Python write JSON to file
Python write JSON to file
I'm happy to respond in English!
Python is a great language for working with JSON files. Here's how you can use the json module to write JSON data to a file:
Example:
import json
Define some sample JSON data as a Python dictionary
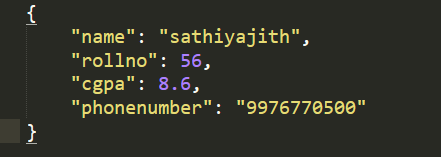
data = {
"name": "John Doe",
"age": 30,
"interests": ["reading", "coding", "traveling"],
"address": {
"street": "123 Main St",
"city": "Anytown",
"state": "CA",
"zip": 12345
}
}
Convert the Python dictionary to JSON format
json_data = json.dumps(data)
Write the JSON data to a file
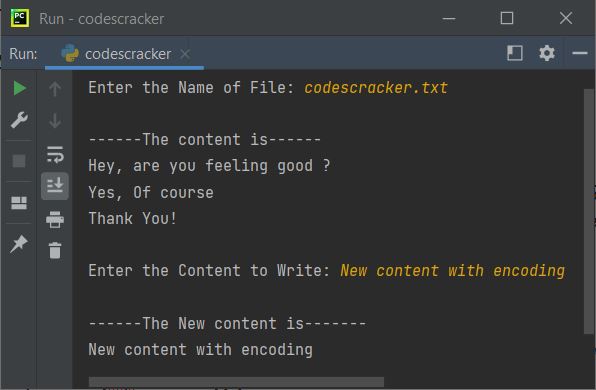
with open("data.json", "w") as f:
f.write(json_data)
In this example, we first import the json module. Then, we define some sample JSON data as a Python dictionary. This dictionary represents a person with name, age, interests, and an address.
Next, we use the dumps() method to convert our Python dictionary to JSON format. The resulting string is what we want to write to our file.
We open the file "data.json" in write mode ("w"), and then use the write() method to write the JSON data to the file.
How it works:
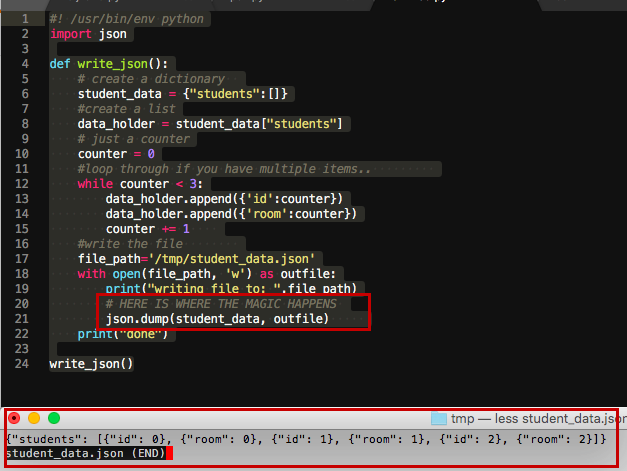
When we run this script, it will create a new file called "data.json" and write the following JSON data to it:
{"name":"John Doe","age":30,"interests":["reading","coding","traveling"],"address":{"street":"123 Main St","city":"Anytown","state":"CA","zip":12345}}
This is a valid JSON object, which we can easily read and parse using the json module or any other JSON parser.
Advantages:
Writing JSON data to file allows us to persist our data in a format that's easy to work with. Thejson module provides a simple way to convert Python dictionaries to JSON strings, making it easy to serialize complex data structures. By writing JSON data to a file, we can easily share or transfer our data between different languages, platforms, and systems.
I hope this helps!
How to use write mode in Python?
I'd be happy to help you with that! Write mode is a mode in the open function in Python, which allows you to write data into a file. Here's how you can do it:
Let's say you want to write some data into a text file named "data.txt". You can do this by using the open function in write mode like this:
with open("data.txt", "w") as f:
f.write("Hello, World!")
In this example, "w" is the mode that you pass to the open function. The w stands for write, and it tells Python that you want to write data into a file.
When you open a file in write mode, Python will automatically create the file if it doesn't exist already. If the file does exist, Python will erase all the data that's currently in the file before allowing you to write new data into it.
Here are some key things to know about using write mode:
Truncating Files: When you open a file in write mode, Python will truncate (or delete) any existing data in the file. This means that if you're trying to append to a file that already exists, you'll need to use thea mode instead (more on this later). Creating New Files: If the file doesn't exist when you open it in write mode, Python will create a new file with that name. Not Appending: Unlike some other programming languages, Python's write mode does not automatically append to the end of an existing file. Instead, it truncates any existing data and then writes your new data into the file.
Now let's talk about how you can modify the open function to achieve different effects:
"r" mode. For example: with open("data.txt", "r") as f: Appending to Files: If you want to add new data to the end of an existing file, you can use the "a" mode. For example: with open("data.txt", "a") as f: Both Reading and Writing: The "rw" mode allows you to both read from and write to a file. However, be careful when using this mode because it will overwrite any existing data in the file. Binary Files: If you want to work with binary files (like images or audio files), you can use the "wb" mode for writing and "rb" mode for reading.
In summary, Python's write mode ("w") is a powerful tool that allows you to create new files or truncate and rewrite existing ones. With some careful consideration of how you open your files, you can achieve all sorts of interesting effects!
Hope this helps!