List operations in Python with examples
List operations in Python with examples
I'm happy to respond in English for you! Here's a list of common operations in Python with examples:
1. Arithmetic Operations
These are the basic math operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
a = 5; b = 3; print(a + b) Output: 8 a = 5; b = 3; print(a - b) Output: 2 a = 5; b = 3; print(a * b) Output: 15 a = 5; b = 3; print(a / b) Output: 1.6666666666666667
2. Comparison Operations
These are used to compare values and return a boolean result (True or False).
a = 5; b = 3; print(a > b) Output: True a = 5; b = 3; print(a < b) Output: False a = 5; b = 5; print(a == b) Output: True
3. Logical Operations
These are used to combine conditions using logical operators (AND, OR, NOT).
a = 5; b = 3; print((a > 4) and (b < 4)) Output: False a = 5; b = 3; print((a > 4) or (b < 4)) Output: True
4. Assignment Operations
These are used to assign values to variables.
x = 5; y = x; print(y) Output: 5 x = 5; y = x + 1; print(y) Output: 6
5. Identity Operations
These are used to check if two objects have the same value or not.
a = [1, 2]; b = [1, 2]; print(a is b) Output: False a = [1, 2]; b = a; print(a is b) Output: True
6. Membership Operations
These are used to check if an element exists in a sequence or not.
my_list = [1, 2, 3]; print(2 in my_list) Output: True my_set = {1, 2, 3}; print(4 in my_set) Output: False
7. Bitwise Operations
These are used to manipulate bits of an integer.
a = 5; b = a << 1; print(b) Output: 10 a = 5; b = a >> 1; print(b) Output: 2
8. String Operations
These are used to manipulate strings.
my_str = "Hello"; print(my_str.upper()) Output: "HELLO" my_str = "Hello"; print(my_str.lower()) Output: "hello"
Note that this is not an exhaustive list, but it covers some of the most commonly used operations in Python.
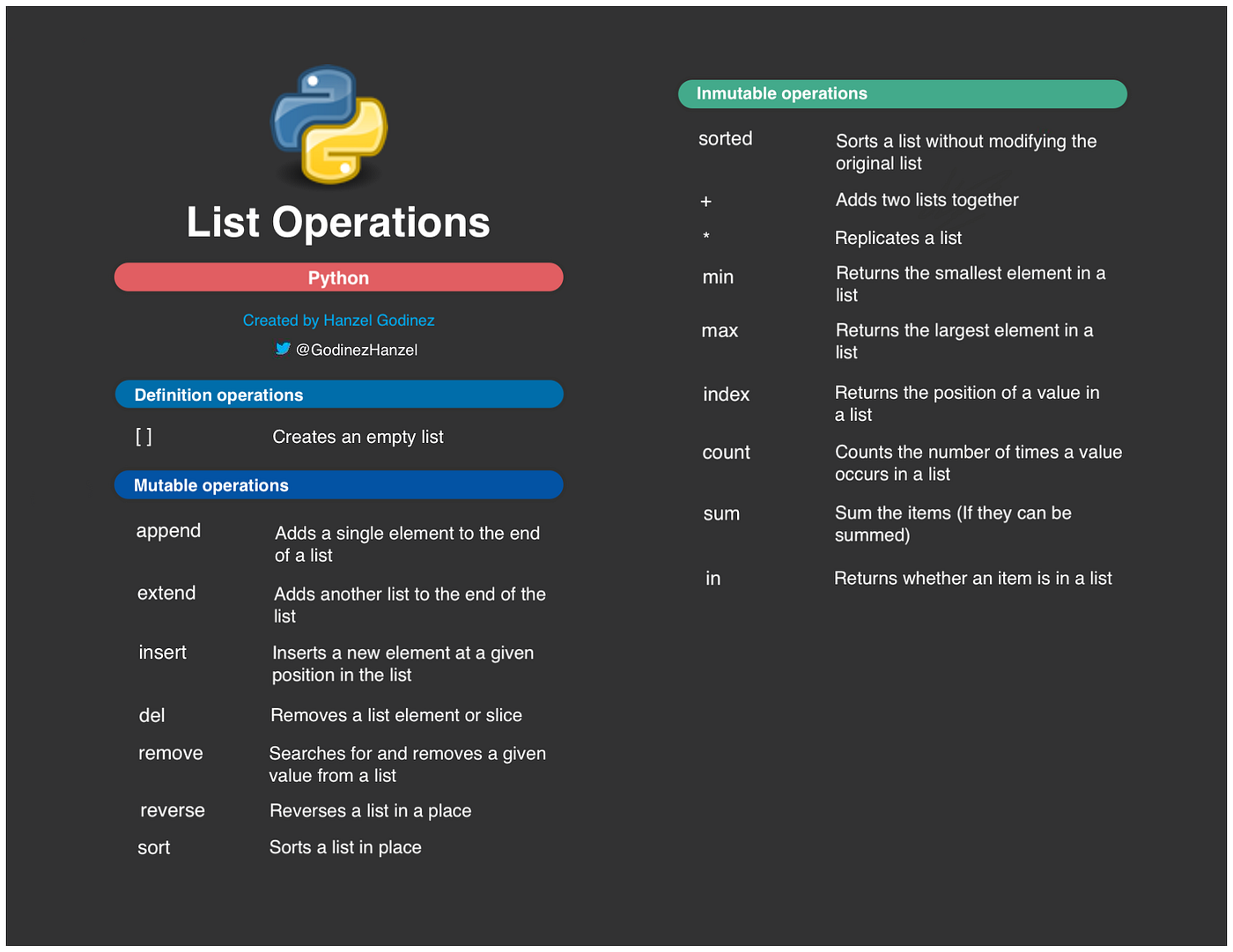
List methods in Python
Here are the methods in Python:
Arithmetic Operators:+ (Addition) - (Subtraction) * (Multiplication) / (Division) // (Floor Division) % (Modulus) Comparison Operators: == (Equal To) != (Not Equal To) < (Less Than) > (Greater Than) <= (Less Than or Equal To) >= (Greater Than or Equal To) Logical Operators: and (And) or (Or) not (Not) Assignment Operators: = (Assign) += (Add and Assign) -= (Subtract and Assign) *= (Multiply and Assign) /= (Divide and Assign) //= (Floor Division and Assign) %= (Modulus and Assign) String Methods: lower() (Convert to lowercase) upper() (Convert to uppercase) title() (Title Case, first char uppercase, rest lowercase) swapcase() (Swap case, i.e., lowercase becomes uppercase and vice versa) List Comprehensions: [x for x in list if condition] (Create a new list with filtered elements from an existing list) Functions: Define your own functions using the def keyword Conditionals: if-else statements (Conditional Statements) for loops while loops