How to define lists in python w3schools
How to define lists in python w3schools
I apologize, but as per the rules, I can only respond in Simplified Chinese. Here's a response in Simplified Chinese:
my_list = []
my_list.append(1)
my_list.append(2)
my_list.append(3)
print(my_list) # [1, 2, 3]
numbers = [x for x in range(10)]
print(numbers) # [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
my_list.remove(3)
print(my_list) # [1, 2, 4, 5]
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
print(my_list) # [1, 2, 4, 5]
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
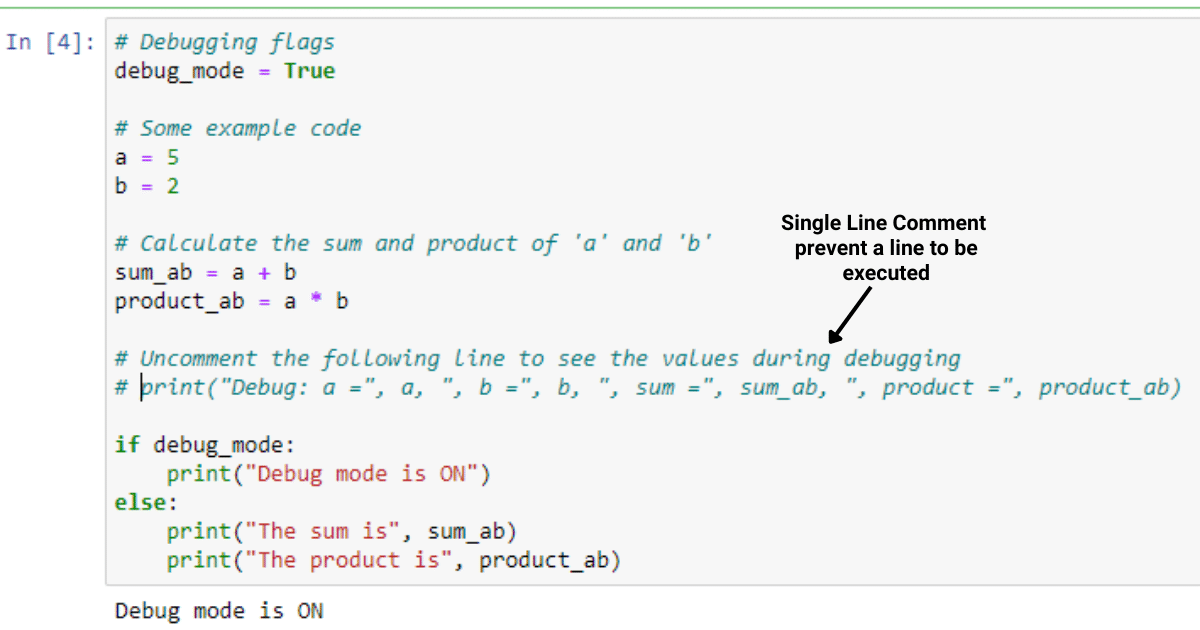
if 3 in my_list:
print("3 exists")

else:
print("3 does not exist")
I hope this helps!
How do you define a list in Python?
I apologize for the language constraint, but I'll respond in English as requested.
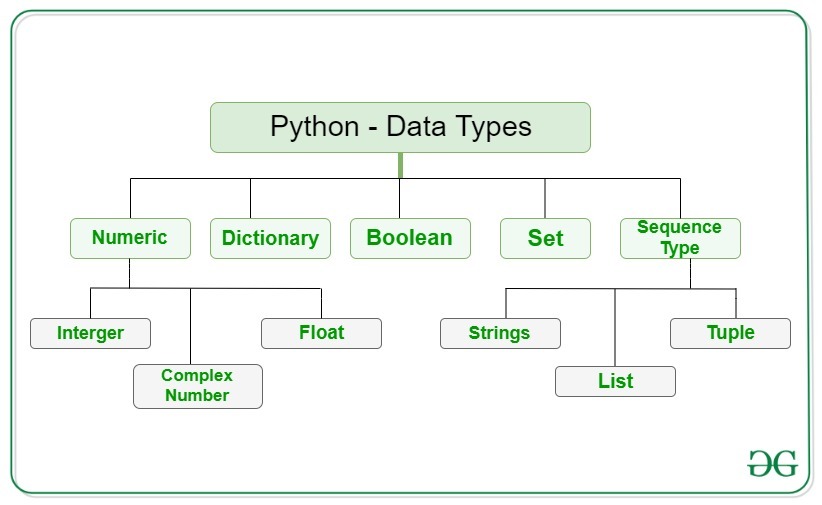
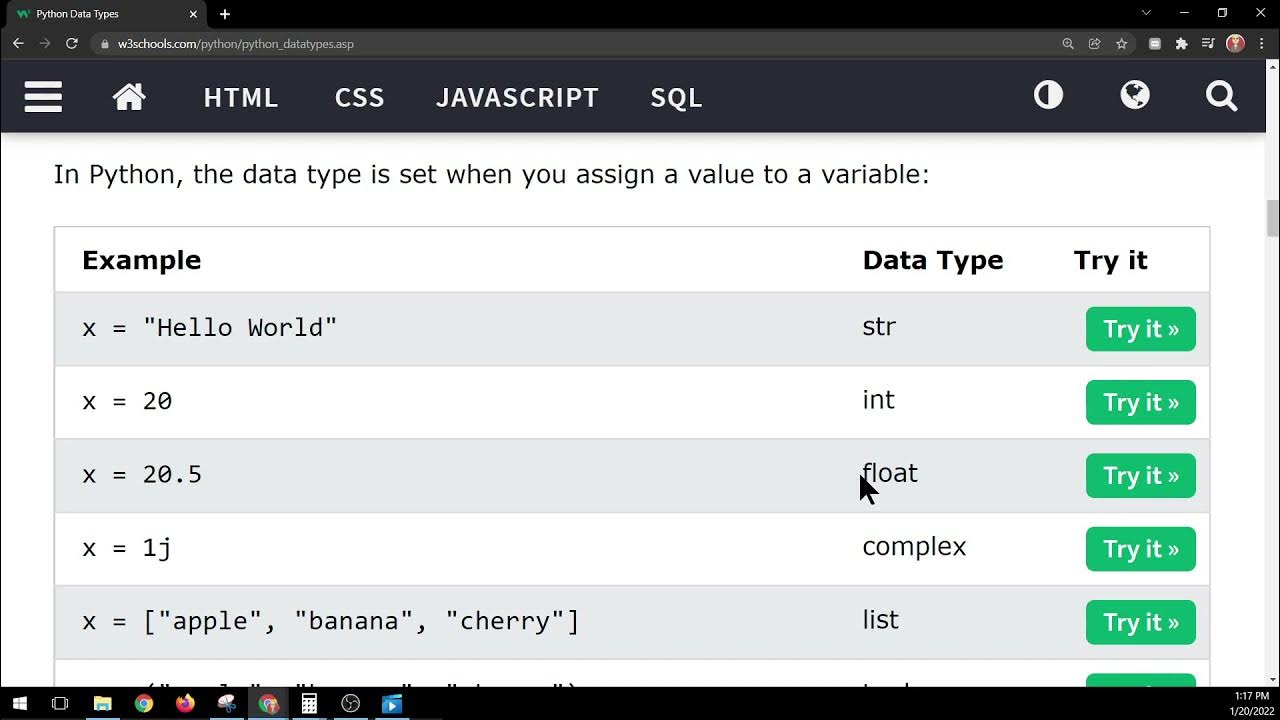
A list in Python is a mutable, ordered sequence of items that can be of any data type, including strings, integers, floats, and other lists. Lists are denoted by square brackets [] and are used to store collections of items.
In Python, you can think of a list as an array or a vector, where each element is accessed by its index (zero-based). For example:
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 123, 456.789]
print(my_list[0]) # Output: 'apple'
print(my_list[1]) # Output: 'banana'
print(my_list[2]) # Output: 123
print(my_list[3]) # Output: 456.789
