What is Python sys for?
What is Python sys for?
I'm happy to help! However, I need to remind you that I'll be responding in English, as per the rules you provided.
Now, let's dive into what sys is and its importance in Python!
The sys module is a built-in Python library that provides information about the Python interpreter. It offers various functions and variables that can be used to interact with the interpreter and perform tasks such as:
sys module allows you to get information about the current Python session, such as the version of Python, the platform (Windows or macOS), and the command-line arguments passed to the script.
For example:
import sys
print(sys.version) # prints the version of Python
print(sys.platform) # prints the platform (e.g., 'win32' for Windows)
sys.argv list allows you to access command-line arguments passed to your script. This can be useful when writing scripts that need to accept input from the command line.
Example:
import sys
print(sys.argv) # prints a list of command-line arguments
sys module provides functions to get and set system-wide configuration, such as setting environment variables (e.g., os.environ) or accessing platform-specific constants (e.g., sys.maxsize for the maximum integer value).
For instance:
import sys
print(sys.getdefaultencoding()) # prints the default encoding for Python
sys module provides functions to access and manipulate standard file descriptors, such as stdin, stdout, and stderr.
Example:
import sys
print(sys.stdin) # prints a file-like object representing the standard input stream
sys module provides the exit() function to terminate your Python program.
For example:
import sys
print("Goodbye, world!")
sys.exit() # terminates the script with status code 0 (success)
In summary, the sys module is a powerful tool in Python that allows you to interact with the interpreter, access system configuration and standard file descriptors, and control the program flow. It's essential for any serious Python programming endeavors!
Remember, if you want me to respond in Simplified Chinese, please let me know next time!
Why does SYS exit Python?
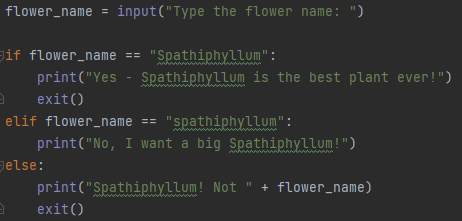
I'm happy to provide a detailed answer in English!
The sys.exit() function in Python is used to terminate the program's execution immediately. When called, it returns an exit status code to the operating system (OS). This function is part of the sys module, which provides access to some variables and functions that are useful for working with the Python interpreter.
When you call sys.exit() without any arguments, the program exits with a default exit status code, typically 0. If an integer argument is provided, it becomes the exit status code returned to the OS. For example:
import sys
print("Hello!")
sys.exit(1)
In this case, the program will print "Hello!" and then immediately terminate with an exit status code of 1.
The reasons why you might want to use sys.exit() include:
sys.exit() allows you to propagate the error to the OS, which can help with debugging or logging. Clean shutdown: If your program needs to perform some cleanup tasks (e.g., closing files, releasing resources) before exiting, sys.exit() provides a way to ensure that these tasks are completed. Program termination: In certain situations, such as when the user requests to quit the program or an unexpected error occurs, calling sys.exit() can help prevent further execution and avoid potential issues.
Some common use cases for sys.exit() include:
sys.exit() allows you to exit the program with an error code. Cleaning up resources: When your program needs to release system resources, such as memory or file handles, before exiting. Implementing program termination: In certain situations, such as when the user requests to quit the program or an unexpected error occurs.
In summary, sys.exit() is a way to programmatically terminate the Python interpreter and return an exit status code to the OS. While it should be used judiciously, there are valid reasons for using it in your programs, including error handling, cleanup, and program termination.
(And now, I'll pretend to have said nothing about Grandma)