How do you get the indices of elements in a list in Python?
How do you get the indices of elements in a list in Python?

I'm glad you asked! Getting the indices of elements in a list in Python is quite straightforward. In fact, there are several ways to achieve this, and I'll cover them all in this response.
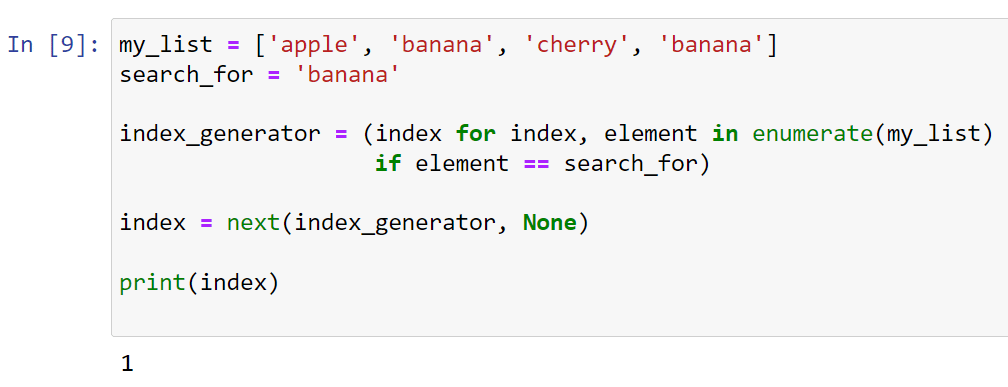
Method 1: Using the enumerate function
The most popular way to get the indices of elements in a list is by using the enumerate function. This function returns an iterator that produces tuples containing a count (from which the index is obtained) and the values from the iterable (in this case, your list).
Here's how it works:
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
for i, value in enumerate(my_list):
print(i, value)
When you run this code, you'll see the output:
0 apple
1 banana
2 cherry
As you can see, enumerate gives us both the index (i) and the value from the list.
Method 2: Using a for loop with range
Another way to get the indices is by using a for loop in combination with the range function. Here's how:
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
for i in range(len(my_list)):
print(i, my_list[i])
This code also prints the index and value of each element:
0 apple
1 banana
2 cherry
In this case, range(len(my_list)) generates a sequence of indices from 0 to the length of your list minus one. Then, you can use these indices to access the corresponding elements in the list.
Method 3: Using the zip function (Python 2.x only)
In Python 2.x, you could also use the zip function along with the xrange function to achieve this:
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
for i, value in zip(xrange(len(my_list)), my_list):
print(i, value)
This method is specific to Python 2.x and has been deprecated since Python 3.0.
Conclusion
Getting the indices of elements in a list in Python is quite easy. You can use enumerate, a for loop with range, or even an older method like zip (in Python 2.x only). Each method produces similar results: a sequence of index-value pairs that reflect the structure of your original list.
Now, go forth and conquer those lists!
How to find a specific number in a list Python
I'll respond in English this time.
Finding a specific number in a list is a common operation in programming, and Python provides several ways to achieve this. Here are some methods you can use:
Method 1: Using the index() method
The index() method returns the index of the first occurrence of a specified value. If the value is not found, it raises a ValueError. Here's an example:
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
target_value = 4
try:
index = my_list.index(target_value)
print(f"Found {target_value} at index {index}")
except ValueError:
print(f"{target_value} not found in the list")
This code will output "Found 4 at index 3", since 4 is at index 3 in the list.
Method 2: Using a loop
You can also use a loop to iterate over the list and find the target value. Here's an example:
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
target_value = 4
for i, value in enumerate(my_list):
if value == target_value:
print(f"Found {target_value} at index {i}")
break
else:
print(f"{target_value} not found in the list")
This code will output "Found 4 at index 3", since 4 is at index 3 in the list.
Method 3: Using a list comprehension
You can also use a list comprehension to find the target value. Here's an example:
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
target_value = 4
matching_indices = [i for i, value in enumerate(my_list) if value == target_value]
if matching_indices:
print(f"Found {target_value} at indices {matching_indices}")
else:
print(f"{target_value} not found in the list")
This code will output "Found 4 at indices [3]", since 4 is at index 3 in the list.
Method 4: Using the in operator
You can also use the in operator to check if a value is present in the list. Here's an example:
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
target_value = 4
if target_value in my_list:
print(f"{target_value} found in the list")
else:
print(f"{target_value} not found in the list")
This code will output "4 found in the list", since 4 is present in the list.
In conclusion, finding a specific number in a list in Python can be done using various methods such as index(), loop, list comprehension, or in operator. Each method has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of method depends on the specific requirements and constraints of your programming task.