Python list vs C array
Python list vs C array

I'll respond in English as you requested.
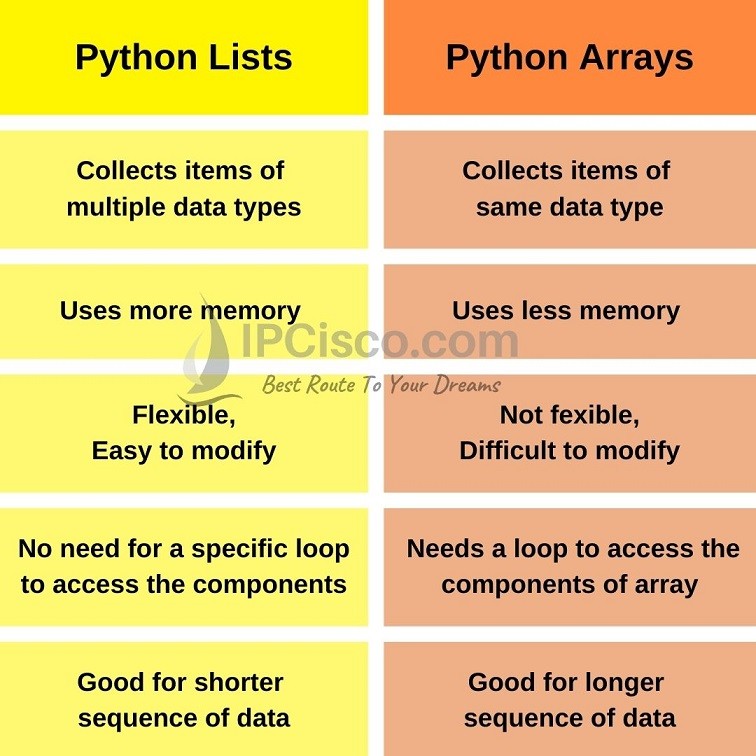
Python's built-in list data structure and C's array are both used to store collections of items, but they have different characteristics and use cases. Understanding the differences between them can help you make informed decisions when working with these data structures in Python and C.
Dynamic Memory Allocation vs Static Memory Allocation
One significant difference between Python lists and C arrays is how memory is allocated for storing elements. In C, when you declare an array, a fixed amount of memory is allocated at compile-time. This means that the size of the array is known before the program starts executing. On the other hand, Python lists use dynamic memory allocation, which means that the memory is allocated at runtime based on the size of the list.
In C, when you declare an array with a specific size, you cannot change its size after compilation. You need to create a new array and copy the elements from the original array if you want to add or remove elements. In Python, you can easily add or remove elements from a list using various methods like append(), insert(), or remove().
Type Safety
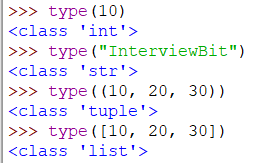
C arrays are strongly typed, meaning that each element in the array must be of the same type. You cannot store different types of data in the same array without explicitly converting them to the correct type. Python lists, on the other hand, are dynamically typed, which means that you can store elements of any type (integers, strings, floats, etc.) in a list.
Memory Management

C arrays require manual memory management using pointers and malloc(), which can be error-prone and lead to memory leaks if not handled correctly. Python lists handle memory management internally, freeing the programmer from worrying about allocating or deallocating memory for each element.
Performance
When it comes to performance, C arrays are generally faster than Python lists because they are closer to the machine's native representation of data (memory layout, cache efficiency, etc.). However, in most cases, the difference in performance is negligible and may not be a significant concern unless you're working on high-performance, memory-bound applications.
Use Cases
C arrays are suitable for:
Performance-critical applications where manual memory management is acceptable. Applications that require strict type safety and control over data storage. Working with low-level system programming or embedded systems development.Python lists are suitable for:
Rapid prototyping, scripting, and development where ease of use and flexibility matter. Applications that don't require explicit memory management or type safety. Data analysis, scientific computing, or machine learning tasks where Python's NumPy library provides an efficient way to work with large arrays.In summary, while both C arrays and Python lists can be used for storing collections of items, their differences in dynamic vs static memory allocation, type safety, memory management, performance, and use cases make them suitable for distinct application domains.
Python list vs array reddit

Here's a response to your question about Python lists vs arrays on Reddit:
Python List vs Array: What's the Difference?
As a beginner or intermediate programmer, you might have stumbled upon the terms "list" and "array" when working with Python. While both terms are used to store collections of items, there is a subtle difference between them in the context of Python.
Arrays (NumPy) vs Lists (Built-in)
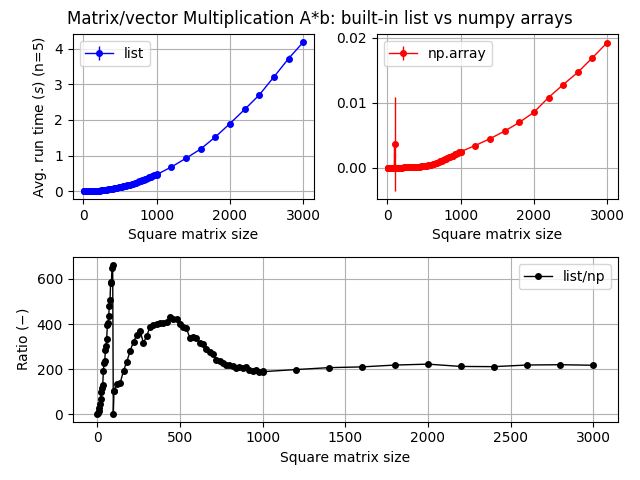
In Python, an array is actually a NumPy ( Numerical Python) object that is designed for efficient numerical computation. It's essentially a multi-dimensional table of values, similar to a list but with more features and performance benefits. Here are some key differences:
Databinding: NumPy arrays can bind data to memory, making them faster and more efficient than lists when working with large datasets.
On the other hand, Python lists are a built-in data structure that is part of the language's standard library. They are often used to store collections of items, such as strings, integers, floats, or even objects. Here are some key differences:

When to Use Each
So, when should you choose a list over an array?
And when should you use a NumPy array?
When working with large numerical datasets or performing complex mathematical operations. When you require efficient vectorized operations for fast computation.In summary, while both lists and arrays are used to store collections of items in Python, they serve different purposes. Lists are built-in, flexible, and suitable for non-numerical data, whereas NumPy arrays are designed for high-performance numerical computations with features like databinding, vectorized operations, and multidimensional support.
I hope this clarifies the difference between Python lists and arrays!