What is data types in Python
What is data types in Python
I'd be happy to help you with that!
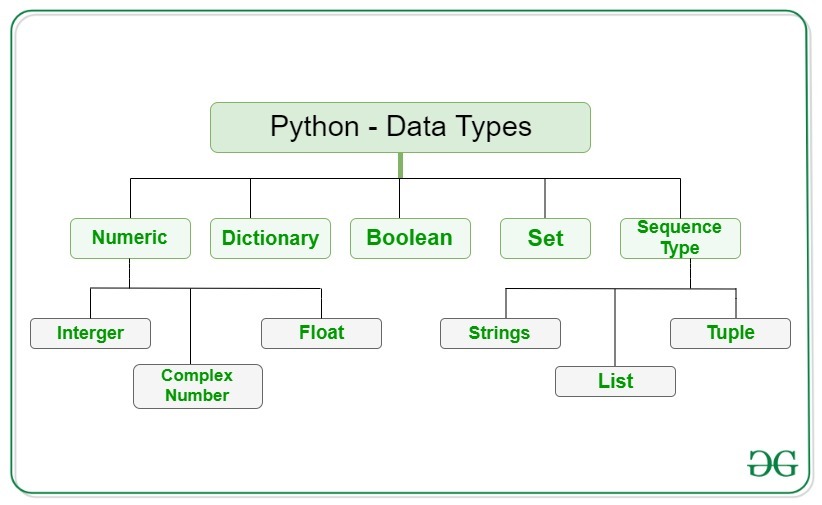
In Python, a data type refers to the category of data that an object belongs to. These categories determine how the data can be used and what operations can be performed on it. Here's a comprehensive list of built-in data types in Python:
Integers (int): Whole numbers, either positive, negative, or zero, such as 1, -1, 0.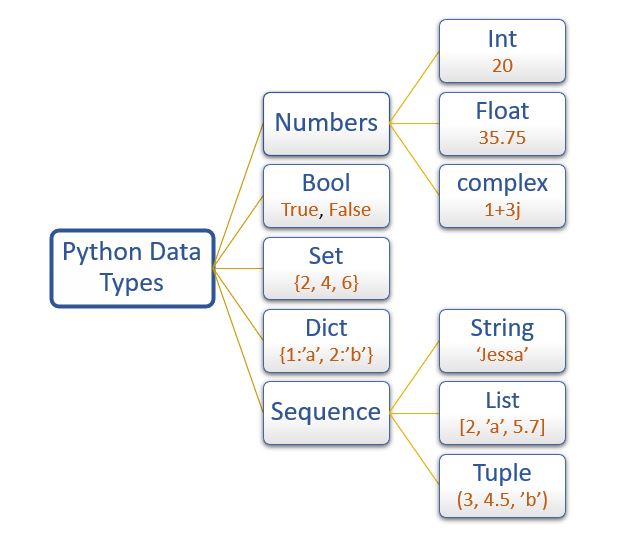
Example: a = 5
Example: b = 3.14159
Example: c = 3 + 4j
Example: is_admin = True
Example: greeting = "Hello World!"
Example: image_data = b'x00x01x02'
Example: fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
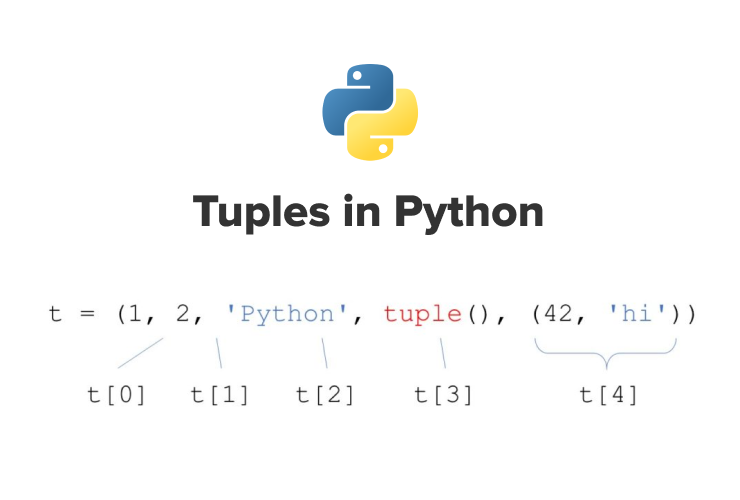
Example: colors = ("red", "green", "blue")
Example: person = {"name": "John", "age": 30}
Example: unique_chars = {"a", "b", "c", "d"}
Example: result = None
Example: class Person: ... person = Person("John", 30)
When working with data in Python, it's essential to understand the differences between these data types. Knowing when to use each type will help you write efficient, readable, and maintainable code.
Data types in python with examples w3schools
I'd be happy to provide information on data types in Python along with examples from W3Schools.
Python is a high-level programming language that supports multiple data types, which are used to define the type of data a variable can hold. Here are some of the most common data types in Python:
x = 5 is an integer.

python
x = 5
print(type(x)) # Output: <class 'int'>
y = 3.14 and z = -0.5.
python
y = 3.14
z = -0.5
print(type(y)) # Output: <class 'float'>
print(type(z)) # Output: <class 'float'>
phrase = "Hello World".
python
phrase = "Hello World"
print(type(phrase)) # Output: <class 'str'>
is_admin = True and is_admin = False.
python
is_admin = True
print(type(is_admin)) # Output: <class 'bool'>
python
my_list = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
print(type(my_list)) # Output: <class 'list'>
python
my_tuple = ("apple", "banana", "cherry")
print(type(my_tuple)) # Output: <class 'tuple'>
python
my_dict = {"name": "John", "age": 30}
print(type(my_dict)) # Output: <class 'dict'>
python
my_set = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
print(type(my_set)) # Output: <class 'set'>
These are the most common data types in Python. Understanding these data types is essential for any programmer working with Python.