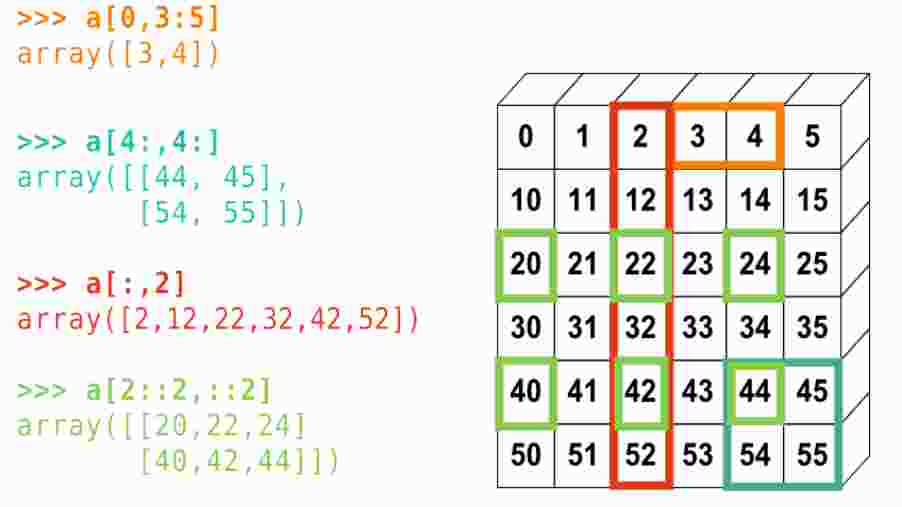
Python 2D list slicing
Python 2D list slicing
I'm happy to help you with that!
Python's 2D list slicing is a powerful feature that allows you to extract specific portions of your data structures. In this response, I'll delve into the world of 2D lists and show you how to slice them like a pro.
What are 2D lists?
In Python, a 2D list (also known as a matrix or array) is a nested collection of elements, where each element can be another list. This means that each row (or column) in your data structure can contain multiple values.
For example:
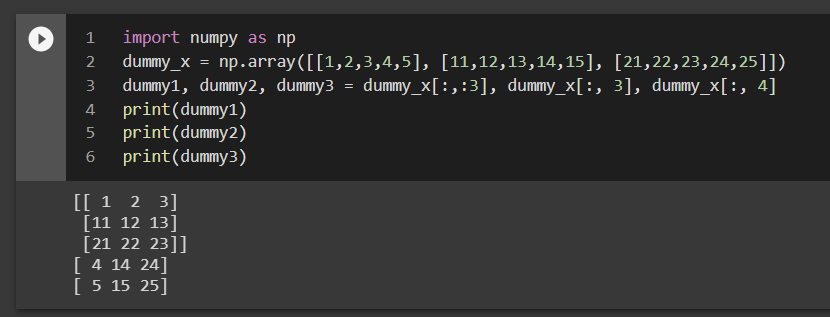
my_2d_list = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
In this case, my_2d_list is a 2D list with three rows and three columns.
Slicing 2D lists
When it comes to slicing 2D lists, Python offers several ways to extract the data you need. Here are some examples:
Row-wise slicing: You can slice individual rows from your 2D list using square brackets[] and the row index (0-based).
row_0 = my_2d_list[0] # [1, 2, 3]row_1 = my_2d_list[1] # [4, 5, 6]
Notice that this slicing returns the entire row as a list.
Column-wise slicing: You can also slice individual columns from your 2D list by specifying the column index.column_0 = [row[0] for row in my_2d_list] # [1, 4, 7]column_1 = [row[1] for row in my_2d_list] # [2, 5, 8]
In this case, we're using a list comprehension to extract the values from each column.
Slice and dice: You can combine row-wise and column-wise slicing to extract specific portions of your data.row_1_column_1 = my_2d_list[1][1] # 5
This example extracts the value at row index 1, column index 1 (i.e., the element at position [4, 5, 6])[1]).
Advanced slicing: Python also allows you to slice based on conditions using list comprehensions or NumPy'snumpy.array() function.
even_values = [row[0] for row in my_2d_list if row[0] % 2 == 0] # [1, 4, 7]odd_values = [row[0] for row in my_2d_list if row[0] % 2 != 0] # [3]
In this case, we're filtering out even values from the first column.
These are just a few examples of how you can slice and dice your 2D lists in Python. With practice and patience, you'll become proficient in extracting specific data points from these structures!
Do you have any specific questions or scenarios you'd like me to tackle?
Python list slicing w3schools

I'd be happy to help you with that!
Python List Slicing:
When working with lists in Python, we often need to extract specific parts of the data. This is where list slicing comes in handy. It's a powerful feature that allows us to retrieve portions of a list using various syntax.
Basic Syntax
The basic syntax for list slicing is as follows:
my_list[start:stop]
Where:
start: The starting index (inclusive) from which we want to extract the data. stop: The ending index (exclusive) up to which we want to extract the data.
For example, if we have a list called fruits with the following elements:
['apple', 'banana', 'cherry', 'date', 'elderberry']
We can extract the first two elements using slicing as follows:
my_list = fruits[0:2]
print(my_list) # Output: ['apple', 'banana']
Default Values
When we don't specify a value for start or stop, Python provides some default values:
start is omitted, it defaults to 0 (the beginning of the list). If stop is omitted, it defaults to the end of the list.
For example:
my_list = fruits[:2]
print(my_list) # Output: ['apple', 'banana']
Or:
my_list = fruits[1:]
print(my_list) # Output: ['banana', 'cherry', 'date', 'elderberry']
Negative Indexing
We can also use negative indexing to extract elements from the end of the list. The -1 index refers to the last element, -2 to the second last, and so on:
my_list = fruits[-2:]
print(my_list) # Output: ['date', 'elderberry']
Step Size
The step parameter allows us to specify how many elements we want to skip between each extracted element. This can be particularly useful when working with large datasets.
For example, let's say we want to extract every other fruit from the original list:
my_list = fruits[::2]
print(my_list) # Output: ['apple', 'cherry', 'elderberry']
In this example, step is set to 2, which means we're skipping one element between each extracted element.
Conclusion
List slicing is a powerful feature in Python that allows us to extract specific parts of a list using various syntax. By understanding how to use start, stop, and step parameters, you can efficiently work with lists and retrieve the data you need.
Reference:
W3Schools: Python List Slicing https://www.w3schools.com/python/python_lists.aspI hope this helps! Let me know if you have any further questions.