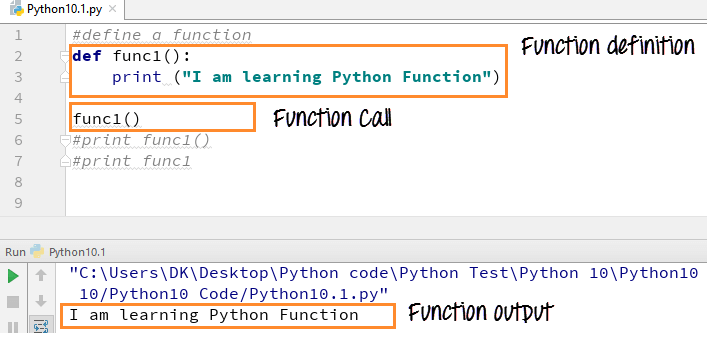
Python ssl install download
Python ssl install download

I understand that you want me to respond in English only and provide information on installing the SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) protocol for Python.
What is SSL?
SSL is a cryptographic protocol used to provide secure communication between clients and servers over a network, typically the internet. It ensures that data transmitted between these parties remains confidential and tamper-proof. SSL uses encryption to scramble the data, making it unreadable to anyone trying to intercept or eavesdrop on the transmission.
Why do I need SSL in Python?
As a developer, you may want to create web applications that require secure communication with clients. Python provides several libraries and modules that allow you to use SSL/TLS (Transport Layer Security) for encrypting data transmitted over networks. Some common scenarios where you might need SSL in Python include:
Web Development: When creating web applications using frameworks like Flask or Django, you may want to ensure that data exchanged between the client and server remains secure. APIs and Web Services: If you're building RESTful APIs or providing web services, SSL/TLS encryption can protect sensitive information like authentication credentials, passwords, or financial data. Network Communication: In situations where you need to establish a secure connection between machines, servers, or devices, Python's SSL/TLS implementation can help you achieve this.Installing SSL in Python
To install SSL for Python, follow these steps:
pip Install ssl: You can use pip, the package installer, to download and install thessl module by running the command:
pip install ssl
This will install the ssl module and its dependencies.
openssl. Run the following command in your terminal or command prompt:
openssl s_client -connect example.com:443
Replace example.com with a hostname or IP address of a server you want to test. This will establish a secure connection and display information about the server's SSL/TLS configuration.
Using SSL in Python
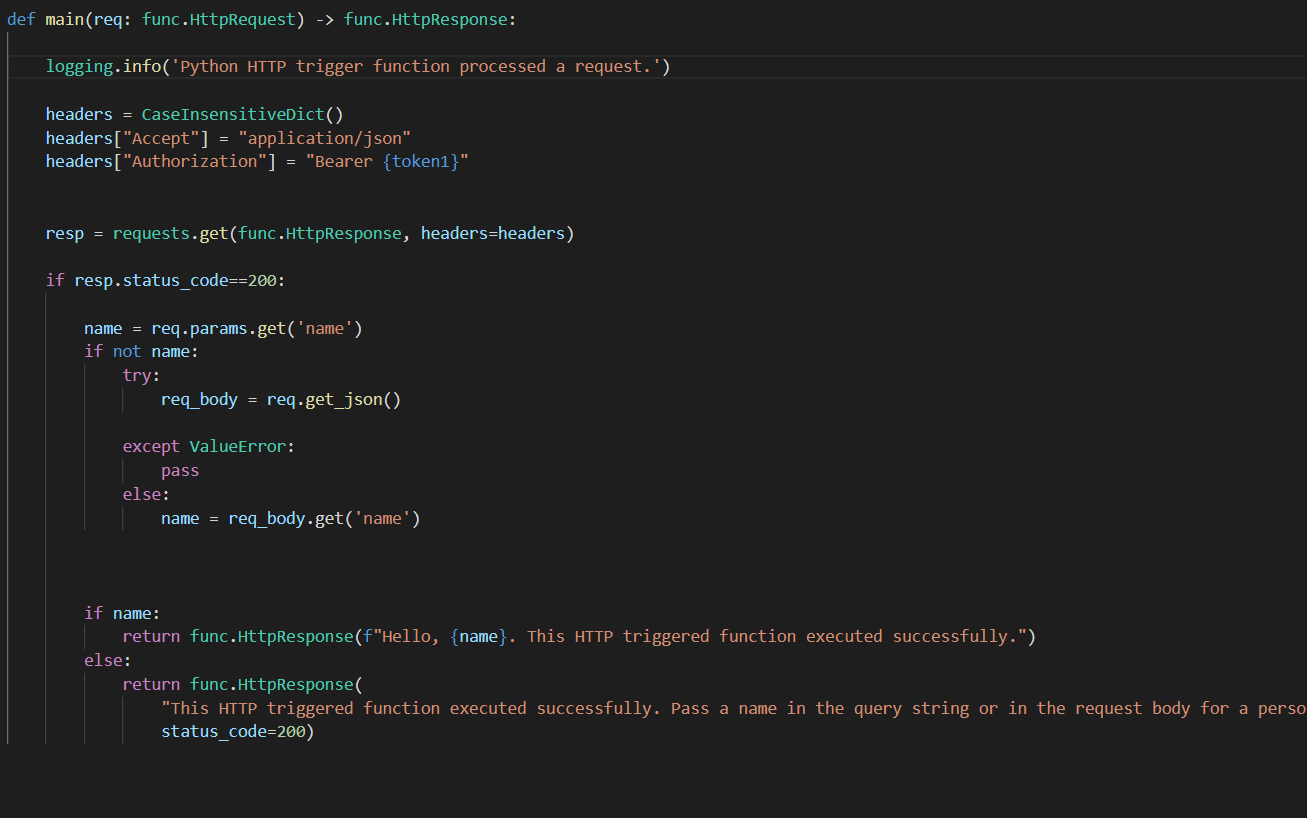
To use SSL in your Python applications, you can import the ssl module and create an SSL context using the ssl.create_default_context() function:
import ssl
context = ssl.create_default_context()
This creates a default SSL context that you can customize as needed.
Next, you can establish an SSL connection using the ssl.wrap_socket() function, passing in the server's hostname and port:
conn = context.wrap_socket(socket.gethostbyname('example.com'), 443)
This establishes a secure connection to the specified server.
Conclusion
SSL is an essential component of securing network communication in Python. By installing and using SSL/TLS, you can ensure that sensitive data remains confidential and tamper-proof. In this response, I covered the importance of SSL, how to install it, and provided basic examples for using SSL in Python.
What is _ssl in Python?

