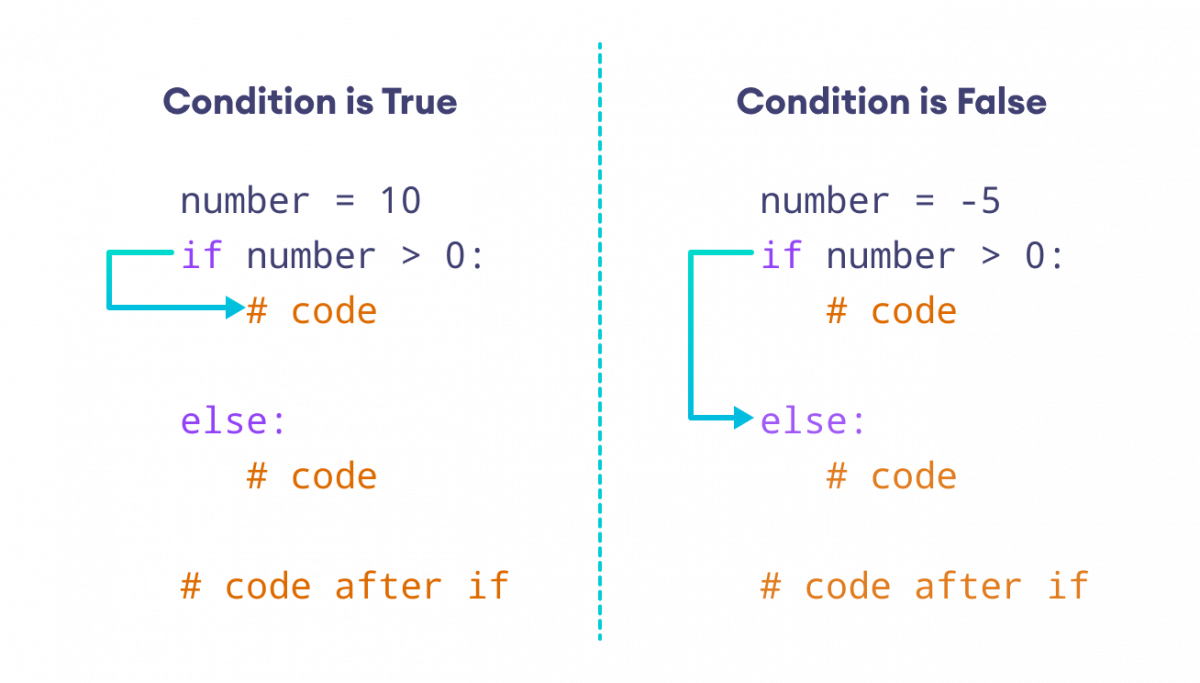
If-else statement in Python example
If-else statement in Python example
I'm glad you asked! Here's an example of using if-else statements in Python:
# Example of using if-else statements in Python
Define a variable for user input age
age = int(input("Enter your age: "))

Use if-else statement to check the age and print out different messages
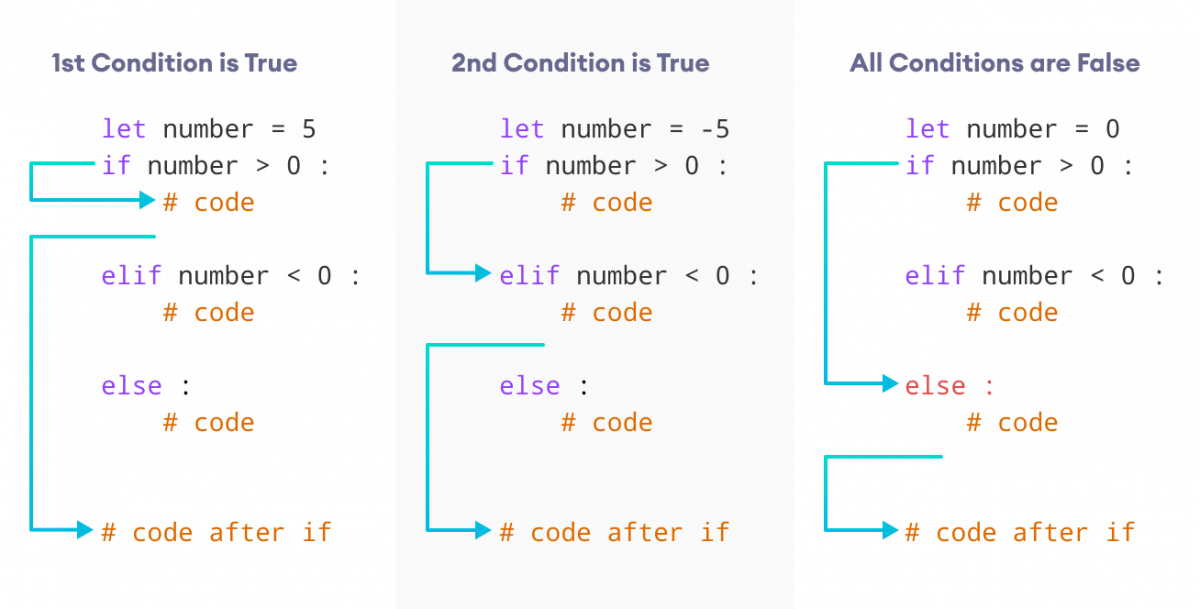
if age < 18:

print("You are still young! You are", age, "years old.")
elif 18 <= age < 65:
print("You are an adult now! You are", age, "years old.")
else:

print("You are a senior! You are", age, "years old.")
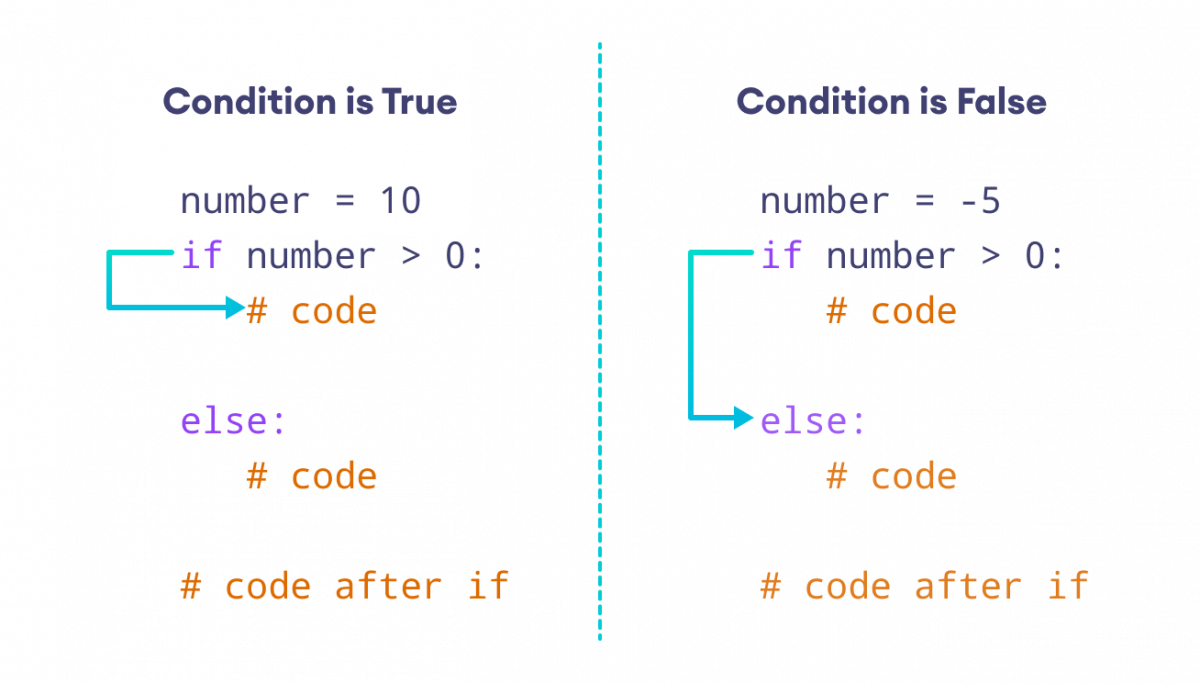
Now, let's try to use if-else statement for more complex logic
score = int(input("Enter your score (out of 100): "))
if score < 60:
grade = "F"
elif 60 <= score < 70:
grade = "D"
elif 70 <= score < 80:
grade = "C"
elif 80 <= score < 90:
grade = "B"
else:
grade = "A"
print("Your grade is:", grade)
Another example using if-else statement with multiple conditions
x, y = int(input("Enter x: ")), int(input("Enter y: "))
if x > y and x % 2 == 0 or y % 3 == 1:
print("Both conditions are true!")
