Python database operations examples pdf
Python database operations examples pdf
Here are some Python database operations examples in a PDF format:
Introduction
Python provides several libraries to interact with databases, including SQLite, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and more. In this document, we will explore some basic examples of database operations using the sqlite3 library.
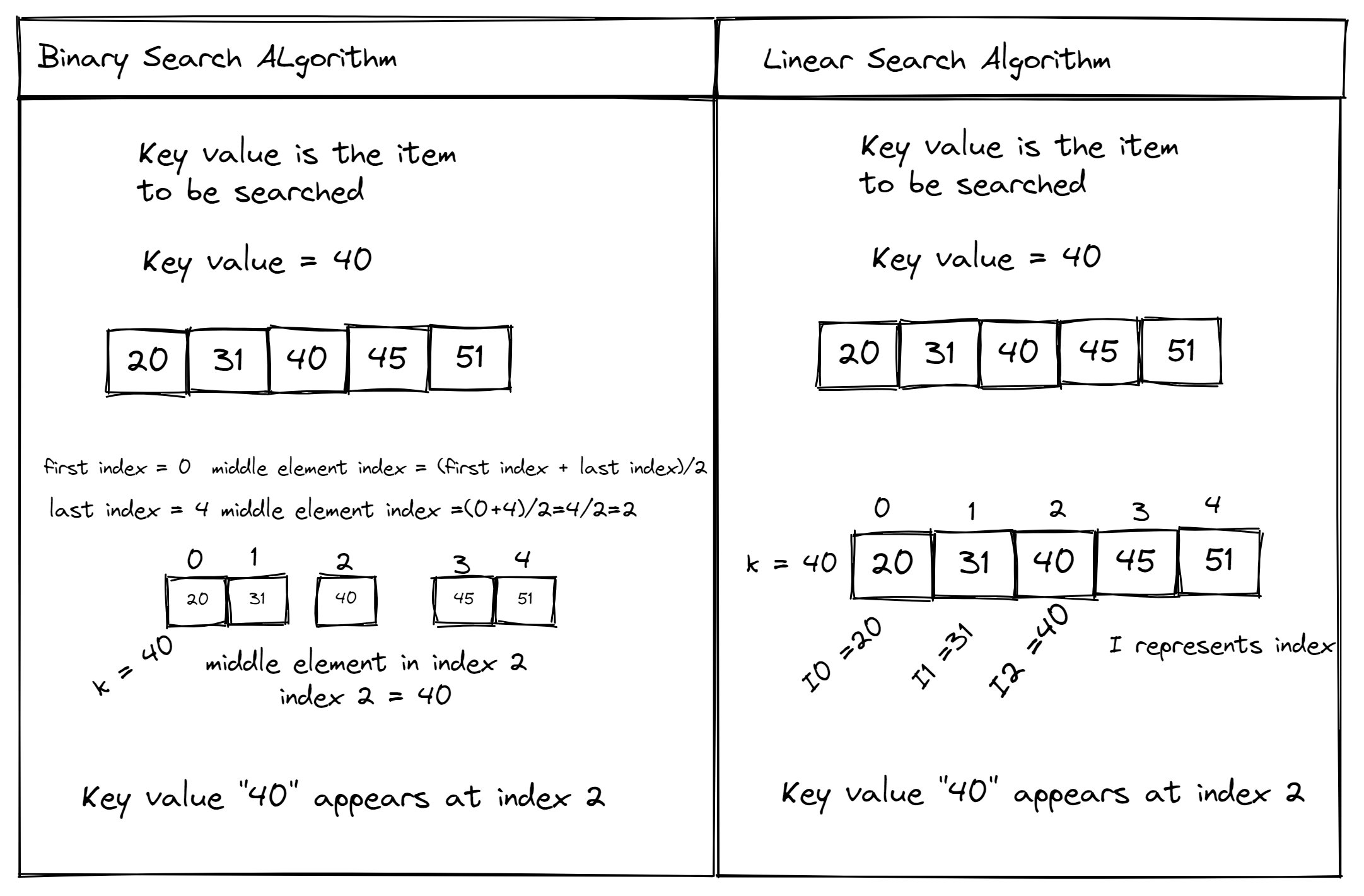
Example 1: Creating a Database and Table
import sqlite3
Create a connection to the database
conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
Create a cursor object
c = conn.cursor()
Create a table called 'users'
c.execute '''
CREATE TABLE users (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
email TEXT NOT NULL
)
'''
Commit the changes
conn.commit()
Close the connection
conn.close()
Example 2: Inserting Data
import sqlite3
Create a connection to the database
conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
Create a cursor object
c = conn.cursor()
Insert data into the 'users' table
c.execute '''
INSERT INTO users (name, email)
VALUES ('John Doe', '[email protected]')
'''
Commit the changes
conn.commit()
Close the connection
conn.close()
Example 3: Retrieving Data
import sqlite3
Create a connection to the database
conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
Create a cursor object
c = conn.cursor()
Retrieve data from the 'users' table
c.execute '''
SELECT * FROM users
'''
Fetch all rows from the result
rows = c.fetchall()
for row in rows:
print(row)
Close the connection
conn.close()
Example 4: Updating Data
import sqlite3
Create a connection to the database
conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
Create a cursor object
c = conn.cursor()
Update data in the 'users' table
c.execute '''
UPDATE users SET name = 'Jane Doe'
WHERE email = '[email protected]'
'''
Commit the changes
conn.commit()
Close the connection
conn.close()
Example 5: Deleting Data
import sqlite3
Create a connection to the database
conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
Create a cursor object
c = conn.cursor()
Delete data from the 'users' table
c.execute '''
DELETE FROM users
WHERE email = '[email protected]'
'''
Commit the changes
conn.commit()
Close the connection
conn.close()
Conclusion
In this document, we have explored some basic examples of database operations using the sqlite3 library in Python. These examples demonstrate how to create a database and table, insert data, retrieve data, update data, and delete data.
Download PDF
Please note that this is just a sample document and you should always ensure that your database operations are secure and follow best practices.
CRUD operations in Python with source code
CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) Operations are fundamental tasks when working with databases. In this response, I'll cover the basics of performing CRUD operations in Python using SQLite as a database.