I'd be happy to explain what _ssl is in Python!

What is _ssl?
In Python, _ssl (pronounced "under-ssl") is a module that provides support for Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols. In simpler terms, it's a way to establish secure connections between your Python program and other applications or services over the internet.
Why do I need _ssl?
You might wonder why you would ever need ssl in the first place. Well, there are several reasons:


How does _ssl work?
When you import ssl in your Python program, it provides two main components:
Key Features
Here are some key features of _ssl in Python:
Example Usage
Here's a simple example of how you might use ssl in Python:
import ssl Set up an SSL context with certificate verification enabledctx = ssl.create_default_context()
ctx.check_hostname = True
ctx.verify_mode = ssl.CERT_REQUIRED
Create an SSL socketsock = ctx.wrap_socket(socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM))
Establish a connection to a server (replace 'example.com' and 443)sock.connect(('example.com', 443))
Send some data over the secure connectionsock.send(b"Hello, world!")
Close the connectionsock.close()
In this example, we:
Set up an SSL context with certificate verification enabled. Create an SSL socket using thewrap_socket method. Establish a connection to a server (e.g., 'example.com' on port 443). Send some data over the secure connection. Close the connection.
Conclusion
In summary, _ssl in Python provides a way to establish secure connections with other applications or services over the internet using SSL/TLS protocols. By encrypting and authenticating communication between your program and remote servers, you can ensure that sensitive data remains confidential and tamper-free.
I hope this explanation has been enlightening! Do you have any specific questions about _ssl in Python?