elif x < y and y % 4 == 2:
print("First condition is false, second condition is true!")
else:
print("None of the conditions are true!")
In this example, we use if-else statements to check different age ranges and print out corresponding messages. We also show more complex examples where if-else statements are used with multiple conditions.
Here's a summary of how to use if-else statements in Python:
Start with anif statement followed by a condition (or conditions) enclosed in parentheses. The condition can be any valid expression using comparison operators like ==, <, >, !=, etc. If the condition is true, the code indented under the if block will be executed. You can use an else clause to specify what code should run if the original if condition is false. You can also add multiple conditions using the and and or logical operators.
I hope you find this example helpful!
How to write if, elif in one line in Python?
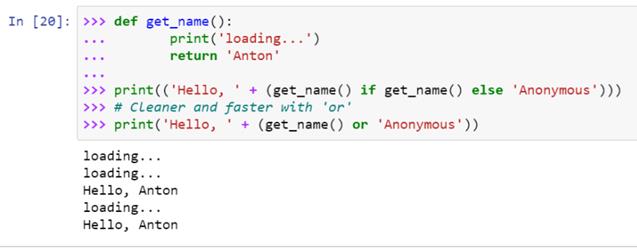
I'd be happy to help!
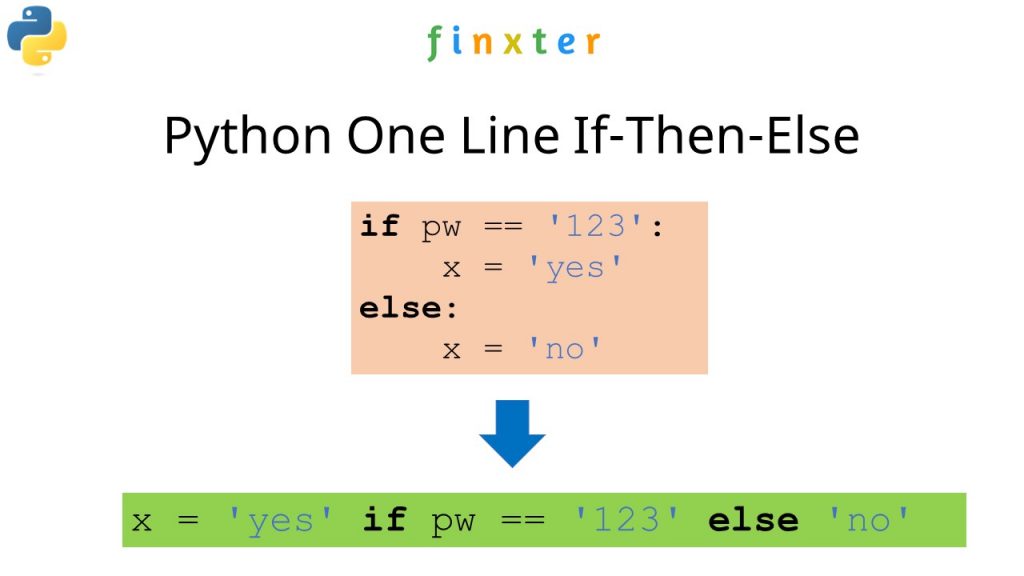
In Python, you can use the if-elif statement on a single line using the following syntax:
result = value if condition else another_value
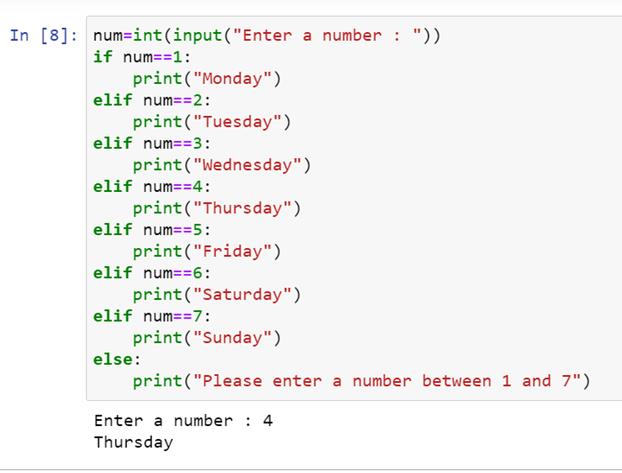
This is equivalent to the following traditional if-elif block:
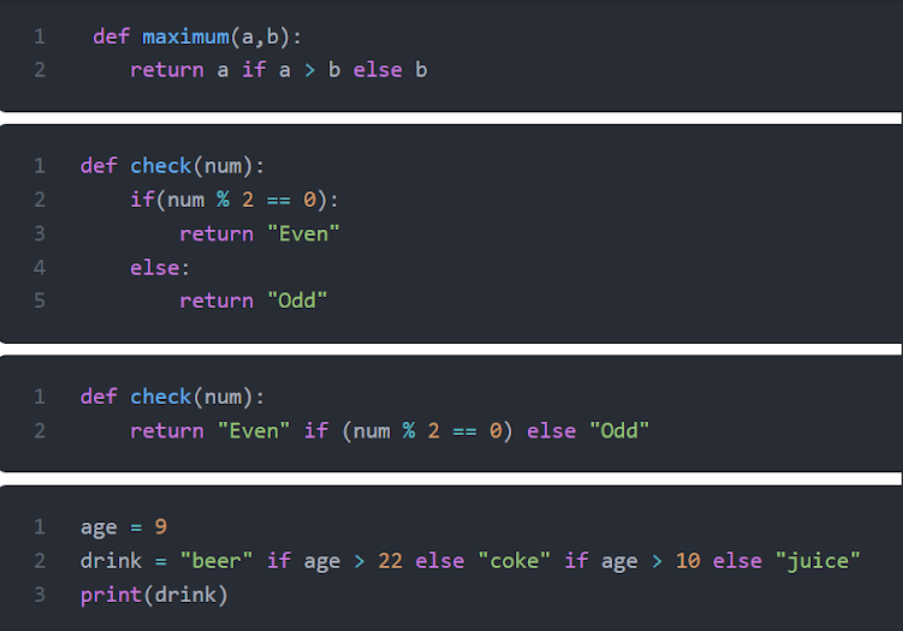
result = Noneif condition:
result = value
elif another_condition:
result = another_value
Let's break it down:
The statement starts withvalue if condition. This checks whether the condition is true. If the condition is true, then value is assigned to result. If the condition is false (i.e., a False or equivalent value), then the code after the else clause is executed. In this case, it's another_value.
Here are some examples:
Simpleif-elif on one line:
x = 5 if x > 3 else 2
This sets x to 5 if the condition x > 3 is true; otherwise, it sets x to 2.
result = "A" if score >= 90 and score < 100 else "B" if score >= 80 and score < 90 else "C"
This sets result to "A" if the score is between 90 and 99, "B" if it's between 80 and 89, and "C" for all other scores.
result = value1 if var1 > 10 else value2 if var2 < 5 else default_value
This sets result to value1 if var1 is greater than 10, value2 if var2 is less than 5, and default_value otherwise.
While this syntax can be useful for simple conditional statements, it's essential to understand that readability and maintainability might suffer when used extensively. For complex logic, traditional if-elif blocks are often more readable and easier to understand.
So, there you have it! The power of the if-elif statement in one line Python.