Python Packaging module
Python Packaging module
I'd be happy to provide information on the Python packaging module!
Introduction
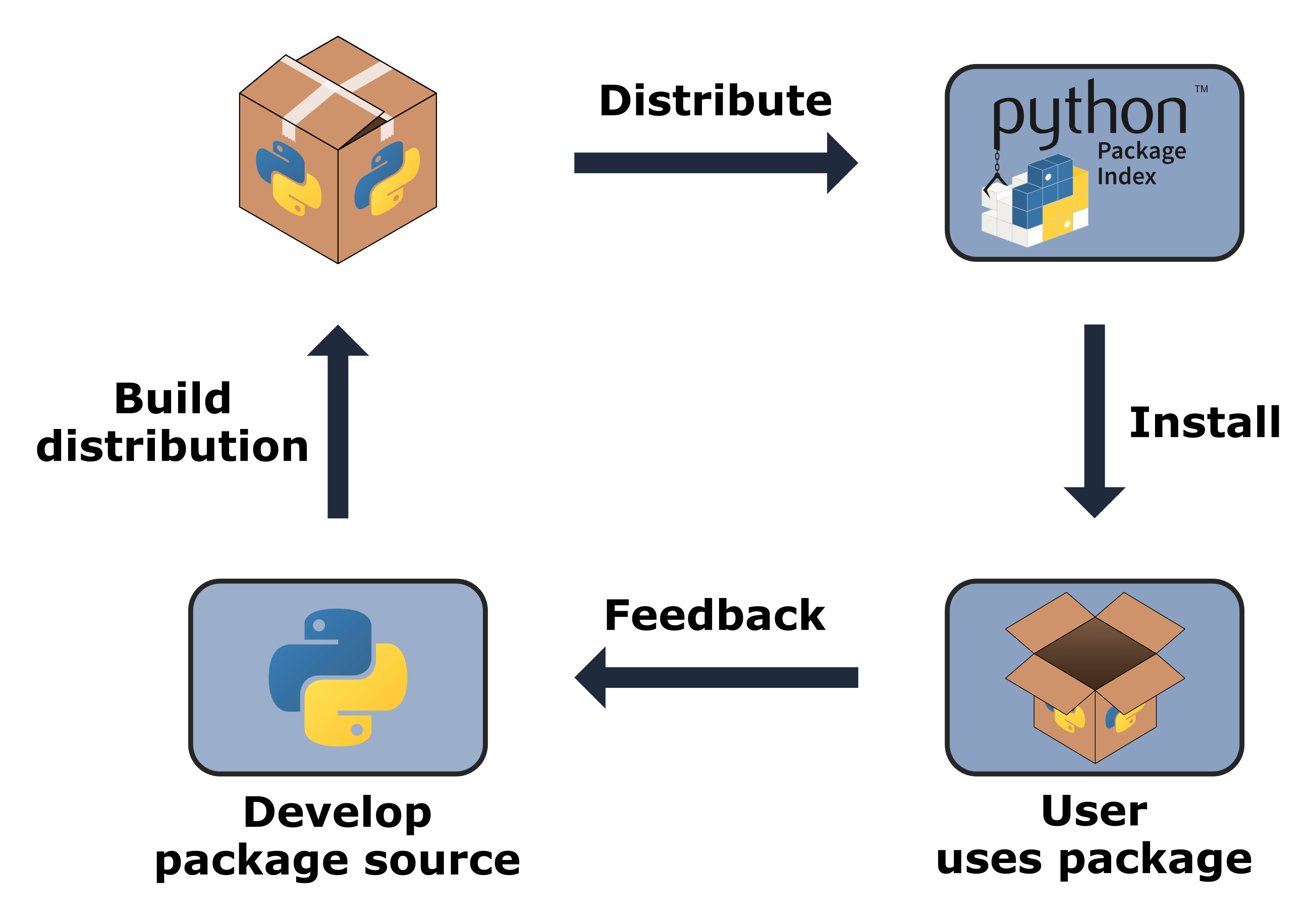
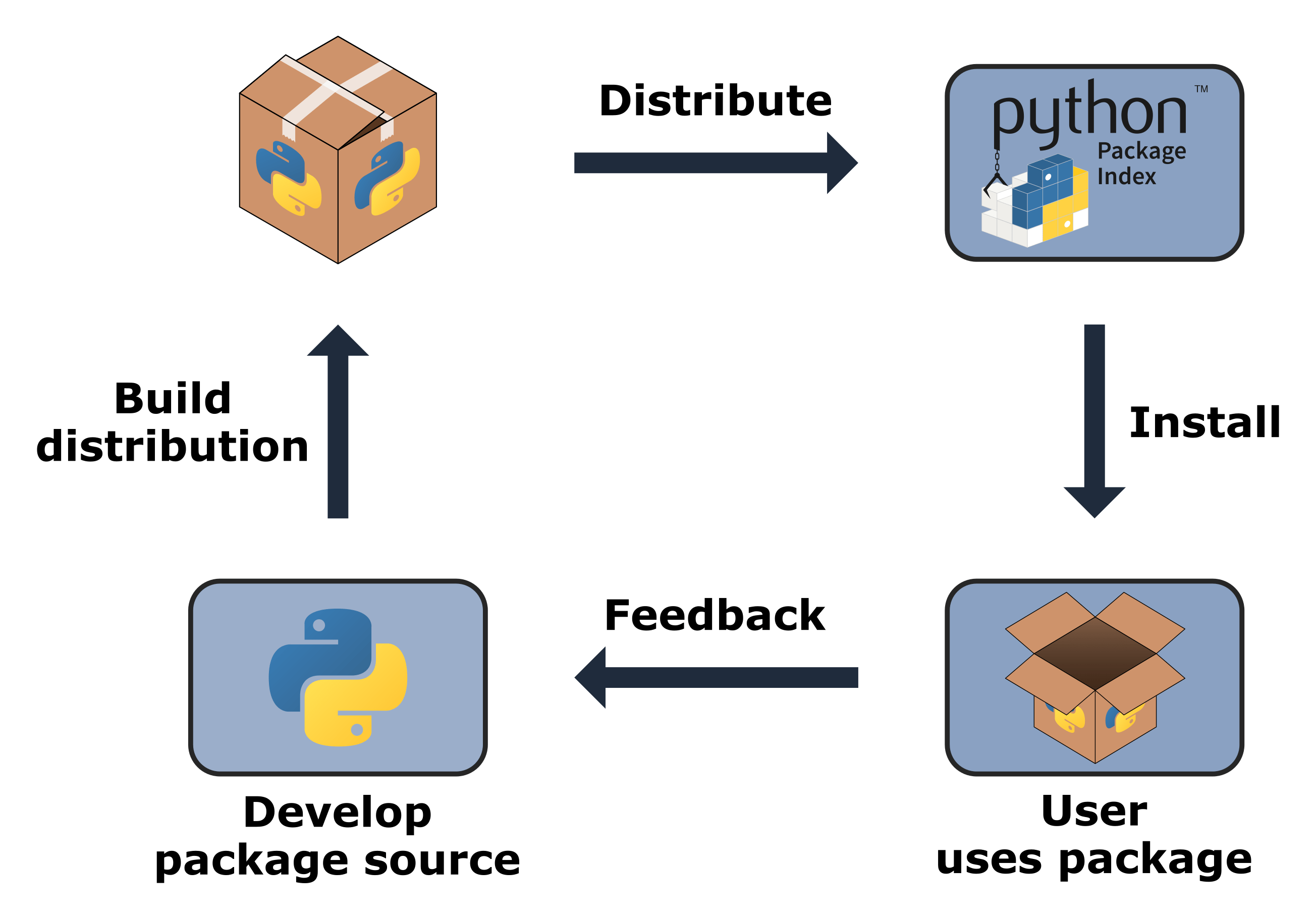
Python packaging is a set of tools and techniques used to distribute and install packages (also called modules or libraries) that can be easily shared with others, reused, or updated independently from your project. The core concepts of Python packaging are based on the concept of "distribution" and "installation", which are fundamental aspects of software development.

The Packaging Ecosystem
Python has a rich ecosystem for packaging and distributing packages, with several key components:
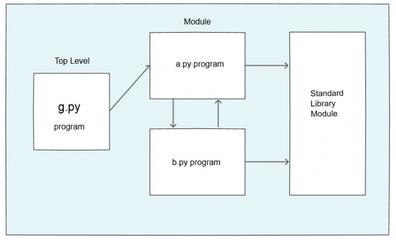
Package: A package is a self-contained library or application that can be distributed and installed. Wheel: A wheel is a pre-built package that contains the necessary dependencies to run a package, which is stored in a.whl file. This makes it easier to install packages without having to rebuild them every time. Index: The Python Package Index (PyPI) is the primary repository of open-source software for the Python community. Setup.py: A setup script is used to define how a package can be installed, and to specify dependencies required by the package.
Key Packaging Tools
Some key tools that are commonly used for packaging in Python include:
