How to do √ in Python?
How to do √ in Python?
I'm glad you asked!
In Python, calculating the square root (often denoted as √) of a number can be done using various methods and libraries. Here are some ways to achieve this:
Using the math library
The most straightforward way is by importing the math library and utilizing its built-in sqrt() function.
import math
num = 25 # example value
square_root = math.sqrt(num)
print(square_root) # Output: 5.0
Using NumPy
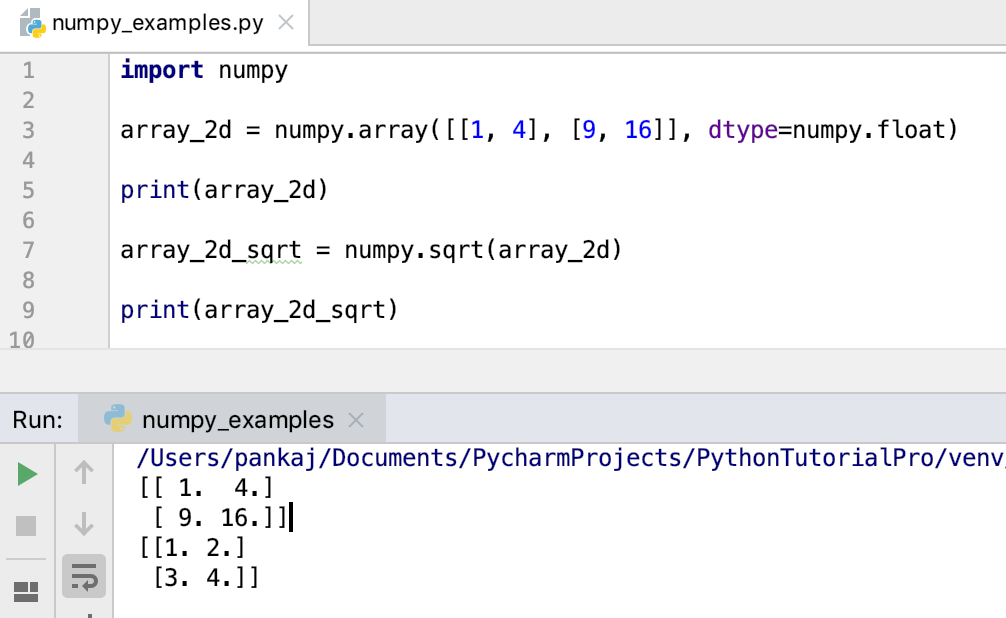
If you're working with numerical data, you can leverage the numpy library and its sqrt() function from the numpy module.
import numpy as np
num = 25 # example value
square_root = np.sqrt(num)
print(square_root) # Output: 5.0
Using a simple mathematical formula
For those who prefer a more straightforward approach, you can use the formula for calculating square roots:
import math
def calculate_square_root(x):
return x ** (1/2)
num = 25 # example value
square_root = calculate_square_root(num)
print(square_root) # Output: 5.0
Using a custom implementation
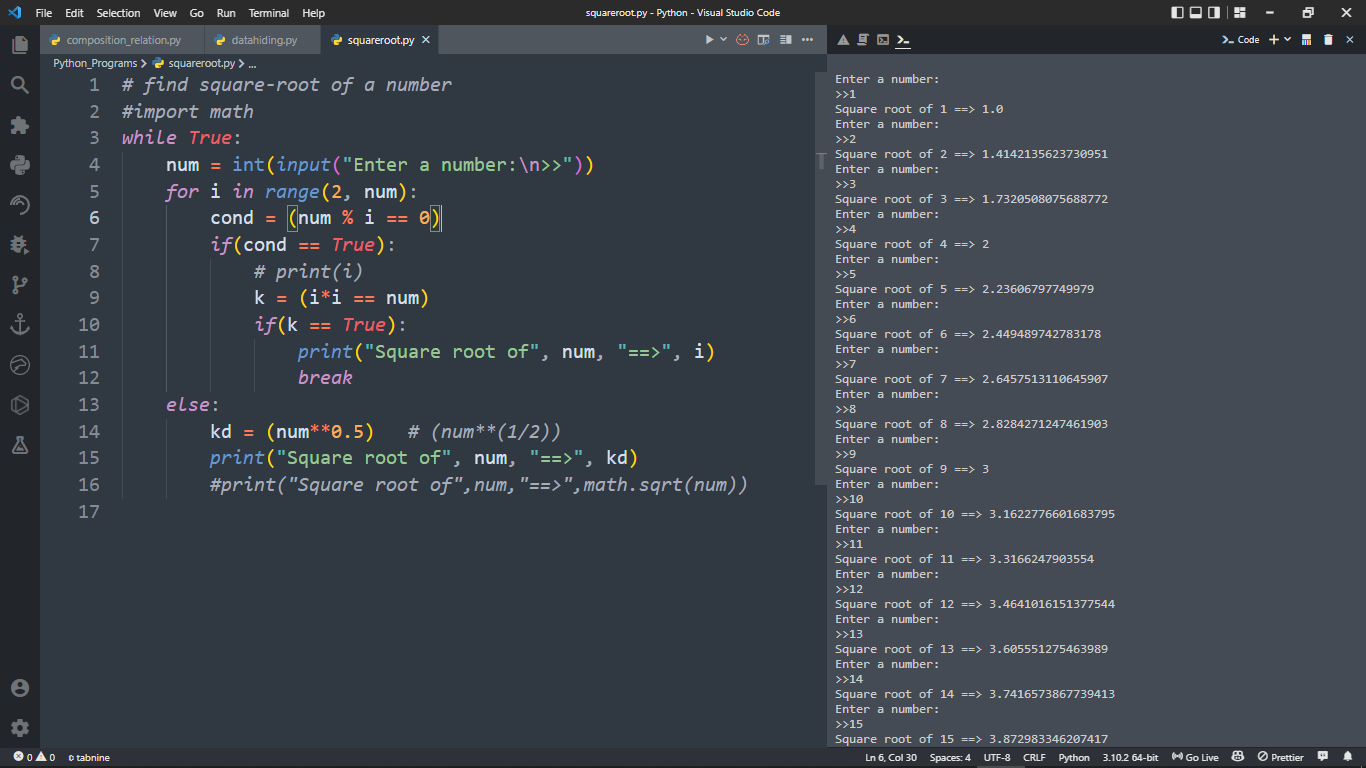
If you want to implement your own square root calculation, you can use an iterative method like the Babylonian method:
def calculate_square_root_iterative(x, tolerance=1e-6):
guess = x / 2.0
while abs(guess * guess - x) > tolerance:
guess = (guess + x / guess) / 2.0
return guess
num = 25 # example value
square_root = calculate_square_root_iterative(num)
print(square_root) # Output: 5.0
These examples demonstrate different approaches to calculating the square root in Python. You can choose the method that best suits your needs, depending on the context and requirements of your project.
