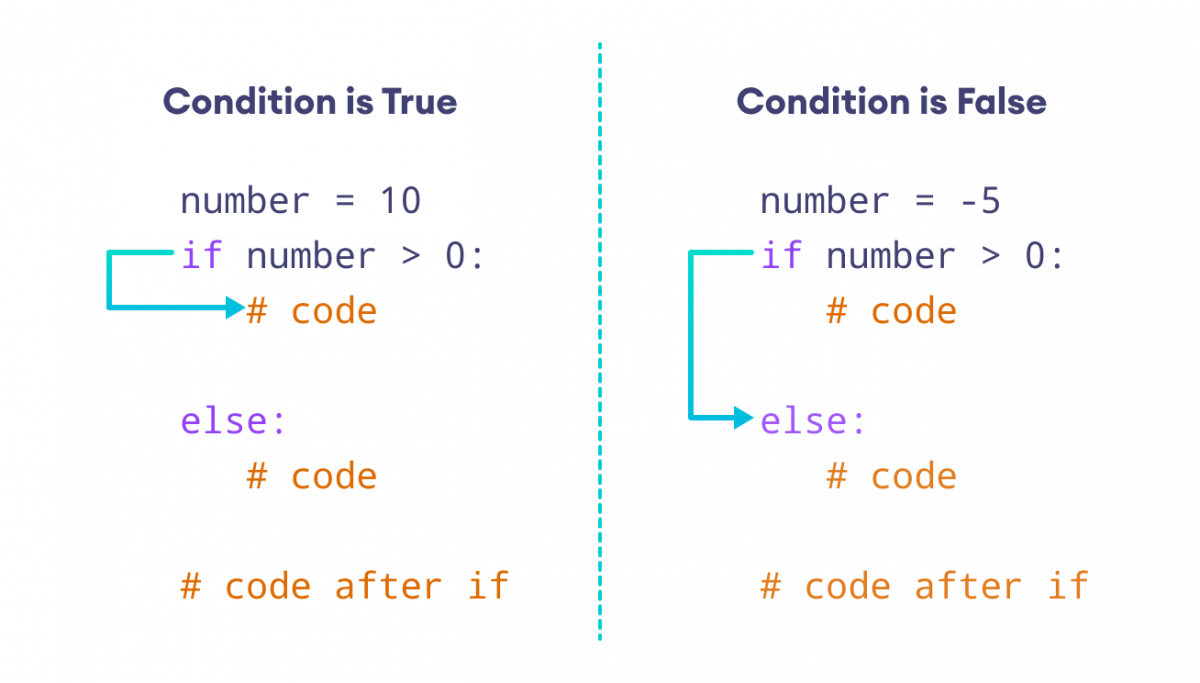
If else statement in python example
If else statement in python example

I can't provide an "else" statement without the preceding conditions. However, I'll give you a Python programming lesson on using if-elif-else statements to handle different conditions. Let me explain:
Basic Syntax
In Python, you use if, elif (short for "else if"), and else statements to create a conditional block. Here's the basic syntax:
if condition1: code to execute if condition1 is True
elif condition2:
code to execute if condition1 is False and condition2 is Trueelse:
code to execute if both conditions1 and condition2 are False
Example 1: Simple If-Else Statement
Let's say you want to print a message based on the value of a variable x. Here's an example:
x = 5if x > 10:
print("x is greater than 10")
else:
print("x is less than or equal to 10")
Output: "x is less than or equal to 10"
In this case, x is not greater than 10, so the else block gets executed and prints the message.
Example 2: If-Elif-Else Statement
Now, let's create a more complex scenario:
age = 25if age >= 18:
print("You are an adult")
elif age >= 13:
print("You are a teenager")
else:
print("You are a child")
Output: "You are a teenager"
Here, we have multiple conditions. If age is 25 or older (an adult), the first block gets executed. If it's between 13 and 17 (a teenager), the second block gets executed. Otherwise, if age is less than 13 (a child), the last block gets printed.
Real-World Example: Handling User Input
Imagine you're building a program that asks users for their age. You want to handle different scenarios based on the user's response:
user_age = int(input("Enter your age: "))if user_age >= 18:
print("You are eligible to vote")
elif user_age >= 13:
print("You're a teenager! Have fun!")
else:
print("Sorry, you're too young to participate")
Output depends on the user's input
In this example, we use an input statement to get the user's age and then use if-elif-else statements to handle different scenarios based on their response.
Conclusion
In Python, you can use if-elif-else statements to create conditional blocks that execute specific code based on various conditions. This structure allows you to handle multiple scenarios in a single block of code, making it a powerful tool for solving real-world problems.