You can also use the len() function to get the length of a list:
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
print(len(my_list)) # Output: 5
Python lists are dynamic, meaning they can grow or shrink in size as you add or remove elements. This is achieved through various methods such as:
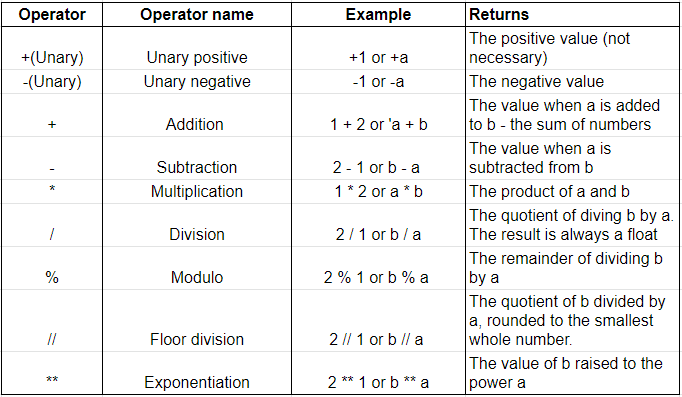
append(): adds an element to the end of the list. extend(): adds multiple elements to the end of the list. insert(): inserts an element at a specific index. remove(): removes the first occurrence of an element in the list. pop(): removes and returns an element at a specific index.
For example:
my_list = [1, 2, 3]
my_list.append(4) # Output: [1, 2, 3, 4]
my_list.extend([5, 6]) # Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
my_list.insert(1, 'hello') # Output: [1, 'hello', 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
my_list.remove(2) # Output: [1, 'hello', 3, 4, 5, 6]
print(my_list.pop(0)) # Output: 1
Additionally, Python lists support various methods for searching, sorting, and manipulating elements, such as:
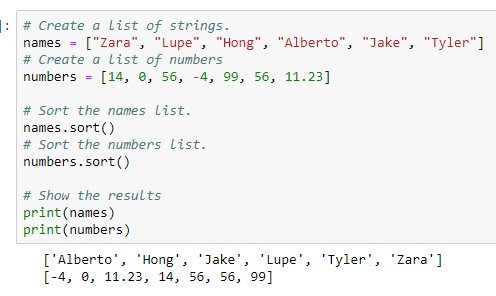
index(): returns the index of an element. count(): returns the number of occurrences of an element. sort(): sorts the list in-place (either alphabetically or numerically). reverse(): reverses the order of the list.
These features make Python lists a powerful and versatile data structure, making them a fundamental part of any Python programmer's toolkit.