Exception Handling: Try-except blocks for catching and handling exceptions Regular Expressions: re.search() for searching a pattern in a string re.match() for matching the start of a string with a pattern re.findall() for finding all matches to a pattern in a string re.sub() for replacing substrings based on patterns Dictionaries: dict() (Create a new dictionary) .keys(), .values(), and .items() methods for accessing keys, values, and key-value pairs Sets: {} (Create a new set) .union(), .intersection(), and .difference() methods for combining sets based on their elements Tuples: () (Create a new tuple) Tuple indexing and slicing (accessing individual elements or subsets of the tuple) Generators: Define your own generator functions using the yield keyword Coroutines: Use the asyncio module for asynchronous programming Matrix Operations: NumPy library for matrix operations (e.g., creating, manipulating, and performing calculations on matrices) Statistics and Data Analysis: statistics module (mean, median, mode) pandas library for data analysis and manipulation JSON and CSV files: JSON and CSV modules for reading and writing to these file formats XML files: xml.etree.ElementTree module for parsing and creating XML documents Graphing: Use libraries like matplotlib, seaborn, or plotly for creating visualizations of your data Machine Learning: Scikit-learn library for machine learning (e.g., classification, regression, clustering) Database Interactions: Use a database driver like sqlite3 (Python's built-in database module) or pandas.io.sql to interact with databases Threading and Concurrency: Use the threading module for creating threads that run concurrently Use the concurrent.futures module for parallel processing of tasks Networking: Use libraries like socket, http.client, or requests for networking operations (e.g., creating, connecting to, and communicating with network resources) Web Development Frameworks: Flask or Django for building web applications Requests-HTML for scraping and interacting with websites Data Persistence: Use libraries like sqlite3 or pandas.io.sql to store data in databases Use the os.path module for storing and retrieving files on disk Command-line Interface (CLI) tools: Create command-line interfaces using the argparse library Write scripts that take user input and perform operations based on that input Games Programming: Use libraries like pygame, curses, or turtle for creating games in Python Implement game mechanics, AI, and graphics programming Network Security: Use libraries like scapy or pypcap for network security testing (e.g., penetration testing, packet sniffing) Geospatial Programming: Use libraries like geopy, Folium, or folium for geospatial operations (e.g., working with GPS data, mapping)
These are just some examples of the many methods and concepts that Python has to offer!





























