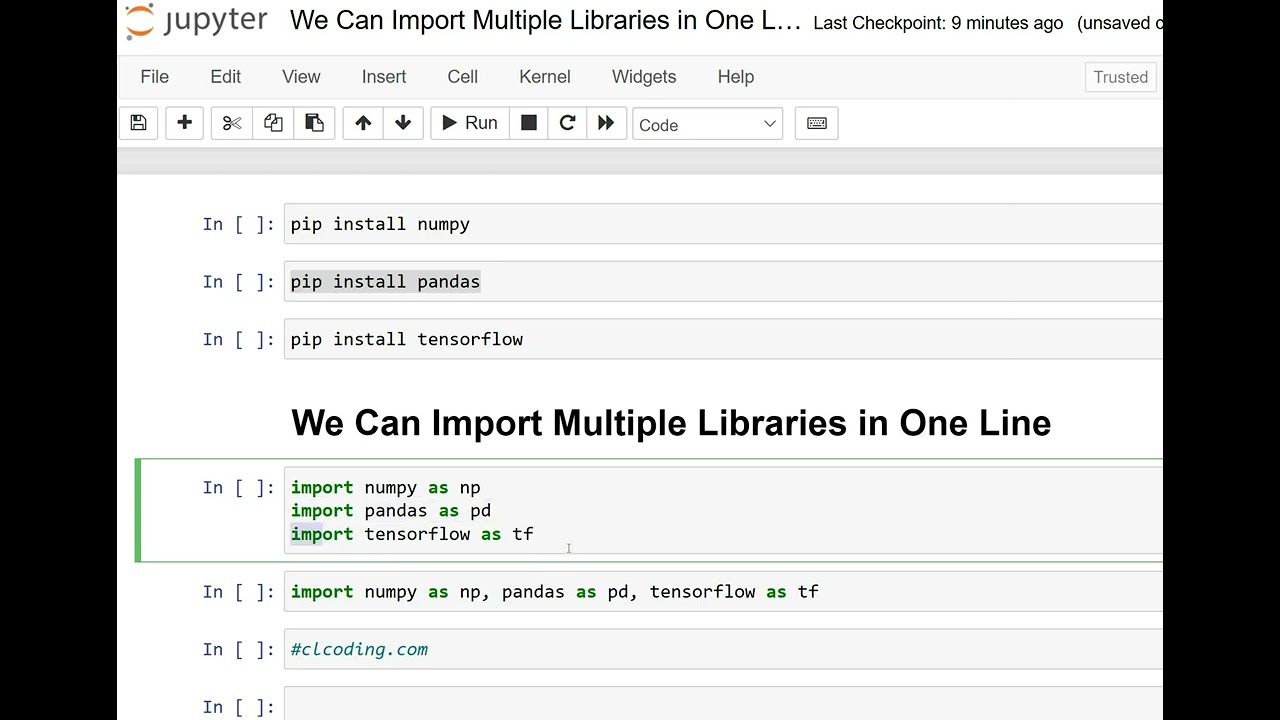
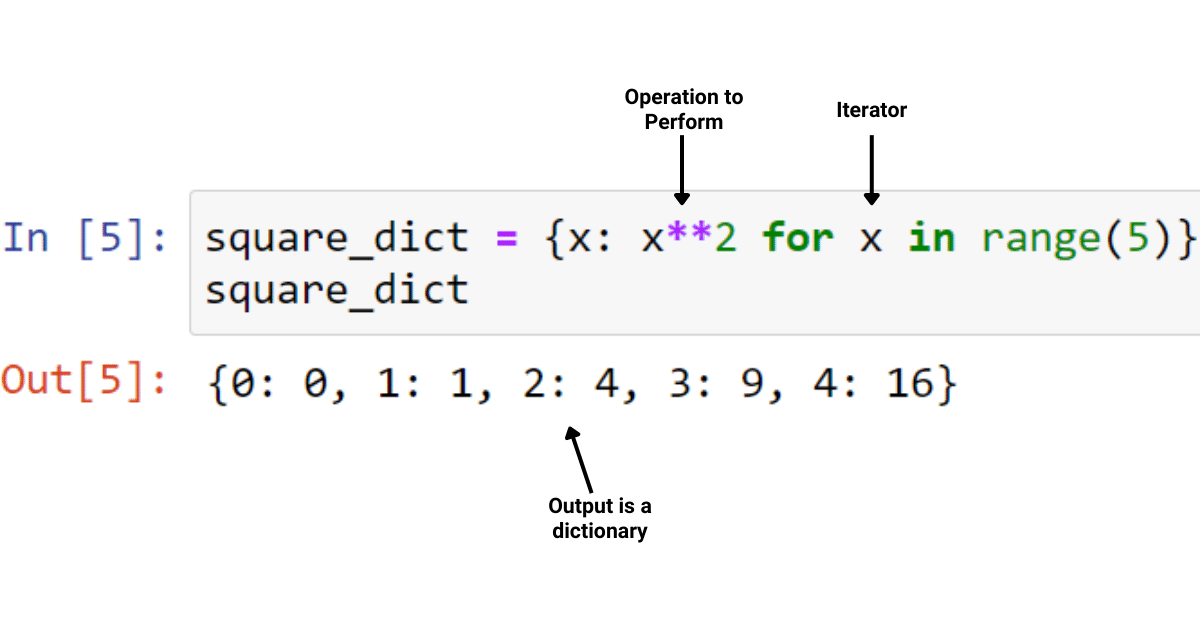
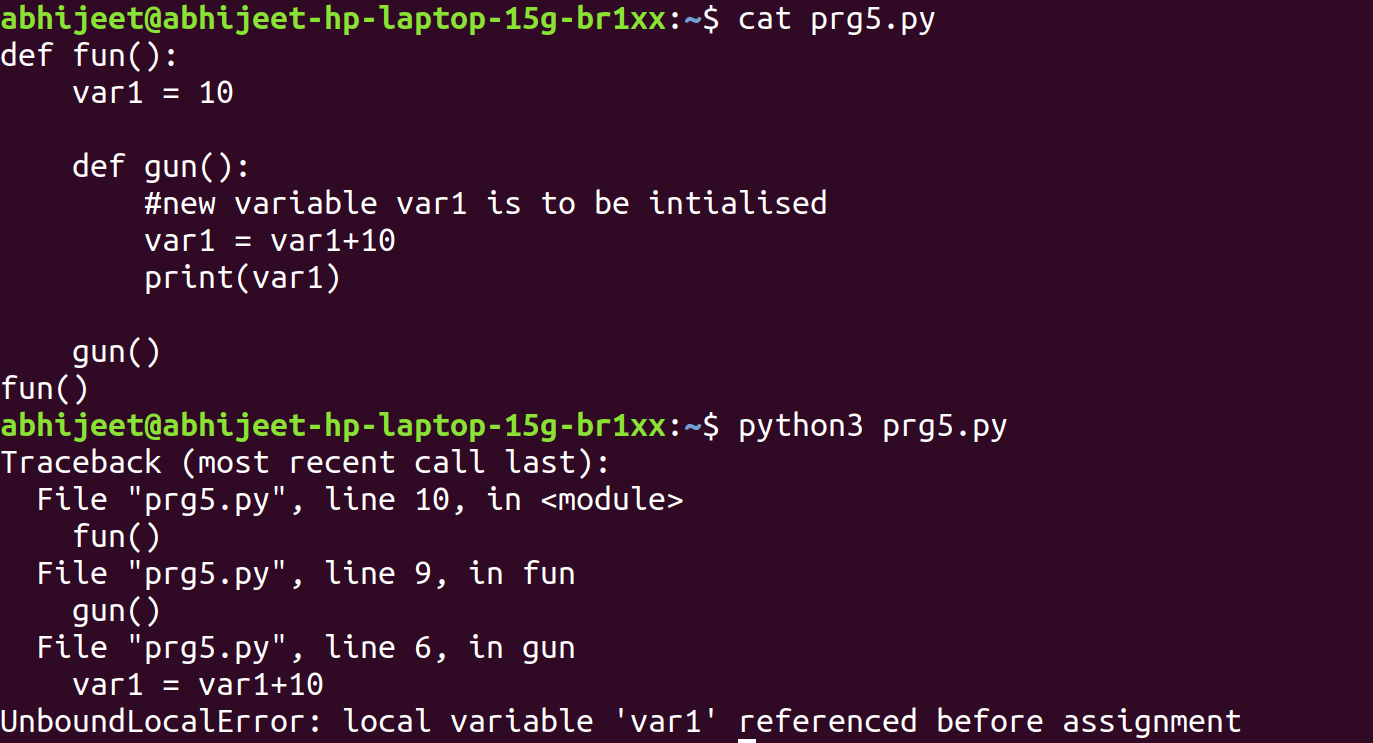
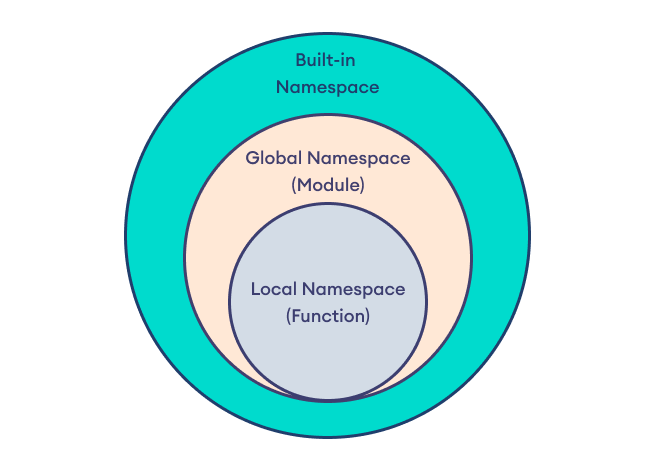