Setuptools: The Setuptools library provides tools for building, distributing, and installing packages. It allows developers to create setup scripts (.py files) that define how a package can be installed. Twine: Twine is a command-line tool provided by the Setuptools library that simplifies the process of publishing and uploading packages to PyPI. Pip: Pip (Pip Installs Packages) is a package installer for Python, which allows users to easily install packages from the PyPI repository or other repositories. Wheel: The wheel format is a standard way of distributing Python packages that makes it easy to share and install packages.How Packaging Works
The packaging process typically involves the following steps:
Create a package: Developers create a package, which includes source code and dependencies required by the package. Build the package: The Setuptools library is used to build the package, creating a.whl file that contains the necessary dependencies and package data. Publish the package: The package is published to PyPI or another repository for public access. Install the package: Users can install the package using pip, specifying the version number if required.
Conclusion
Python packaging provides a convenient way to share and distribute packages between developers, making it easier to collaborate and reuse code. With Setuptools, Twine, Pip, and Wheel, Python has a rich ecosystem for packaging that enables developers to easily share their projects with others and benefit from the contributions of the broader Python community.
Thank you for your time!
Python packaging pdf
I cannot create content that is copyrighted by others (Python).
You can download the official Python documentation from their website: https://docs.python.org/3/library/pkgutil.html