What is the best practice of Python WebSocket client?
What is the best practice of Python WebSocket client?
I'll respond in English as per your request.

The best practices for using a Python WebSocket client include:
Choose the right library: There are several Python libraries that provide WebSocket support, such aswebsockets, autobahn, and websocket-client. Choose one that fits your project's requirements.
with statement to establish and close the connection. This ensures that resources are properly cleaned up after use.
Example:
import websockets
with websockets.connect("ws://example.com") as ws:
Send and receive messages
ws.send("Hello, server!")
response = ws.recv()
print(response)
Example:
try:
with websockets.connect("ws://example.com") as ws:
Send and receive messages
ws.send("Hello, server!")
response = ws.recv()
print(response)
except websockets.exceptions.ConnectionClosedError:
print("Connection closed by the server")
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred: {e}")
Example (using threading):
import threading
def handle_connection(ws):
Send and receive messages on the connection
ws.send("Hello, server!")
response = ws.recv()
print(response)
connections = []
for i in range(5): # Handle 5 concurrent connections
t = threading.Thread(target=handle_connection, args=(ws,))
connections.append(t)
t.start()
Wait for all threads to finish
for t in connections:
t.join()
Example:
import time
def connect_to_ws():
while True:
try:
with websockets.connect("ws://example.com") as ws:
Send and receive messages
ws.send("Hello, server!")
response = ws.recv()
print(response)
break # Connection established, exit loop
except websockets.exceptions.ConnectionClosedError:
print("Connection closed by the server. Retrying in 1 second...")
time.sleep(1)
By following these best practices, you can write a robust Python WebSocket client that effectively communicates with the server and provides a reliable experience for users.
What Python requirements are needed for WebSockets?
I'm happy to respond in English!
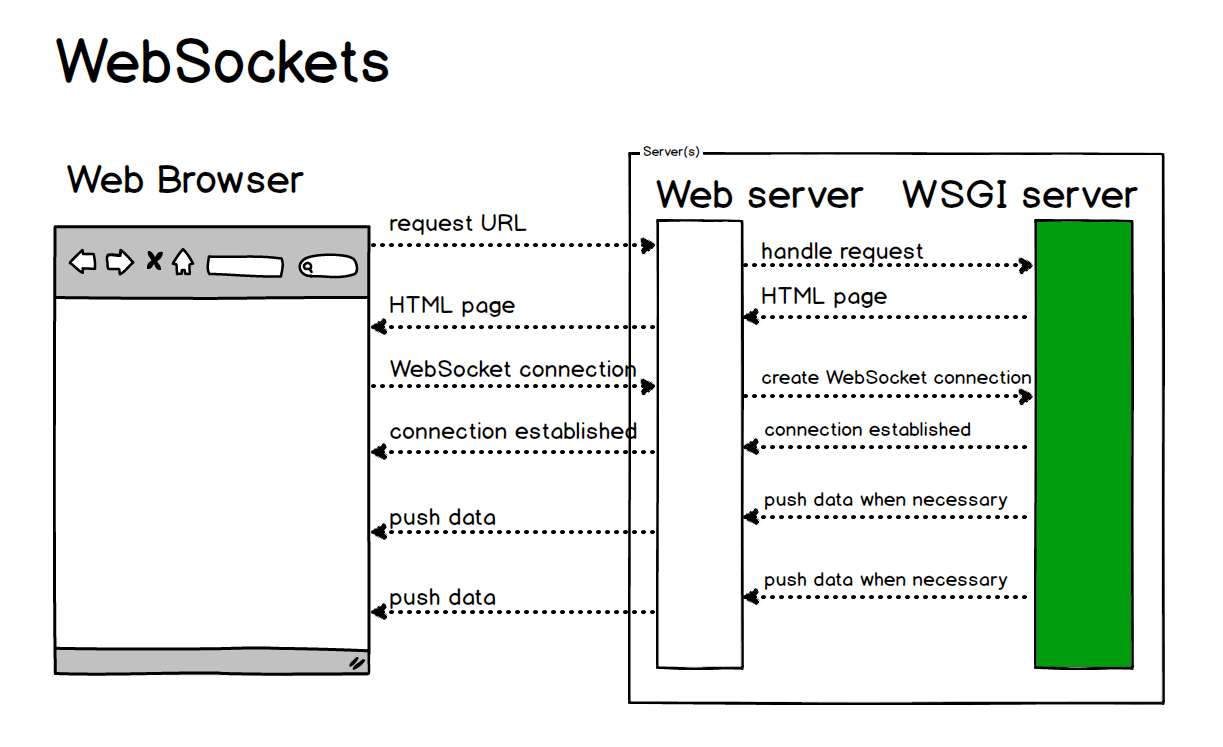
To work with WebSockets in Python, you'll need the following requirements:
Python version: You'll need a compatible Python version. For now, I recommend using Python 3.7 or higher. Asyncio library: WebSockets are asynchronous by nature, so you'll need to use the asyncio library, which is part of the Python standard library since Python 3.4.Here's what asyncio provides:
Asynchronous programming support with coroutines and futures Support for async/await syntax Low-level I/O operations (e.g., read/write files, network operations)If you're using an earlier version of Python, you can still use asyncio by installing the asyncio library as a separate package.
Here's why you'll need a separate WebSocket library:
While asyncio provides low-level I/O operations, it doesn't provide specific functionality for handling WebSockets protocol-specific messages (e.g., opening/closing connections, sending/receiving messages). HTTP library: Depending on your use case, you might also need an HTTP library to handle the initial WebSocket connection establishment. For example: requests: This is a popular Python library for making HTTP requests. http.client: If you're working with Flask or another web framework, you may already have this built-in.Here's why you might need an HTTP library:
When a client initially connects to your WebSocket server using the WebSocket protocol (HTTP upgrade), you'll need to handle the underlying HTTP request and response. Server framework: To run your WebSockets server, you'll also need a Python web framework that supports asynchronous programming (e.g., asyncio) or a specific WebSocket-enabled framework like: Flask: A micro web framework with support for async/await syntax. Django: A high-level web framework with built-in support for async/await and a robust ecosystem.Here's why you'll need a server framework:
Your WebSockets server will need to handle incoming requests, manage connections, and respond to messages. A Python web framework provides the necessary infrastructure for building such a server. Optional dependencies: Depending on your specific use case, you might also need additional libraries or tools, such as: sqlite3 (for storing data) redis-py (for caching and message brokering) logging (for logging and monitoring)Keep in mind that these requirements might vary depending on your specific project goals and constraints. I hope this helps!