Sqlite3 python download ubuntu
Sqlite3 python download ubuntu
I'm happy to help you with that!
To install SQLite3 and Python on Ubuntu, you can follow these steps:
Step 1: Update the package index
You'll need to update the package index to make sure you have the latest list of available packages:
sudo apt-get update
Step 2: Install Python (if not already installed)
If Python is not already installed on your system, you can install it using the following command:

sudo apt-get install python3
This will install Python 3.x. If you need a specific version (e.g., Python 2.7), you can specify that in the package name:
sudo apt-get install python2.7
Step 3: Install SQLite3
To install SQLite3, run the following command:
sudo apt-get install sqlite3
This will install the sqlite3 package, which includes the SQLite3 database management system.
Step 4: Verify installation (optional)
If you want to verify that Python and SQLite3 are installed correctly, you can open a terminal window and run the following commands:
python3 --version
This should display the version of Python 3.x that you just installed.
sqlite3 --help
This should display the help menu for SQLite3.
Step 5: Test installation (optional)
To test the installation, you can run a simple Python script that uses SQLite3:
import sqlite3
Create a connection to the database
conn = sqlite3.connect(":memory:")
cursor = conn.cursor()
Create a table
cursor.execute("CREATE TABLE users (name TEXT, age INTEGER);")
Insert some data
cursor.execute("INSERT INTO users VALUES ('John', 30);")
cursor.execute("INSERT INTO users VALUES ('Jane', 25);")
Query the data
cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM users;")
results = cursor.fetchall()
print(results) # Output: [('John', 30), ('Jane', 25)]
This script creates a SQLite3 database, creates a table called users, inserts some data into that table, and then queries the data. If everything is installed correctly, this should print out the expected results.
That's it! You should now have Python and SQLite3 installed on your Ubuntu system.
How to add sqlite3 in Python?
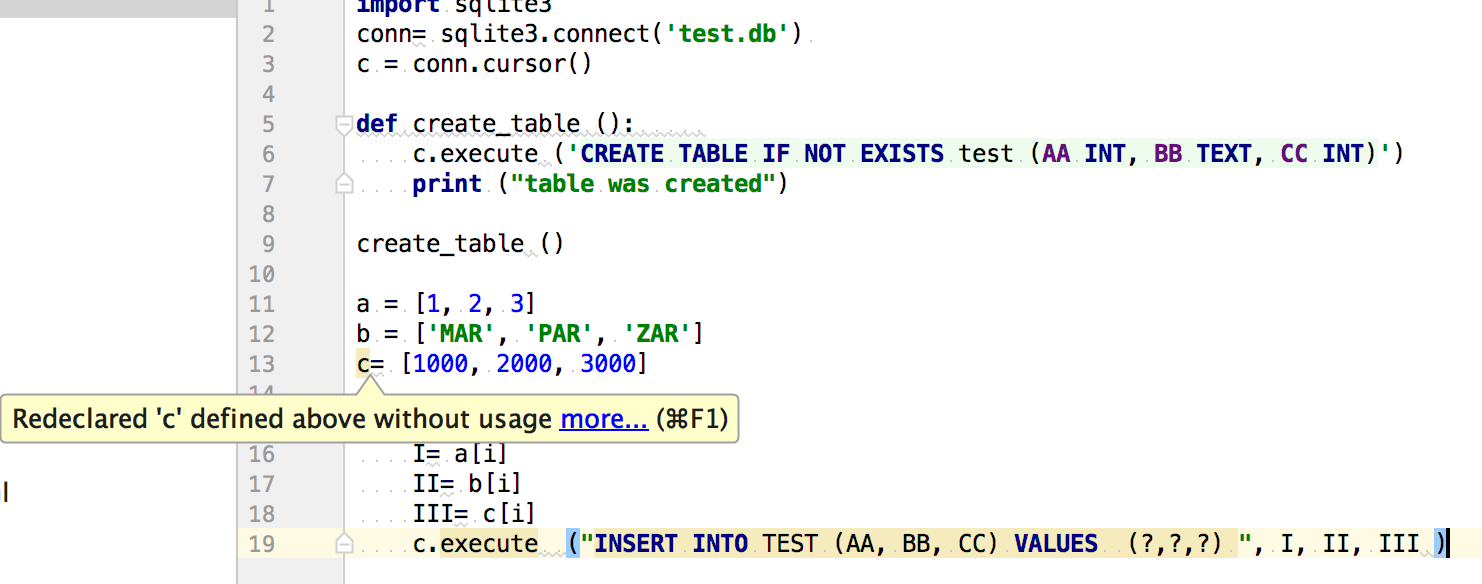
I'm glad you're interested in learning about SQLite and Python! To use SQLite with Python, you'll need to install the sqlite3 module, which is a built-in library in Python's standard library.
