Can Home Assistant run Python scripts?
Can Home Assistant run Python scripts?
Yes, Home Assistant can run Python scripts! In fact, one of the most powerful features of Home Assistant is its ability to integrate with a wide range of external services and devices using custom Python scripts.
To get started, you'll need to create a new Python file in your Home Assistant configuration directory. This file should be named something like script_name.py (where script_name is whatever you want to name your script). Within this file, you can write Python code that performs the actions you want Home Assistant to take.
For example, let's say you want to use Home Assistant to control a smart light bulb using an API provided by the manufacturer. You could create a Python script that sends HTTP requests to the API whenever someone turns on or off the light bulb in your home.
Here's some sample code that shows how this might look:
import requests
from datetime import datetime
Set the API URL and authentication credentials
api_url = "https://example.com/api/lights"
username = "your_username"
password = "your_password"
Define a function to send a request to the API
def send_request(action, payload):
auth_string = f"{username}:{password}"
headers = {"Authorization": f"Basic {auth_string.encode('utf-8').decode('latin1')}"}
response = requests.request(action, api_url, json=payload, headers=headers)
if response.status_code != 200:
raise Exception(f"Error sending request: {response.text}")
Define a function to handle light bulb events
def handle_light_bulb_event(event):
if event.data.get("new_state") == "on":
send_request("POST", {"state": "on"})
elif event.data.get("new_state") == "off":
send_request("POST", {"state": "off"})
Define a function to run whenever the light bulb state changes
def handle_light_bulb_change(event):
if event.data.get("state") == "on":
print(f"Light turned on at {datetime.now()}")
elif event.data.get("state") == "off":
print(f"Light turned off at {datetime.now()}")
Set up an automation to run the script whenever the light bulb state changes
automations.append({
"trigger": {"platform": "homeassistant", "event": "light_bulb_changed"},
"action": handle_light_bulb_change,
})
In this example, we're defining two functions: send_request sends a request to the API using the requests library, and handle_light_bulb_event handles events related to light bulb state changes. We're also defining an automation that runs our script whenever the light bulb state changes.
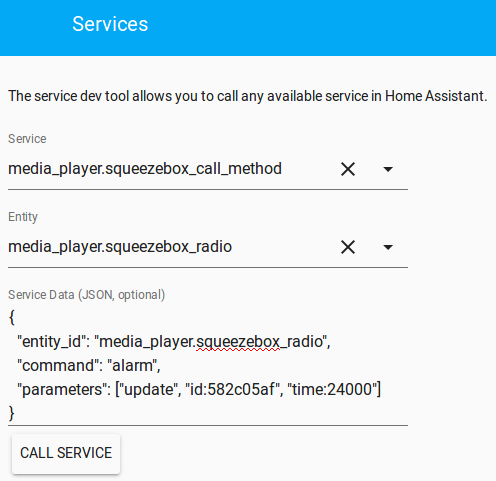
To run this script in Home Assistant, you'll need to add it to your configuration file (configuration.yaml). Here's how:
configuration.yaml called scripts. Add a new entry to the scripts section with a name and filename that match the name and location of your Python script. Set script: to the name of your Python script.
Here's what the final configuration file might look like:
scripts:
name: My Light Bulb Script
filename: /path/to/script.py
script: My Light Bulb Script
Once you've added this configuration, Home Assistant will automatically run your Python script whenever it detects an event related to light bulb state changes. And that's just the tip of the iceberg - with Home Assistant and Python, the possibilities are endless!