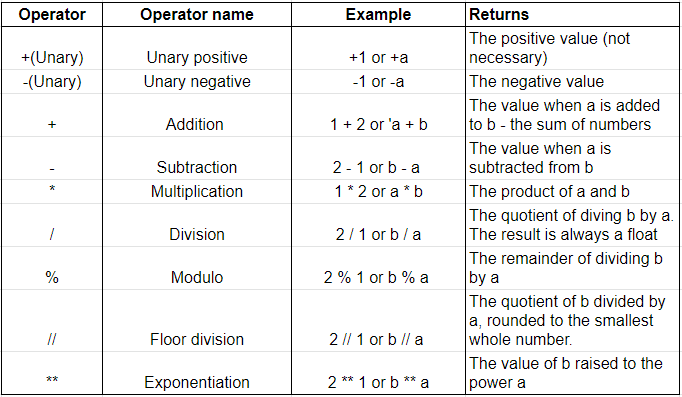
Python scripting examples
Python scripting examples
Here's a list of basic to advanced level Python scripting examples:
Basic Examples
Hello World Script
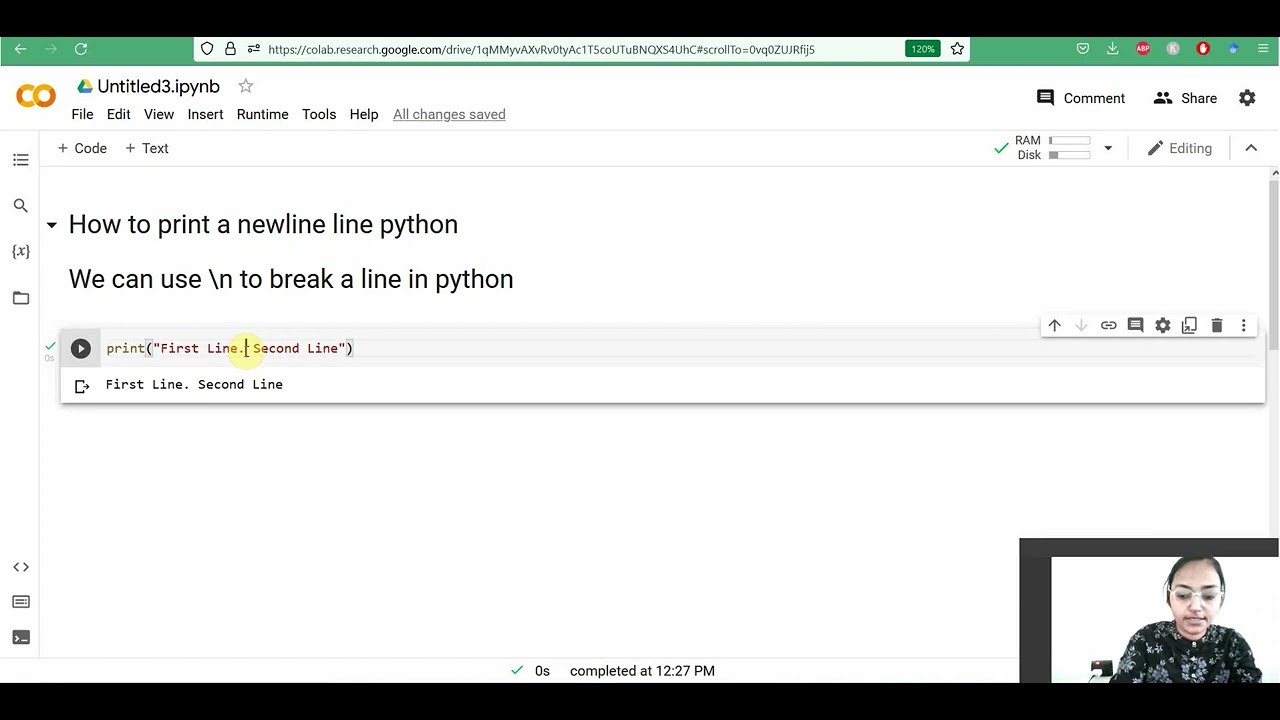
print("Hello, World!")
This script simply prints "Hello, World!" on the screen.