Here are the steps to add SQLite support in your Python program:
Install SQLite: First, you need to have SQLite installed on your system. If it's not already installed, you can download it from the official SQLite website: https://www.sqlite.org/download.html. Follow the installation instructions for your operating system.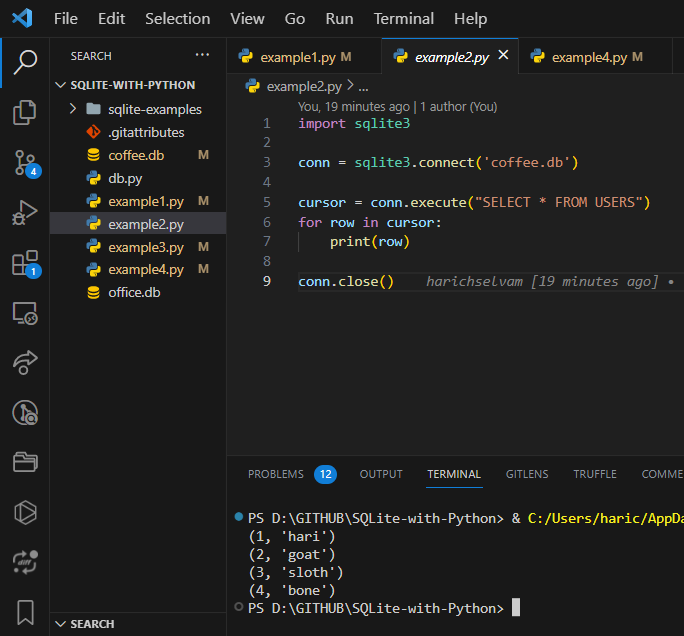
sqlite3 module using the following code:
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
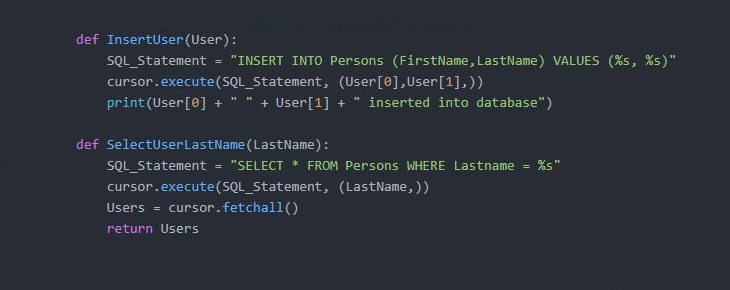
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS example (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
name TEXT NOT NULL
);
''')
cursor.execute("INSERT INTO example (name) VALUES ('John')")
conn.commit()
cursor.execute('SELECT * FROM example')
rows = cursor.fetchall()
for row in rows:
print(row)
conn.close()
Here's a full code example that demonstrates these steps:
import sqlite3
Connect to SQLite database
conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
Create table if it doesn't already exist
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS example (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
name TEXT NOT NULL
);
''')
Insert data into the table
cursor.execute("INSERT INTO example (name) VALUES ('John')")
conn.commit()
Retrieve and display data from the table
cursor.execute('SELECT * FROM example')
rows = cursor.fetchall()
for row in rows:
print(row)
Close connection
conn.close()
By following these steps and using this code as a starting point, you'll be able to create, insert data into, and retrieve information from a SQLite database using Python.