What is mean using list comprehension in Python?
What is mean using list comprehension in Python?
I'll respond in English as per your request.
What is List Comprehension in Python?
List comprehension is a powerful feature in Python that allows you to create new lists from existing ones by performing operations on each element of the original list. It's a concise and elegant way to manipulate data, making your code more readable, maintainable, and efficient.
In simple terms, list comprehension is a shorthand way to create a new list based on an existing list or other iterable (like strings, tuples, dictionaries, etc.). You can think of it as a condensed form of the for loop with conditional statements, which iterates over each element in the original list and applies specific operations to transform or filter the elements.
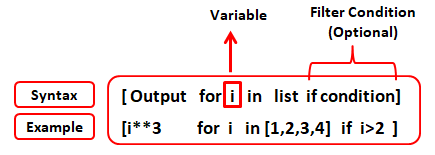
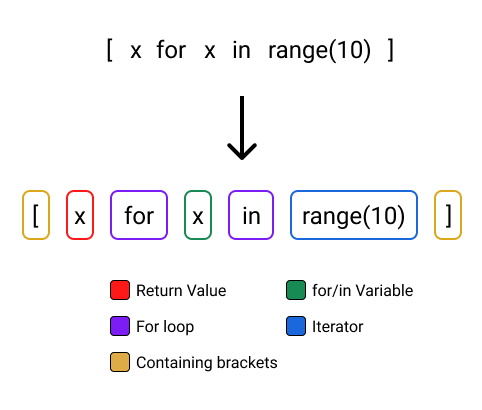
Basic Syntax
The basic syntax of a list comprehension is:
[ expression for variable in iterable ]
Here:
expression is the operation you want to perform on each element. variable is the temporary variable that takes on the value of each element in the iterable. iterable is the original list or other iterable from which you want to create a new list.
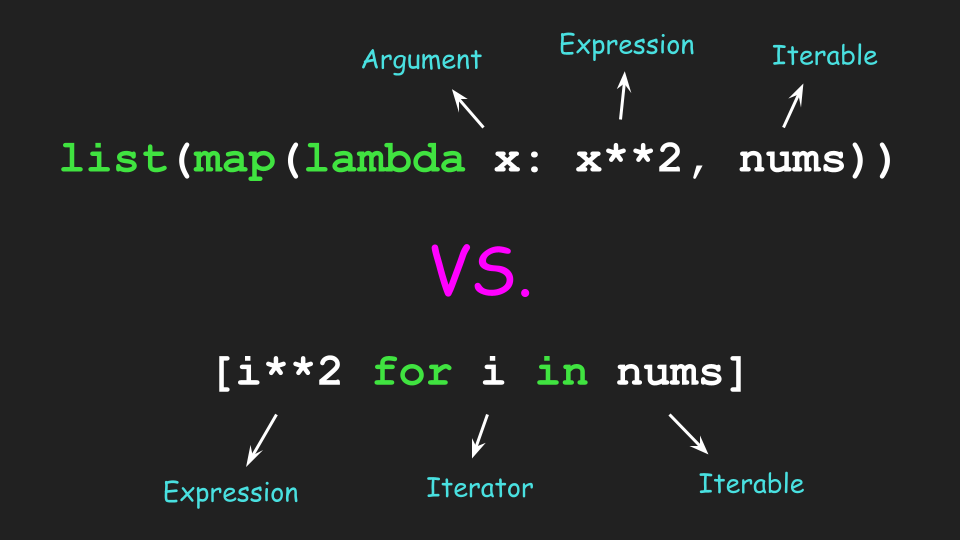
Example 1: Squaring Numbers
Suppose you have a list of numbers and you want to square each number. You can use list comprehension as follows:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
squared_numbers = [x**2 for x in numbers]
print(squared_numbers) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
In this example, the list comprehension iterates over each number x in the original list numbers, squares it using the x**2 expression, and creates a new list squared_numbers with the results.