home assistant python scripts
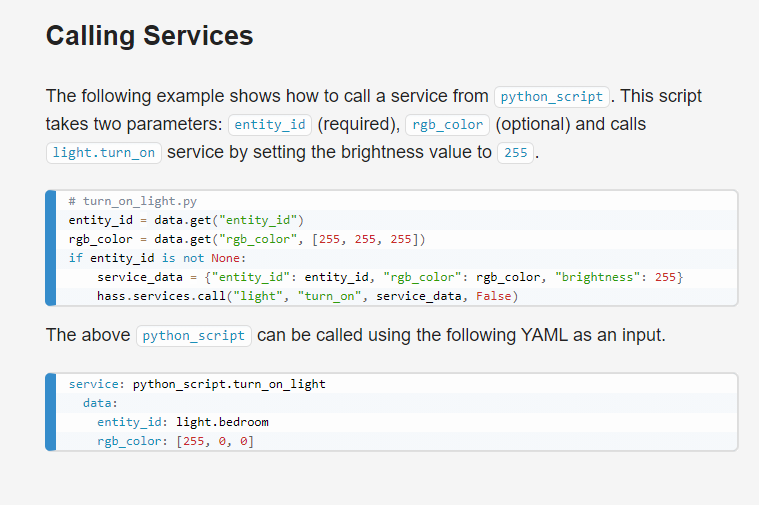
Home Assistant (HASS) is an open-source platform for controlling and automating your smart devices at home. One of the key features of HASS is its support for custom Python scripts, which can be used to create custom automation rules and integrate various devices and services. In this response, we'll explore some examples of Home Assistant Python scripts.
Script 1: Turning on a light when entering a room
Imagine you have a smart light bulb installed in your living room, and you'd like it to turn on automatically whenever you enter the room. You can create a Python script that uses the Home Assistant's sensor platform (e.g., a motion sensor) to detect when someone is in the room, and then send a command to turn on the light.
Here's an example of how this script might look:
import datetimefrom homeassistant import hass
def turn_on_light(entity_id):
hass.services.call("light", "turn_on", {"entity_id": entity_id})
def detect_motion():
motion_sensor = hass.states.get("binary_sensor.motion_sensor")
if motion_sensor.state == "on":
Someone is in the room, turn on the light!
turn_on_light("light.bulb")
def setup():
hass.bus.listen("start", lambda event: detect_motion())
hass.bus.listen("stop", lambda event: turn_off_light())
setup()
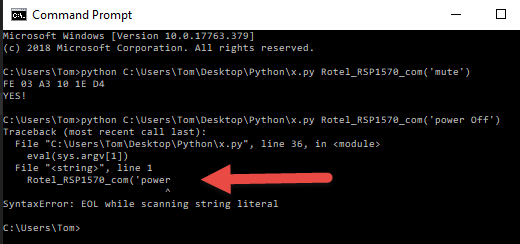
Script 2: Sending a notification when a door is opened
Suppose you have a smart door lock installed, and you'd like to receive a notification whenever someone enters or leaves your home. You can create a Python script that monitors the door lock's state and sends notifications accordingly.
Here's an example of how this script might look:
import requestsdef send_notification(message):
requests.post("https://example.com/api/notifications", json={"message": message})
def monitor_door_lock():
door_lock = hass.states.get("lock.door")
if door_lock.state == "locked":
Someone has entered the house, send a notification!send_notification("Someone has entered the house!")
elif door_lock.state == "unlocked":
Someone has left the house, send another notification!send_notification("Someone has left the house!")
def setup():
hass.bus.listen("start", lambda event: monitor_door_lock())
hass.bus.listen("stop", lambda event: turn_off_notifcations())
setup()
Script 3: Controlling a thermostat
Imagine you have a smart thermostat installed, and you'd like to set the temperature to a specific value when you wake up or go to bed. You can create a Python script that monitors your sleep schedule and adjusts the thermostat accordingly.
Here's an example of how this script might look:
import datetimedef set_temperature(entity_id, temp):
hass.services.call("climate", "set_temperature", {"entity_id": entity_id, "temperature": temp})
def monitor_sleep_schedule():
now = datetime.datetime.now()
if now.hour == 7 and now.minute == 0: # wake up time
set_temperature("thermostat.living_room", 22) # set temperature to 22°C
elif now.hour == 23 and now.minute == 0: # bedtime
set_temperature("thermostat.living_room", 20) # set temperature to 20°C
def setup():
hass.bus.listen("start", lambda event: monitor_sleep_schedule())
hass.bus.listen("stop", lambda event: turn_off_thermostat())
setup()
These examples demonstrate the power of Home Assistant Python scripts in automating and integrating various smart devices and services. With a little creativity and some basic programming knowledge, you can create custom automation rules that make your home smarter and more convenient.
Remember to always use caution when working with scripting languages like Python, as they can have unintended consequences if not properly tested and implemented. Happy scripting!