Simple Calculatordef add(x, y):
return x + y
print(add(5, 3))
This script defines a simple function that adds two numbers together and prints the result.
Intermediate Examples
Guessing Gameimport random
number = random.randint(1, 100)
guesses = 0
while True:
user_guess = int(input("Guess a number between 1 and 100: "))
guesses += 1
if user_guess < number:
print("Too low!")
elif user_guess > number:
print("Too high!")
else:
print(f"Congratulations, it took you {guesses} guesses!")
break
This script creates a simple guessing game where the user tries to guess a random number between 1 and 100.
Hangman Gameword = "hello"
wrong_guesses = 0
for letter in word:
print("_", end=" ")
while True:
user_guess = input("Guess a letter: ")
if len(user_guess) != 1:
print("Invalid guess, try again!")
continue
for i, letter in enumerate(word):
if letter == user_guess:
print(f"Found! {_ for _ in word}.")
else:
print("_", end=" ")
if all(letter != "_" for letter in word):
print("Congratulations, you won!")
break
elif wrong_guesses >= 5:
print("Sorry, you lost!")
break
This script creates a simple hangman game where the user tries to guess a random word by inputting letters.
Advanced Examples
Web Scrapingimport requests
url = "https://www.example.com"
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200:
print(response.text)
else:
print("Error occurred:", response.status_code)
This script sends a GET request to a URL and prints the HTML response.
Scheduling Tasksimport schedule
import time
def job():
print("Job executed!")
schedule.every(1).day.at("14:30").do(job) # run every day at 14:30
while True:
schedule.run_pending()
time.sleep(1)
This script schedules a task to be executed every day at 14:30 and runs it indefinitely.
Chatbotimport random
conversations = {
"hello": ["Hello! How can I help you today?", "Hi, what's on your mind?"],
"goodbye": ["Goodbye, have a great day!", "See you later!"],
}
while True:
user_input = input("User: ")
if user_input.lower() in conversations:
print(random.choice(conversations[user_input.lower()]))
elif user_input.lower() == "quit":
print("Goodbye!")
break
else:
print("I didn't quite catch that. Can you rephrase?")
This script creates a simple chatbot that responds to common phrases and phrases.
Data Analysisimport pandas as pd
data = {
"Name": ["John", "Jane", "Bob"],
"Age": [25, 30, 35],
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df.mean()) # print the mean of each column
print(df.median()) # print the median of each column
This script creates a simple DataFrame using pandas and calculates the mean and median of each column.
What is the difference between Python script and shell script?
The age-old debate: Python scripts vs shell scripts! Both are programming languages, but they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics.
What are shell scripts?
Shell scripts are programs written in a specific scripting language that interacts with an operating system (OS) using the command-line interface (CLI). The most popular shells include Bash, Zsh, and PowerShell. Shell scripts typically perform tasks such as:
Automation: Automate repetitive commands or processes. Data processing: Manipulate text files, sort data, or perform simple calculations. System administration: Manage system resources, create users, or modify file permissions.Shell scripts are executed by the shell (e.g., Bash) and are often used for:
Scripting: Automating tasks and workflows. System configuration: Managing system settings and configurations. Data analysis: Processing and manipulating data in a pipeline-like manner.What are Python scripts?
Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language known for its ease of use, readability, and flexibility. Python scripts can:
Automate tasks: Perform complex automation tasks using libraries likeos and subprocess. Data analysis and science: Process data, perform statistical analyses, and create visualizations with popular libraries like NumPy, Pandas, and Matplotlib. Web development: Build web applications using Flask or Django, handle HTTP requests, and interact with databases.
Python scripts are executed by the Python interpreter and are often used for:
Rapid prototyping: Quickly test ideas and concepts without worrying about performance optimization. Data analysis and machine learning: Perform complex data analyses, build machine learning models, and deploy them as web applications. Automation: Automate tasks that require more control and flexibility than shell scripts can offer.Key differences
Language: Shell scripts are written in a specific scripting language (e.g., Bash), while Python scripts are written in the Python programming language. Interpretation: Shell scripts are interpreted by the shell, whereas Python scripts are executed by the Python interpreter. Purpose: Shell scripts focus on system administration, automation, and data processing, while Python scripts focus on data analysis, machine learning, and web development. Syntax: Shell scripts use a syntax similar to command-line commands (e.g.,ls, mkdir), whereas Python scripts use the syntax of the Python programming language (e.g., print("Hello World")). Portability: Python scripts are more portable across different operating systems and platforms, while shell scripts are often specific to a particular OS or shell.
In summary, if you need to automate simple tasks, perform basic data processing, or manage system resources, a shell script might be the better choice. However, if you require more control, flexibility, and complex data analysis capabilities, a Python script is likely your best bet.