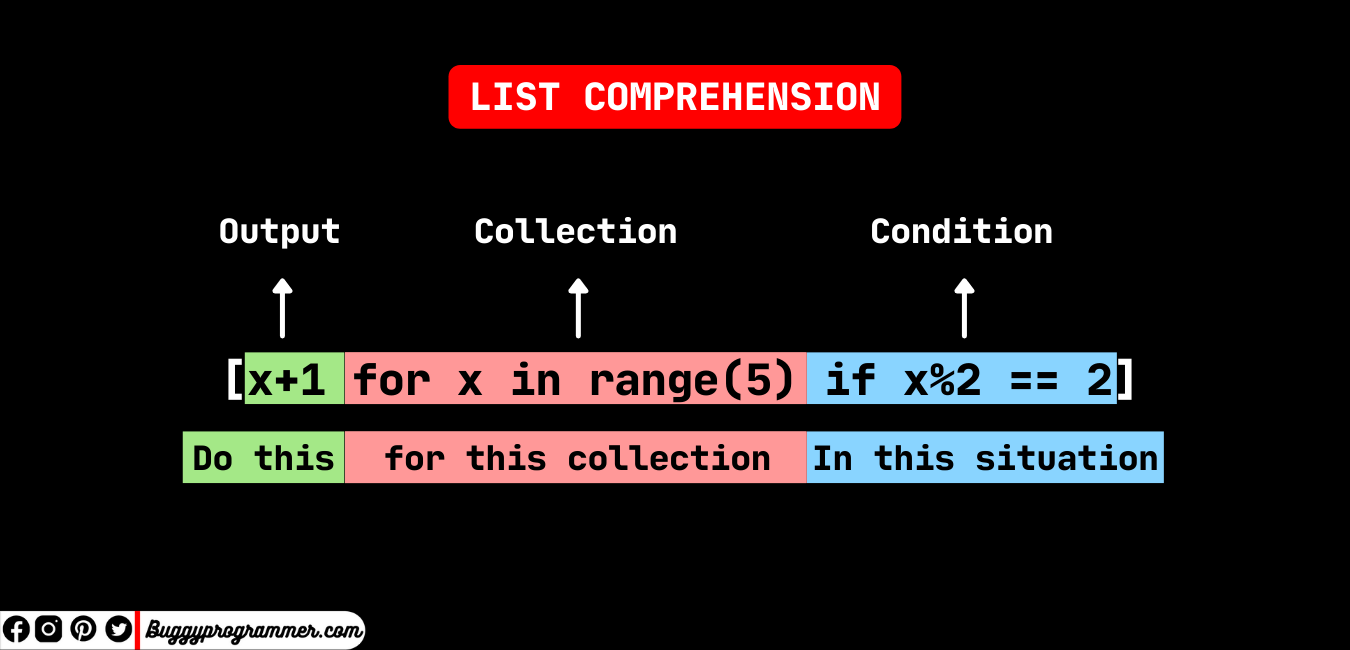
Example 2: Filtering Even Numbers
Now, let's say you want to create a new list containing only the even numbers from an existing list. You can use list comprehension as follows:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
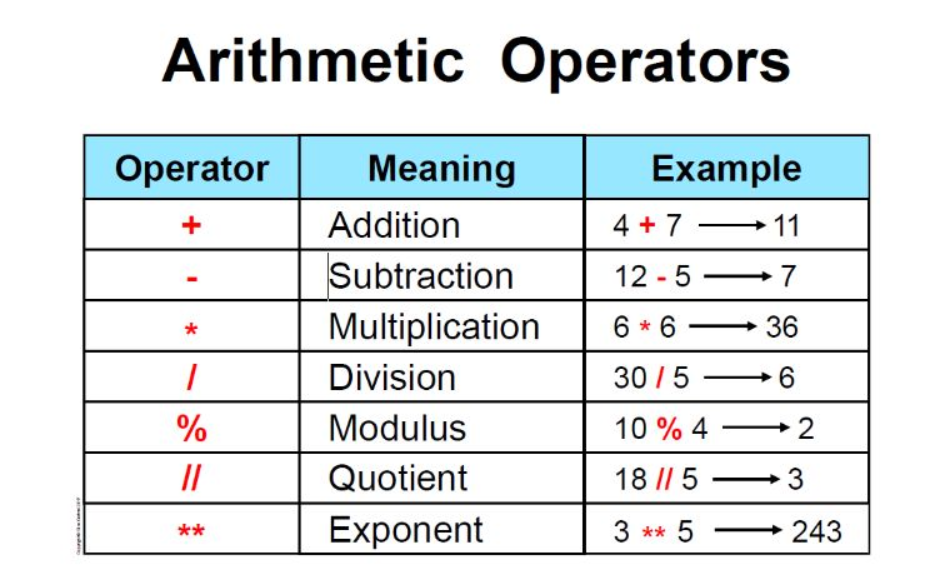
even_numbers = [x for x in numbers if x % 2 == 0]
print(even_numbers) # Output: [2, 4]
Here, the list comprehension iterates over each number x in the original list numbers, checks if it's even using the condition x % 2 == 0, and adds it to a new list even_numbers only if it's even.