Setting up the Database
To begin with CRUD operations in Python, you'll need to install the sqlite3 library if it's not already installed:
pip install sqlite3
Next, let's create a simple SQLite database and table for demonstration purposes. Create a new file named crud_operations.py, add the following code, and run it using your favorite Python IDE or terminal.
import sqlite3
Connect to the SQLite database
conn = sqlite3.connect('my_database.db')
Create a cursor object to execute queries
c = conn.cursor()
Create a table called 'users' with columns: id, name, age
c.execute("""CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS users (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
name TEXT,
age INTEGER
)""")
CRUD Operations
Now that our database and table are set up, let's explore the CRUD operations.
Create (Insert)To create a new user in our users table, we'll use the execute() method to execute an INSERT statement. Here's how you can do it:
# Insert a new user with name 'John' and age 25
c.execute("INSERT INTO users (name, age) VALUES ('John', 25)")
Commit the changes
conn.commit()
To retrieve all users from our users table, we'll use the fetchall() method to execute a SELECT statement. Here's how you can do it:
# Retrieve all users
c.execute("SELECT * FROM users")
users = c.fetchall()
Print the retrieved data
for user in users:
print(f"Name: {user[1]}, Age: {user[2]}")
To update a specific user's details, we'll use the execute() method to execute an UPDATE statement. Here's how you can do it:
# Update John's age to 30
c.execute("UPDATE users SET age = 30 WHERE name = 'John'")
Commit the changes
conn.commit()
To delete a specific user, we'll use the execute() method to execute a DELETE statement. Here's how you can do it:
# Delete John from the table
c.execute("DELETE FROM users WHERE name = 'John'")
Commit the changes
conn.commit()
Putting it all Together
Here's the complete code that demonstrates CRUD operations in Python with SQLite:
import sqlite3
Connect to the SQLite database
conn = sqlite3.connect('my_database.db')
Create a cursor object to execute queries
c = conn.cursor()
Create a table called 'users' with columns: id, name, age
c.execute("""CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS users (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
name TEXT,
age INTEGER
)""")
Insert a new user with name 'John' and age 25
c.execute("INSERT INTO users (name, age) VALUES ('John', 25)")
conn.commit()
Retrieve all users
c.execute("SELECT * FROM users")
users = c.fetchall()
Print the retrieved data
for user in users:
print(f"Name: {user[1]}, Age: {user[2]}")
Update John's age to 30
c.execute("UPDATE users SET age = 30 WHERE name = 'John'")
conn.commit()
Delete John from the table
c.execute("DELETE FROM users WHERE name = 'John'")
conn.commit()
Close the connection
conn.close()
That's it! CRUD operations in Python using SQLite are now a breeze.