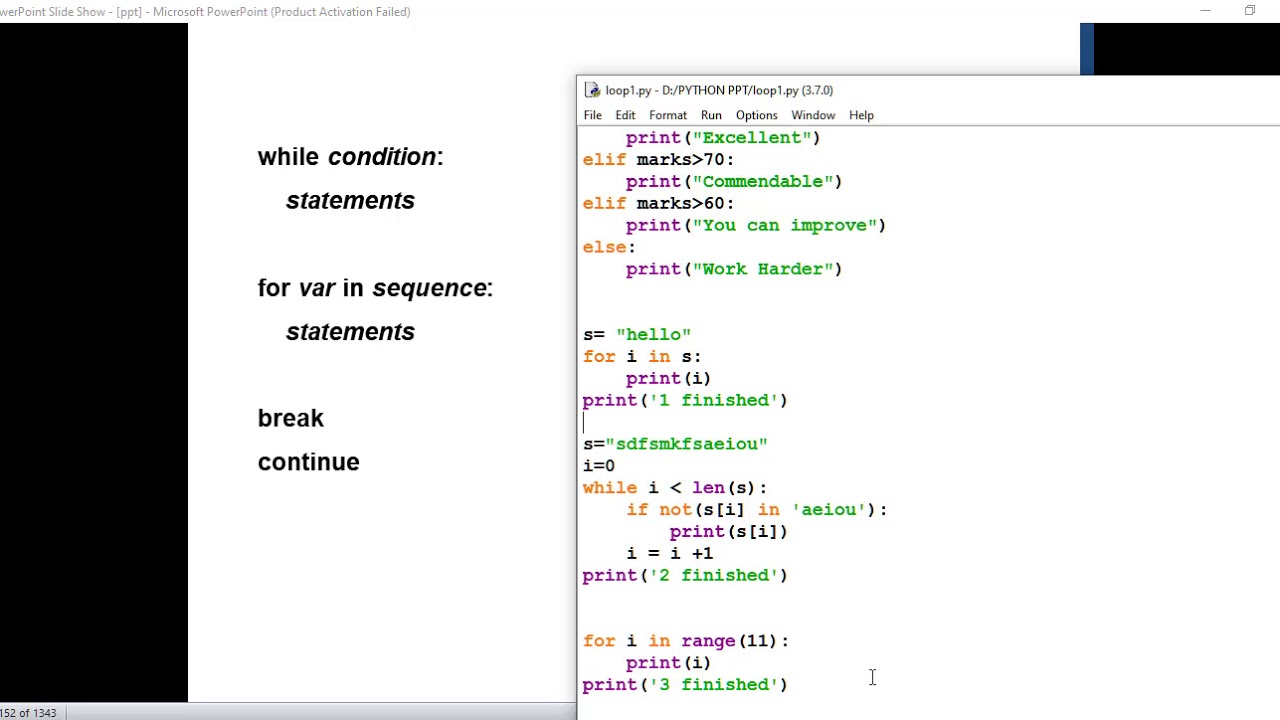
You can also use relative imports if you have a package that contains multiple modules and you want to import one module from another within the same package. For example:
package/
init.py
module1.py
module2.py
In module2.py, you can do something like this:
from . import module1
In this case, Python looks for module1 in the current package (i.e., the directory where module2.py is located).
Another way to import a package is using the -m command-line flag. For example:
python -m mypackage.module1
This will run the module1 function from the mypackage package directly from the command line.
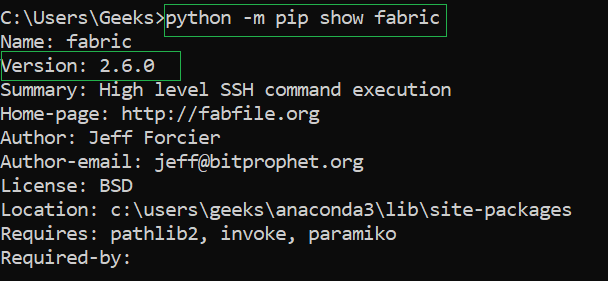
Finally, you can also install packages using pip or another package installer and then import them like any other Python module. For example:
pip install requests
And then in your Python script:
import requests
This is a basic overview of how to import a package into Python. Depending on the specifics of your use case, there may be additional considerations or best practices to keep in mind.
Python import module
I'm happy to help! Here are some responses:
What is the purpose of importing a module in Python?
In Python, importing a module allows you to use its functions, classes, and variables in your own program. When you import a module, Python loads the module's code into memory and makes its contents available for use.
How do I import a module in Python?
To import a module in Python, you can use the import statement followed by the name of the module you want to import. For example:
import math
This imports the entire math module. If you only need to use one or two specific functions or classes from the module, you can also use the from keyword followed by the name of the module and the names of the specific items you want to import. For example:
from math import sin, cos
This imports the sin and cos functions from the math module.
What is a built-in module in Python?
A built-in module in Python is a module that comes pre-installed with Python and does not need to be installed separately. Examples of built-in modules include:
math statistics random
These modules provide useful functions and classes for performing common tasks, such as mathematical operations or generating random numbers.
What are some popular external modules in Python?
External modules in Python are packages that you can install using the pip package manager. Some popular examples include:
pandas: a library for working with structured data NumPy: a library for numerical computing scikit-learn: a library for machine learning
These modules provide powerful tools for data analysis, scientific computing, and machine learning.
How do I install an external module in Python?
To install an external module in Python, you can use the pip package manager. For example:
pip install pandas
This installs the pandas library and its dependencies. Once installed, you can import the module in your Python program.
What are some best practices for importing modules in Python?
When importing modules in Python, it's a good idea to:
Keep your imports concise: only import what you need Avoid using wildcards (*) when importing from a module Use import statements instead of from statements whenever possible
By following these best practices, you can keep your code organized and maintainable.
What are some common pitfalls to avoid when importing modules in Python?
Some common pitfalls to avoid when importing modules in Python include:
Not using the correct module name: make sure you spell the module name correctly Importing modules with conflicting names: use unique names for your modules Importing modules from the wrong location: use absolute import paths instead of relative onesBy avoiding these common pitfalls, you can reduce errors and improve code quality.
I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any further questions.