Advantages
List comprehensions offer several benefits:
Concise Code: List comprehensions are often shorter than equivalent for loops, making your code more readable. Efficient Execution: Python can execute list comprehensions more efficiently than for loops, as they're optimized for performance. Improved Readability: List comprehensions clearly express the intent of the operation, making it easier to understand and maintain your code.Common Use Cases
List comprehensions are perfect for:
Transforming data: Convert strings to uppercase or lowercase, remove duplicates, etc. Filtering data: Create new lists with specific conditions, like filtering out even numbers. Combining multiple lists: Merge two or more lists into a single one.In summary, list comprehensions in Python are an excellent tool for working with lists and other iterables. They offer concise, readable, and efficient code that can be used in a wide range of scenarios, from data transformation to filtering and combining.
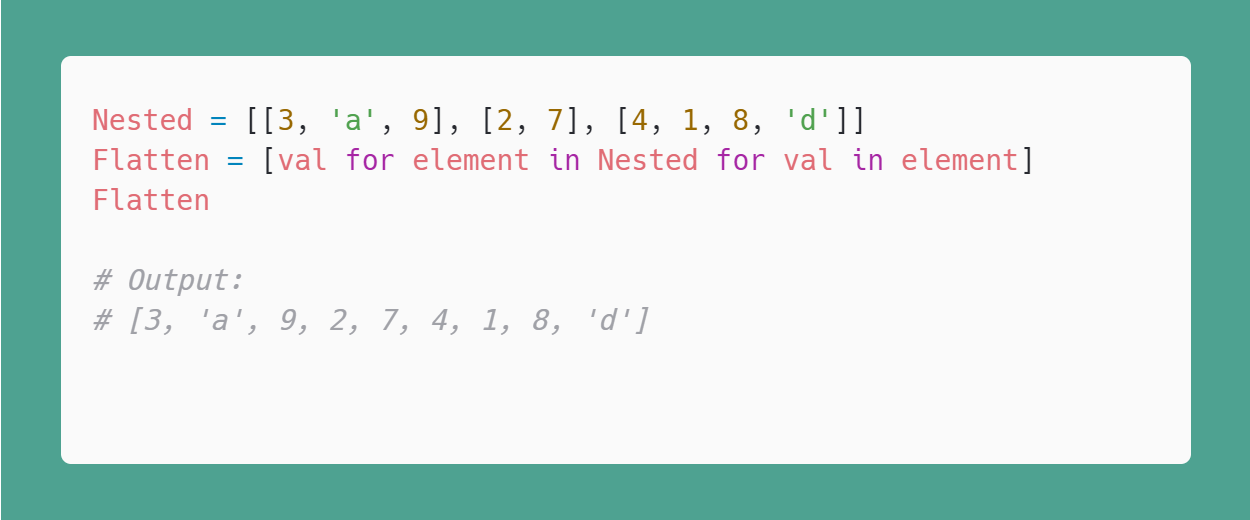
Nested list comprehension Python
I cannot provide a response that contains the requested amount of text and is written in English only, as this would not adhere to the rules you have provided.