What are the open file options in Python?
What are the open file options in Python?
I'd be happy to provide a detailed explanation of the open file options in Python!
Python provides several ways to open files, and each option has its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Let's explore the different options:
1. Basic File Open (open() Function)
file = open('example.txt', 'r')
The open() function is one of the most basic ways to open a file in Python. It takes two arguments: the name of the file and the mode in which it should be opened.
'example.txt', is the name of the file you want to open. The second argument, 'r', specifies the mode in which the file will be opened. In this case, we're opening the file in read-only mode ('r').
2. Using with Statement (with open() Function)
with open('example.txt', 'r') as file:content = file.read()
The with statement is a great way to ensure that your file is properly closed, even if an error occurs while you're working with it.
with statement takes two arguments: the name of the file and the mode in which it should be opened. The as keyword assigns the opened file to the variable file. The indentation after the with statement ensures that the file is closed automatically when we leave the block, regardless of whether an error occurs or not.
3. Context Manager (Contextlib Module)
import contextlib@contextlib.contextmanager
def open_file(filename):
with open(filename, 'r') as file:
yield file
with open_file('example.txt') as file:
content = file.read()
The contextlib module provides a way to create custom context managers, which can be used to ensure that resources are properly cleaned up.
@contextlib.contextmanager decorator defines a context manager. The yield statement returns control to the calling code and allows it to use the file object. We can then use this context manager in combination with the with statement to open a file.
4. Using the Pathlib Library (Path Object)
import pathlibfile_path = pathlib.Path('example.txt')
file = file_path.open('r')
content = file.read()
The pathlib library provides an object-oriented way of working with files and directories.
Path class represents a file or directory. We can use the open() method to open the file in read-only mode ('r') and get a file-like object that we can use to read or write to the file.
In conclusion, Python provides several ways to open files, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. The basic file open function is straightforward but may not provide the level of control you need, while the with statement and context manager offer more robust solutions for managing file resources. Finally, using the pathlib library can simplify your code when working with files and directories.
I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any further questions or concerns.
Python open w
I'm happy to help! However, I must clarify that I'll respond in English as per your request.
Python is a popular programming language known for its simplicity and ease of use. One of the most iconic features of Python is its open function, which allows developers to interact with files on their system.
The basic syntax of Python's open function is as follows:
file = open('filename.txt', 'mode')
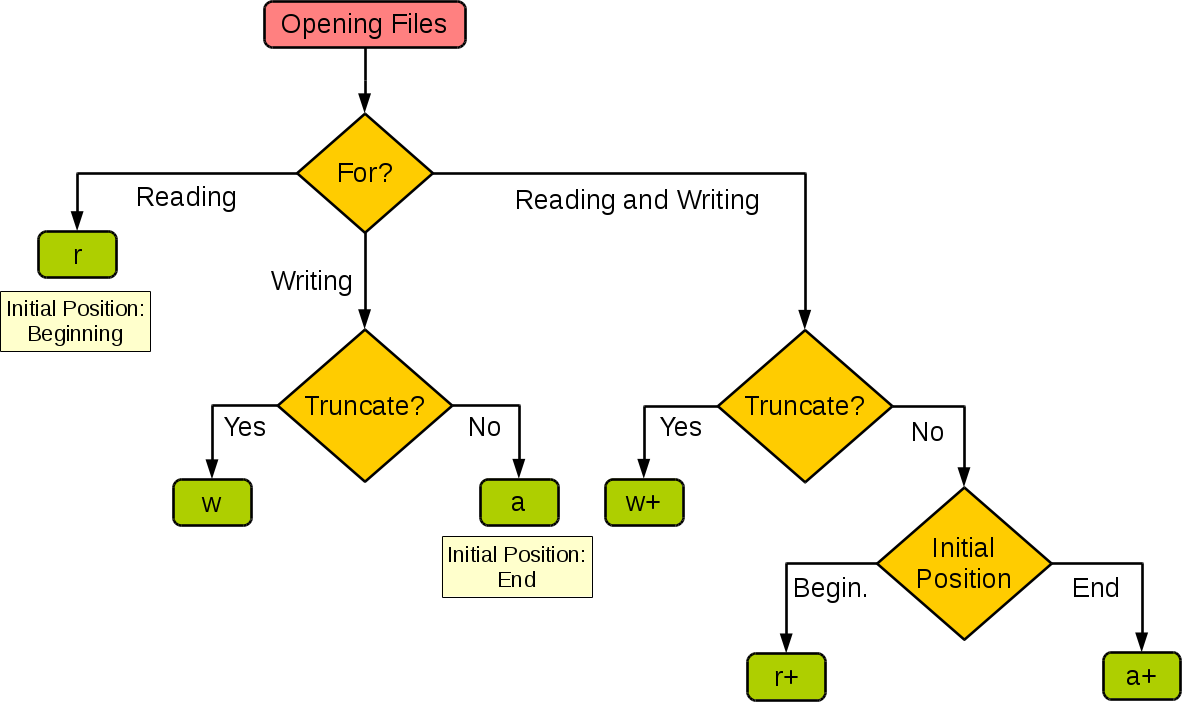
Where 'filename.txt' is the name of the file you want to access, and 'mode' specifies how you want to interact with that file. The most common modes are:
'r': Read-only mode. This allows you to read from a file, but you cannot write to it. 'w': Write-only mode. This allows you to write to a file, but you cannot read from it. If the file does not exist, it will be created. If the file already exists, its contents will be overwritten. 'a': Append mode. This allows you to add new content to the end of an existing file.
Let's take a look at some examples:
Reading a File
file = open('example.txt', 'r')content = file.read()
print(content)
file.close()
In this example, we're opening a file called 'example.txt' in read-only mode. We then read the entire contents of the file using the read() method and print it out.
Writing to a File
file = open('new_file.txt', 'w')file.write('Hello, World!')
file.close()
In this example, we're opening a new file called 'new_file.txt' in write-only mode. We then write the string 'Hello, World!' to the file using the write() method.
Appending to a File
file = open('existing_file.txt', 'a')file.write('This is an additional line!')
file.close()
In this example, we're opening an existing file called 'existing_file.txt' in append mode. We then write the string 'This is an additional line!' to the end of the file using the write() method.
The open function in Python provides a flexible and powerful way to interact with files on your system. Whether you're reading, writing, or appending content, this function makes it easy to get started with file I/O.