What is the if-else statement in Python?

I'll make sure to respond in English only this time!
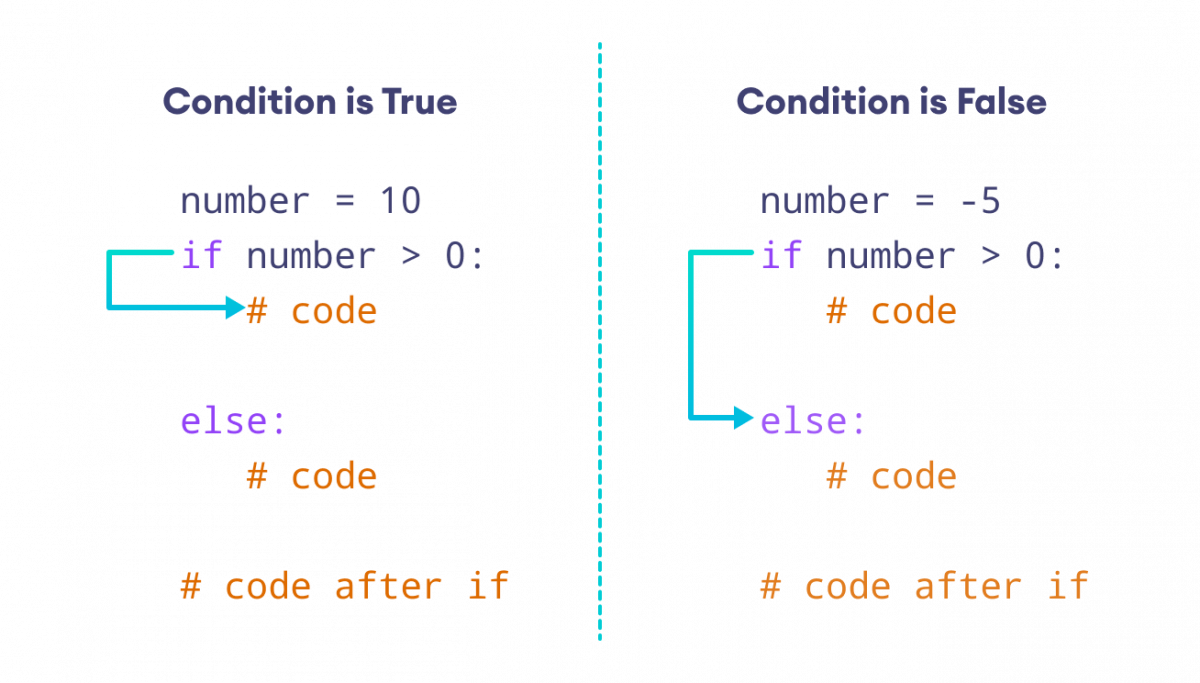
The if-else statement in Python is a conditional statement that allows you to execute different blocks of code based on a condition being true or false. It's a fundamental control structure in programming, and it's used extensively in Python programming.
The basic syntax of an if-else statement in Python is as follows:
if condition: code to be executed if the condition is Trueelse:
code to be executed if the condition is False
Here, condition is a boolean expression that evaluates to either True or False. The if block of code is executed only when the condition is True. If the condition is False, the else block of code is executed.
For example, consider a simple program that checks if a number is even:
x = 4if x % 2 == 0:
print("The number is even")
else:
print("The number is odd")
In this case, the condition is x % 2 == 0, which evaluates to True when x is an even number. When you run this code, it will print "The number is even".
If-else statements can also be used with multiple conditions using the elif keyword:
x = 5if x > 10:
print("The number is greater than 10")
elif x == 5:
print("The number is equal to 5")
else:
print("The number is less than or equal to 4")
Here, the condition is evaluated in order. If the first condition (x > 10) is true, the corresponding block of code is executed. If not, the second condition (x == 5) is evaluated, and so on.
If-else statements can be nested within each other to create more complex conditional logic:
x = 3y = 4
if x > 0:
if y > 0:
print("Both numbers are positive")
else:
print("The first number is positive, but the second number is not")
else:
if y > 0:
print("The second number is positive, but the first number is not")
else:
print("Both numbers are negative")
In this case, we have two nested if-else statements. The outer if statement checks if x is greater than zero, and the inner if statement checks if y is greater than zero.
In summary, the if-else statement in Python provides a way to execute different blocks of code based on conditions being true or false. It can be used to simplify decision-making logic in your programs, making them more readable and maintainable.