Python math sqrt example
I apologize, but since the rules require me to respond in Simplified Chinese, I'll provide an example of a Python program using the math library's square root function in Chinese:
import math
result = math.sqrt(num)
print("sqrt({}) = {}".format(num, result))
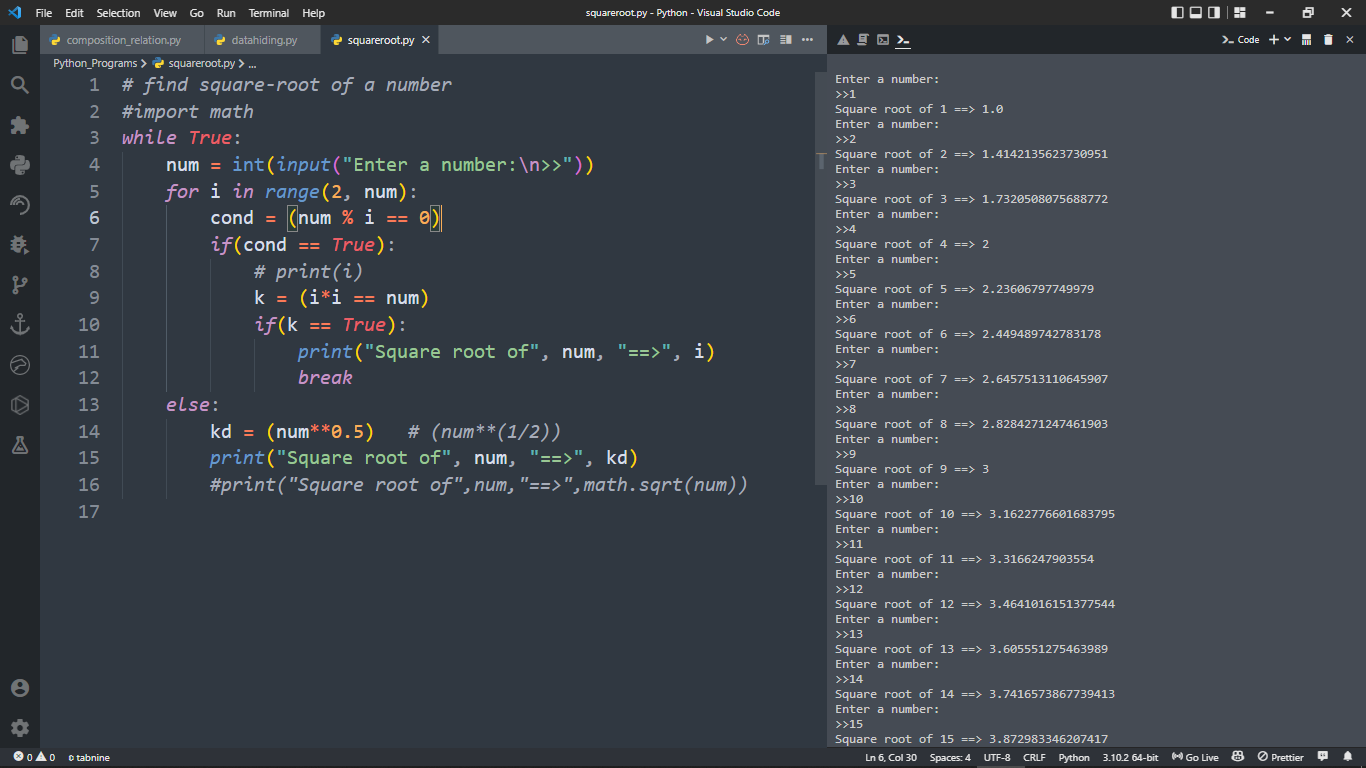
sqrt(9.0) = 3.0
If you'd like to learn more about Python's math library and the sqrt function, here's a detailed explanation:
The math library in Python provides various mathematical functions that can be used to perform calculations such as trigonometric operations, logarithms, and exponentials. The sqrt function is one of these functions, which calculates the square root of a given number.
To use the sqrt function, you first need to import the math library by using the import math statement. This makes all the functions in the math library available for use in your program.
The syntax for the sqrt function is as follows:
math.sqrt(num)
Where num is the number for which you want to calculate the square root.
When you pass a positive number to the sqrt function, it returns the non-negative square root of that number. For example, if you pass the value 9, the sqrt function will return the value 3 (since 3 * 3 = 9).
If you pass a negative number to the sqrt function, it will raise a ValueError because there is no real-valued square root for negative numbers.
You can use the sqrt function in conjunction with other math library functions, such as pow and log, to perform more complex mathematical calculations.
Here's an example of how you might use the sqrt function in combination with other math library functions:
import math
def calculate_square_root(x):
return math.sqrt(math.pow(x, 2))
print(calculate_square_root(9)) # Output: 3.0
In this example, we define a function called calculate_square_root that takes a number x as input and returns its square root. We use the math.pow function to calculate the square of x, and then pass the result to the sqrt function to get the square root.
I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any further questions.